Ad Hoc Networks : Technologies and Protocols - University of ...
Ad Hoc Networks : Technologies and Protocols - University of ...
Ad Hoc Networks : Technologies and Protocols - University of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
98 Multicasting in <strong>Ad</strong> <strong>Hoc</strong> <strong>Networks</strong><br />
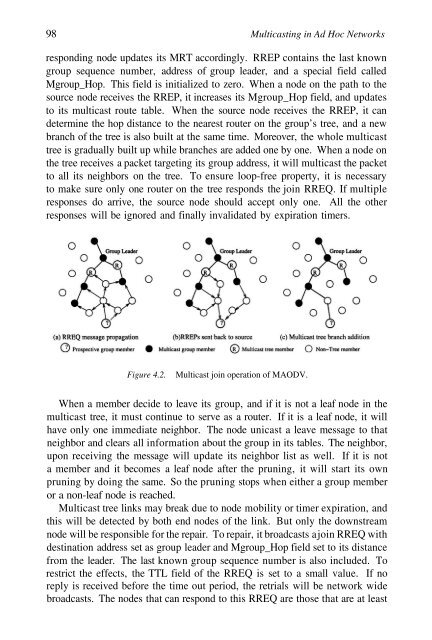
responding node updates its MRT accordingly. RREP contains the last known<br />
group sequence number, address <strong>of</strong> group leader, <strong>and</strong> a special field called<br />
Mgroup_Hop. This field is initialized to zero. When a node on the path to the<br />
source node receives the RREP, it increases its Mgroup_Hop field, <strong>and</strong> updates<br />
to its multicast route table. When the source node receives the RREP, it can<br />
determine the hop distance to the nearest router on the group’s tree, <strong>and</strong> a new<br />
branch <strong>of</strong> the tree is also built at the same time. Moreover, the whole multicast<br />
tree is gradually built up while branches are added one by one. When a node on<br />
the tree receives a packet targeting its group address, it will multicast the packet<br />
to all its neighbors on the tree. To ensure loop-free property, it is necessary<br />
to make sure only one router on the tree responds the join RREQ. If multiple<br />
responses do arrive, the source node should accept only one. All the other<br />
responses will be ignored <strong>and</strong> finally invalidated by expiration timers.<br />
Figure 4.2. Multicast join operation <strong>of</strong> MAODV.<br />
When a member decide to leave its group, <strong>and</strong> if it is not a leaf node in the<br />
multicast tree, it must continue to serve as a router. If it is a leaf node, it will<br />
have only one immediate neighbor. The node unicast a leave message to that<br />
neighbor <strong>and</strong> clears all information about the group in its tables. The neighbor,<br />
upon receiving the message will update its neighbor list as well. If it is not<br />
a member <strong>and</strong> it becomes a leaf node after the pruning, it will start its own<br />
pruning by doing the same. So the pruning stops when either a group member<br />
or a non-leaf node is reached.<br />
Multicast tree links may break due to node mobility or timer expiration, <strong>and</strong><br />
this will be detected by both end nodes <strong>of</strong> the link. But only the downstream<br />
node will be responsible for the repair. To repair, it broadcasts a join RREQ with<br />
destination address set as group leader <strong>and</strong> Mgroup_Hop field set to its distance<br />
from the leader. The last known group sequence number is also included. To<br />
restrict the effects, the TTL field <strong>of</strong> the RREQ is set to a small value. If no<br />
reply is received before the time out period, the retrials will be network wide<br />
broadcasts. The nodes that can respond to this RREQ are those that are at least