- Page 2 and 3:
AD HOC NETWORKS Technologies and Pr
- Page 4 and 5:
AD HOC NETWORKS Technologies and Pr
- Page 6 and 7:
Contents List of Figures List of Ta
- Page 8 and 9:
Contents vii 4.7. Conclusions and F
- Page 10 and 11:
Contents ix 9.2. Potential Attacks
- Page 12 and 13:
List of Figures 1.1 Internet in the
- Page 14 and 15:
List of Figures xiii 6.3 COMPOW com
- Page 16 and 17:
List of Figures xv 9.1 9.2 An IDS a
- Page 18 and 19:
List of Tables 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5
- Page 20 and 21:
Contributing Authors Samir R. Das i
- Page 22 and 23:
Preface Wireless mobile networks an
- Page 24 and 25:
Acknowledgments xxiii We wish to ex
- Page 26 and 27:
Chapter 1 AD HOC NETWORKS Emerging
- Page 28 and 29:
Introduction and Definitions 3 coul
- Page 30 and 31:
Introduction and Definitions 5 Secu
- Page 32 and 33:
Ad Hoc Network Applications 7 tunis
- Page 34 and 35:
Ad Hoc Network Applications 9 The d
- Page 36 and 37:
Ad Hoc Network Applications 11 Figu
- Page 38 and 39:
Design Challenges 13 example of cro
- Page 40 and 41:
Evaluating Ad Hoc Network Protocols
- Page 42 and 43:
Overview of the Chapters in this Bo
- Page 44 and 45:
Overview of the Chapters in this Bo
- Page 46 and 47:
Conclusions 21 1.6 Conclusions This
- Page 48 and 49:
Chapter 2 COLLISION AVOIDANCE PROTO
- Page 50 and 51:
Performance of collision avoidance
- Page 52 and 53:
Performance of collision avoidance
- Page 54 and 55:
Performance of collision avoidance
- Page 56 and 57:
Performance of collision avoidance
- Page 58 and 59:
Performance of collision avoidance
- Page 60 and 61:
Performance of collision avoidance
- Page 62 and 63:
Performance of collision avoidance
- Page 64 and 65:
Performance of collision avoidance
- Page 66 and 67:
Performance of collision avoidance
- Page 68 and 69:
Performance of collision avoidance
- Page 70 and 71:
Framework and Mechanisms for Fair A
- Page 72 and 73:
Framework and Mechanisms for Fair A
- Page 74 and 75:
Framework and Mechanisms for Fair A
- Page 76 and 77:
Framework and Mechanisms for Fair A
- Page 78 and 79:
Framework and Mechanisms for Fair A
- Page 80 and 81:
Framework and Mechanisms for Fair A
- Page 82 and 83:
Framework and Mechanisms for Fair A
- Page 84 and 85:
Conclusion 59 In the first part of
- Page 86 and 87:
Conclusion 61 [13] [14] [15] [16] [
- Page 88 and 89:
Chapter 3 ROUTING IN MOBILE AD HOC
- Page 90 and 91:
Flooding 65 vector and link state p
- Page 92 and 93:
Flooding 67 centralized approximati
- Page 94 and 95:
Proactive Routing 69 status of each
- Page 96 and 97:
Proactive Routing 71 Topology Broad
- Page 98 and 99:
On-demand Routing 73 reply packets
- Page 100 and 101:
On-demand Routing 75 during the lin
- Page 102 and 103:
Proactive Versus On-demand Debate 7
- Page 104 and 105:
Proactive Versus On-demand Debate 7
- Page 106 and 107:
Location-based Routing 81 to find a
- Page 108 and 109:
Location-based Routing 83 Figure 3.
- Page 110 and 111:
Concluding Remarks 85 relative meri
- Page 112 and 113:
Concluding Remarks 87 [14] [15] [16
- Page 114 and 115:
Concluding Remarks 89 [42] [43] [44
- Page 116 and 117:
Chapter 4 MULTICASTING IN AD HOC NE
- Page 118 and 119:
Introduction 93 The mobility of the
- Page 120 and 121:
Classifications of Protocols 95 red
- Page 122 and 123:
Multicasting Protocols 97 this sect
- Page 124 and 125:
Multicasting Protocols 99 as close
- Page 126 and 127:
Multicasting Protocols 101 In ODMRP
- Page 128 and 129:
Multicasting Protocols 103 hoc netw
- Page 130 and 131:
Multicasting Protocols 105 A member
- Page 132 and 133:
Multicasting Protocols 107 Figure 4
- Page 134 and 135:
Broadcasting 109 “talk” to a ra
- Page 136 and 137:
Broadcasting 111 broadcasted packet
- Page 138 and 139:
Protocol Comparisons 113 are cluste
- Page 140 and 141:
Overarching Issues 115 is user data
- Page 142 and 143:
Overarching Issues 117 and RTS/CTS
- Page 144 and 145:
Conclusions and Future Directions 1
- Page 146 and 147:
Conclusions and Future Directions 1
- Page 148 and 149:
Chapter 5 TRANSPORT LAYER PROTOCOLS
- Page 150 and 151:
TCP and Ad-hoc Networks 125 Modifie
- Page 152 and 153:
TCP and Ad-hoc Networks 127 mechani
- Page 154 and 155:
TCP and Ad-hoc Networks 129 timeout
- Page 156 and 157:
TCP and Ad-hoc Networks 131 to freq
- Page 158 and 159:
TCP and Ad-hoc Networks 133 Figure
- Page 160 and 161:
Transport Layer for Ad-hoc Networks
- Page 162 and 163:
Modified TCP 137 MAC layers without
- Page 164 and 165:
Modified TCP 139 Figure 5.6. TCP-EL
- Page 166 and 167:
TCP-aware Cross-layered Solutions 1
- Page 168 and 169:
TCP-aware Cross-layered Solutions 1
- Page 170 and 171:
TCP-aware Cross-layered Solutions 1
- Page 172 and 173:
Ad-hoc Transport Protocol 147 in it
- Page 174 and 175:
Ad-hoc Transport Protocol Figure 5.
- Page 176 and 177:
Summary 151 References [1] [2] [3]
- Page 178 and 179:
Chapter 6 ENERGY CONSERVATION Robin
- Page 180 and 181:
Energy Consumption in Ad Hoc Networ
- Page 182 and 183:
Energy Consumption in Ad Hoc Networ
- Page 184 and 185:
Communication-Time Energy Conservat
- Page 186 and 187:
Communication-Time Energy Conservat
- Page 188 and 189:
Communication-Time Energy Conservat
- Page 190 and 191:
Communication-Time Energy Conservat
- Page 192 and 193:
Communication-Time Energy Conservat
- Page 194 and 195:
Communication-Time Energy Conservat
- Page 196 and 197: Communication-Time Energy Conservat
- Page 198 and 199: Communication-Time Energy Conservat
- Page 200 and 201: Idle-time Energy Conservation 175 a
- Page 202 and 203: Idle-time Energy Conservation 177 T
- Page 204 and 205: Idle-time Energy Conservation 179 k
- Page 206 and 207: Idle-time Energy Conservation 181 F
- Page 208 and 209: Idle-time Energy Conservation 183 F
- Page 210 and 211: Idle-time Energy Conservation 185 t
- Page 212 and 213: Idle-time Energy Conservation 187 c
- Page 214 and 215: Idle-time Energy Conservation 189 F
- Page 216 and 217: Conclusion 191 [6] [7] [8] [9] [10]
- Page 218 and 219: Conclusion 193 [33] [34] [35] [36]
- Page 220 and 221: Conclusion 195 [59] [60] [61] [62]
- Page 222 and 223: Chapter 7 USE OF SMART ANTENNAS IN
- Page 224 and 225: Smart Antenna Basics and Models 199
- Page 226 and 227: Medium Access Control with Directio
- Page 228 and 229: Medium Access Control with Directio
- Page 230 and 231: Medium Access Control with Directio
- Page 232 and 233: Medium Access Control with Directio
- Page 234 and 235: Medium Access Control with Directio
- Page 236 and 237: Medium Access Control with Directio
- Page 238 and 239: Medium Access Control with Directio
- Page 240 and 241: Medium Access Control with Directio
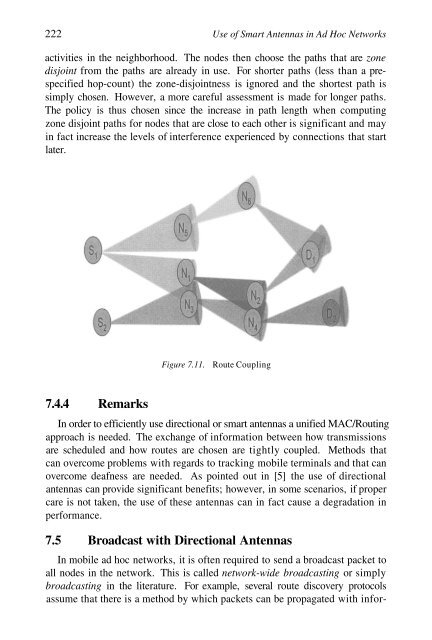
- Page 242 and 243: Routing with Directional Antennas 2
- Page 244 and 245: Routing with Directional Antennas 2
- Page 248 and 249: Broadcast with Directional Antennas
- Page 250 and 251: Broadcast with Directional Antennas
- Page 252 and 253: Summary 227 [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
- Page 254 and 255: Chapter 8 QOS ISSUES IN AD-HOC NETW
- Page 256 and 257: Introduction 231 The concept of ad-
- Page 258 and 259: Physical Layer 233 The 802.11a stan
- Page 260 and 261: Medium Access Layer 235 neighbors,
- Page 262 and 263: Medium Access Layer 237 Figure 8.5.
- Page 264 and 265: QoS Routing 239 where is the number
- Page 266 and 267: QoS at other Networking Layers 241
- Page 268 and 269: Inter-Layer Design Approaches 243 8
- Page 270 and 271: Conclusion 245 are specifically des
- Page 272 and 273: Conclusion 247 [13] S. Mangold, S.
- Page 274 and 275: Chapter 9 SECURITY IN MOBILE AD-HOC
- Page 276 and 277: Potential Attacks 251 attacks, such
- Page 278 and 279: Attack Prevention Techniques 253 9.
- Page 280 and 281: Intrusion Detection Techniques 255
- Page 282 and 283: Intrusion Detection Techniques 257
- Page 284 and 285: Intrusion Detection Techniques 259
- Page 286 and 287: Intrusion Detection Techniques 261
- Page 288 and 289: Intrusion Detection Techniques 263
- Page 290 and 291: Conclusion 265 an important and sti
- Page 292 and 293: Conclusion 267 [24] [25] [26] [27]
- Page 294 and 295: Index Ad hoc network multicast rout