- Page 2:
Current Cancer Research For other t
- Page 8:
Editor Marcelo G. Kazanietz, Ph.D.
- Page 14:
Contents Part I Regulation of PKC I
- Page 18:
Contents 21 PKC and Resistance to C
- Page 24:
xii Contributors Maria T. Diaz-Meco
- Page 28:
xiv Contributors Lauren Van Wassenh
- Page 32:
Chapter 1 Protein Kinase C in Cance
- Page 36:
1 Protein Kinase C in Cancer Signal
- Page 40:
1 Protein Kinase C in Cancer Signal
- Page 44:
Chapter 2 Regulation of Conventiona
- Page 48:
2 Regulation of Conventional and No
- Page 52:
2 Regulation of Conventional and No
- Page 56:
2 Regulation of Conventional and No
- Page 60:
2 Regulation of Conventional and No
- Page 64:
2 Regulation of Conventional and No
- Page 68:
2 Regulation of Conventional and No
- Page 72:
2 Regulation of Conventional and No
- Page 76:
26 P.M. Blumberg et al. 3.1 Introdu
- Page 80:
28 P.M. Blumberg et al. 1981; Diamo
- Page 84:
30 P.M. Blumberg et al. 3.4 DAG-Lac
- Page 88:
32 P.M. Blumberg et al. 3.6 Role of
- Page 92:
34 P.M. Blumberg et al. Interesting
- Page 96:
36 P.M. Blumberg et al. the proximi
- Page 100:
38 P.M. Blumberg et al. 3.14 C1 Dom
- Page 104:
40 P.M. Blumberg et al. the A and B
- Page 108:
42 P.M. Blumberg et al. The above r
- Page 112:
44 P.M. Blumberg et al. 3.19 Role o
- Page 116:
46 P.M. Blumberg et al. 3.20 Conclu
- Page 120:
48 P.M. Blumberg et al. Churchill,
- Page 124:
50 P.M. Blumberg et al. the isoster
- Page 128:
52 P.M. Blumberg et al. Pu, Y., Pea
- Page 132:
Chapter 4 Diacylglycerol Signaling:
- Page 136:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling OH O P D
- Page 140:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling intermed
- Page 144:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling cPKC (α
- Page 148:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling 4.3 DAG
- Page 152:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling DGKα DG
- Page 156:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling the spat
- Page 160:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling adhesion
- Page 164:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling prolifer
- Page 168:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling Gomez-Me
- Page 172:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling Maruyama
- Page 176:
4 Diacylglycerol Signaling Cepsilon
- Page 180:
Chapter 5 Regulation of PKC by Prot
- Page 184:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 188:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 192:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 196:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 200:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 204:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 208:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 212:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 216:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 220:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 224:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 228:
5 Regulation of PKC by Protein-Prot
- Page 232:
Chapter 6 Introduction: PKC Isozyme
- Page 236:
6 Introduction: PKC Isozymes in the
- Page 240:
6 Introduction: PKC Isozymes in the
- Page 244:
6 Introduction: PKC Isozymes in the
- Page 248:
6 Introduction: PKC Isozymes in the
- Page 252:
118 E. Rozengurt Keywords Protein k
- Page 256:
120 E. Rozengurt The initial descri
- Page 260:
122 E. Rozengurt mechanisms, involv
- Page 264:
124 E. Rozengurt PKC DAG DAG P Ser
- Page 268:
126 E. Rozengurt Each translocation
- Page 272:
128 E. Rozengurt multisite phosphor
- Page 276:
130 E. Rozengurt Table 7.1. Identif
- Page 280:
132 E. Rozengurt gastrointestinal p
- Page 284:
134 E. Rozengurt receptor for bacte
- Page 288:
136 E. Rozengurt (Zhang et al. 2005
- Page 292:
138 E. Rozengurt PKD-mediated phosp
- Page 296:
140 E. Rozengurt Clearly, more expe
- Page 300:
142 E. Rozengurt In conclusion, stu
- Page 304:
144 E. Rozengurt Doppler, H., Storz
- Page 308:
146 E. Rozengurt Johannes, F. J., P
- Page 312:
148 E. Rozengurt Mellor, H., & Park
- Page 316:
150 E. Rozengurt Rey, O., Yuan, J.,
- Page 320:
152 E. Rozengurt Van Lint, J. V., S
- Page 324:
154 E. Rozengurt Zugaza, J. L., Sin
- Page 328:
156 J.D. Black Keywords PKC • Cel
- Page 332:
158 J.D. Black A and B (Malumbres a
- Page 336:
160 J.D. Black epithelial cells sti
- Page 340:
162 J.D. Black Fig. 8.1 Model of th
- Page 344:
164 J.D. Black the ERK/MAPK signali
- Page 348:
166 J.D. Black inhibit cyclin D1 ex
- Page 352:
168 J.D. Black Fig. 8.2 Model of PK
- Page 356:
170 J.D. Black hindered by the fact
- Page 360:
172 J.D. Black of murine and human
- Page 364:
174 J.D. Black in these cells (Balc
- Page 368:
176 J.D. Black Fig. 8.3 The timing
- Page 372:
178 J.D. Black Alisi, A., Spagnuolo
- Page 376:
180 J.D. Black Classon, M., & Dyson
- Page 380:
182 J.D. Black Hocevar, B. A., Morr
- Page 384:
184 J.D. Black Nakagawa, S., Fujii,
- Page 388:
186 J.D. Black Soh, J. W., & Weinst
- Page 392:
188 J.D. Black Zhou, W., Takuwa, N.
- Page 396:
190 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 400:
192 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 404:
194 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 408:
196 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 412:
198 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 416:
200 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 420:
202 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 424:
204 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 428:
206 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 432:
208 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 436:
210 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 440:
212 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 444:
214 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 448:
216 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 452:
218 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 456:
220 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 460:
222 M.E. Reyland and A.P. Bradford
- Page 464:
224 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat Li
- Page 468:
226 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat IK
- Page 472:
228 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat Co
- Page 476:
230 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat Th
- Page 480:
232 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat Th
- Page 484:
234 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat 10
- Page 488:
236 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat et
- Page 492:
238 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat et
- Page 496:
240 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat Du
- Page 500:
242 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat Ma
- Page 504:
244 M.T. Diaz-Meco and J. Moscat Wo
- Page 508:
Chapter 11 Introduction: PKC and Ca
- Page 512: 11 Introduction: PKC and Cancer The
- Page 516: 11 Introduction: PKC and Cancer Sun
- Page 520: 254 K. Yoshida undergo apoptosis is
- Page 524: 256 K. Yoshida on Ataxia telangiect
- Page 528: 258 K. Yoshida induction of p53 (Ma
- Page 532: 260 K. Yoshida Oda et al. 2000; Tai
- Page 536: 262 K. Yoshida Brodie, C., & Blumbe
- Page 540: 264 K. Yoshida Niedel, J. E., Kuhn,
- Page 544: Chapter 13 PKCs as Mediators of the
- Page 548: 13 PKCs as Mediators of the Hedgeho
- Page 552: 13 PKCs as Mediators of the Hedgeho
- Page 556: 13 PKCs as Mediators of the Hedgeho
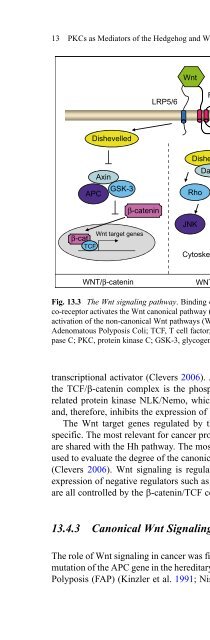
- Page 560: 13 PKCs as Mediators of the Hedgeho
- Page 566: 278 N.A. Riobo numerous colon polyp
- Page 570: 280 N.A. Riobo It is remarkable tha
- Page 574: 282 N.A. Riobo Some Wnt isoforms, k
- Page 578: 284 N.A. Riobo James, R.G., Conrad,
- Page 582: 286 N.A. Riobo Rohatgi, R., Milenko
- Page 586: 288 Q.J. Wang (Blumberg 1988). DAG
- Page 590: 290 Q.J. Wang Gbg PKCh PKD PI4K III
- Page 594: 292 Q.J. Wang 2003b). At the mitoch
- Page 598: 294 Q.J. Wang tumors and their prop
- Page 602: 296 Q.J. Wang regulating integrin r
- Page 606: 298 Q.J. Wang 14.6 Concluding Remar
- Page 610: 300 Q.J. Wang Harrison, B. C., Kim,
- Page 614:
302 Q.J. Wang Storz, P., Doppler, H
- Page 618:
Chapter 15 Transgenic Mouse Models
- Page 622:
15 Transgenic Mouse Models to Inves
- Page 626:
15 Transgenic Mouse Models to Inves
- Page 630:
15 Transgenic Mouse Models to Inves
- Page 634:
15 Transgenic Mouse Models to Inves
- Page 638:
15 Transgenic Mouse Models to Inves
- Page 642:
15 Transgenic Mouse Models to Inves
- Page 646:
15 Transgenic Mouse Models to Inves
- Page 650:
15 Transgenic Mouse Models to Inves
- Page 654:
324 M.F. Denning common subtype of
- Page 658:
326 M.F. Denning Fig. 16.1 PKC isoz
- Page 662:
328 M.F. Denning and CXCR2 ligands
- Page 666:
330 M.F. Denning Fig. 16.2 Model of
- Page 670:
332 M.F. Denning 16.3 Basal Cell Ca
- Page 674:
334 M.F. Denning Fig. 16.3 PKC in m
- Page 678:
336 M.F. Denning some benign nevi a
- Page 682:
338 M.F. Denning Cataisson, C., Pea
- Page 686:
340 M.F. Denning Gilhooly, E. M., M
- Page 690:
342 M.F. Denning Nishizuka, Y. (198
- Page 694:
344 M.F. Denning Sikkink, S. K., Re
- Page 698:
Chapter 17 PKC and Breast Cancer *
- Page 702:
17 PKC and Breast Cancer Relative E
- Page 706:
17 PKC and Breast Cancer The array
- Page 710:
17 PKC and Breast Cancer 17.7 Growt
- Page 714:
17 PKC and Breast Cancer showed tha
- Page 718:
17 PKC and Breast Cancer de Vente,
- Page 722:
17 PKC and Breast Cancer Palmantier
- Page 726:
Chapter 18 PKC and Prostate Cancer
- Page 730:
18 PKC and Prostate Cancer In Dunni
- Page 734:
18 PKC and Prostate Cancer may be c
- Page 738:
18 PKC and Prostate Cancer an inhib
- Page 742:
18 PKC and Prostate Cancer protein-
- Page 746:
18 PKC and Prostate Cancer expressi
- Page 750:
18 PKC and Prostate Cancer PKCbII a
- Page 754:
18 PKC and Prostate Cancer Gonzalez
- Page 758:
18 PKC and Prostate Cancer Sakamoto
- Page 762:
Chapter 19 Protein Kinase C and Lun
- Page 766:
19 Protein Kinase C and Lung Cancer
- Page 770:
19 Protein Kinase C and Lung Cancer
- Page 774:
19 Protein Kinase C and Lung Cancer
- Page 778:
19 Protein Kinase C and Lung Cancer
- Page 782:
19 Protein Kinase C and Lung Cancer
- Page 786:
19 Protein Kinase C and Lung Cancer
- Page 790:
19 Protein Kinase C and Lung Cancer
- Page 794:
19 Protein Kinase C and Lung Cancer
- Page 798:
19 Protein Kinase C and Lung Cancer
- Page 802:
19 Protein Kinase C and Lung Cancer
- Page 806:
Chapter 20 Introduction Patricia S.
- Page 810:
20 Introduction The first compound
- Page 814:
20 Introduction Tamaoki, T., & Naka
- Page 818:
410 A. Basu DNA. Because chemothera
- Page 822:
412 A. Basu to doxorubicin was asso
- Page 826:
414 A. Basu PKC in vitro (Chambers
- Page 830:
416 A. Basu decreasing the levels o
- Page 834:
418 A. Basu of cisplatin-sensitive
- Page 838:
420 A. Basu 21.3.4 Mechanism of PKC
- Page 842:
422 A. Basu In contrast, PKCi but n
- Page 846:
424 A. Basu Brodie, C., & Blumberg,
- Page 850:
426 A. Basu Higgins, C. F. (1993).
- Page 854:
428 A. Basu Pulaski, L., Szemraj, J
- Page 858:
Chapter 22 PKCd as a Target for Che
- Page 862:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 866:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 870:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 874:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 878:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 882:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 886:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 890:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 894:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 898:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 902:
22 PKCd as a Target for Chemotherap
- Page 906:
456 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields fa
- Page 910:
458 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields By
- Page 914:
460 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields In
- Page 918:
462 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields en
- Page 922:
464 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields A
- Page 926:
466 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields sm
- Page 930:
468 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields PK
- Page 934:
470 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields 23
- Page 938:
472 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields in
- Page 942:
474 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields pr
- Page 946:
476 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields un
- Page 950:
478 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields Ad
- Page 954:
480 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields Go
- Page 958:
482 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields Mu
- Page 962:
484 V. Justilien and A.P. Fields Wa
- Page 966:
486 Index Apoptotic effectors, 192
- Page 970:
488 Index Cell survival (cont.) pro
- Page 974:
490 Index Lung cancer (cont.) physi
- Page 978:
492 Index Proliferation and cell-cy
- Page 982:
494 Index Tumor suppression and pro