Praca Dyplomowa - Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing - AGH
Praca Dyplomowa - Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing - AGH
Praca Dyplomowa - Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing - AGH
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND<br />
RMSE – root mean square error – RMS error of adjusted observations with respect to mean<br />
of adjusted observations<br />
√ ∑( ̅)<br />
20<br />
(2.19)<br />
To orient two images or more, tie points have to be defined. These points may be natural<br />
points which are visible on both pictures. However, they may be marked before. These points<br />
may be defined in a specific shape – coded points, where every software may have different<br />
pattern. In some cases the points (or at least few of them) should have known coordinates<br />
(XYZ), for orientation to global coordinate system, but for close range <strong>and</strong> in the project it is<br />
not necessary. Points should be arranged around the object <strong>and</strong>/or could be on the object.<br />
Picture should cover as best (as biggest area as possible) the object with marked points around<br />
it. Referenced points should not be located in a common plane, this situation may give errors.<br />
Depending on methods (algorithm, transformation etc.), or step in orientation different<br />
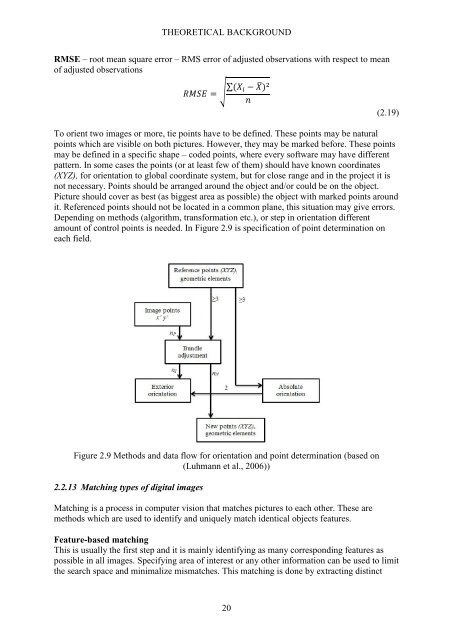
amount of control points is needed. In Figure 2.9 is specification of point determination on<br />
each field.<br />
Figure 2.9 Methods <strong>and</strong> data flow for orientation <strong>and</strong> point determination (based on<br />
(Luhmann et al., 2006))<br />
2.2.13 Matching types of digital images<br />
Matching is a process in computer vision that matches pictures to each other. These are<br />
methods which are used to identify <strong>and</strong> uniquely match identical objects features.<br />
Feature-based matching<br />
This is usually the first step <strong>and</strong> it is mainly identifying as many corresponding features as<br />
possible in all images. Specifying area of interest or any other information can be used to limit<br />
the search space <strong>and</strong> minimalize mismatches. This matching is done by extracting distinct