2 Servomoteurs rotatifs sans ressort de rappel - Siemens Schweiz AG
2 Servomoteurs rotatifs sans ressort de rappel - Siemens Schweiz AG
2 Servomoteurs rotatifs sans ressort de rappel - Siemens Schweiz AG
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
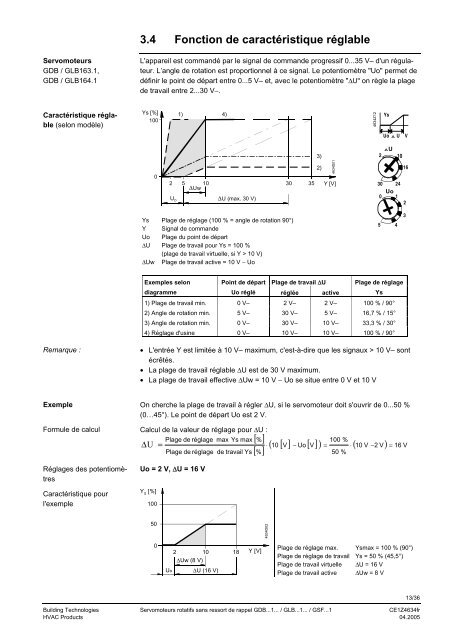
3.4 Fonction <strong>de</strong> caractéristique réglable<strong>Servomoteurs</strong>GDB / GLB163.1,GDB / GLB164.1L'appareil est commandé par le signal <strong>de</strong> comman<strong>de</strong> progressif 0...35 V– d'un régulateur.L’angle <strong>de</strong> rotation est proportionnel à ce signal. Le potentiomètre "Uo" permet <strong>de</strong>définir le point <strong>de</strong> départ entre 0...5 V– et, avec le potentiomètre "∆U" on règle la plage<strong>de</strong> travail entre 2...30 V−.Caractéristique réglable(selon modèle)Ys [%]1001)4)4634Z12YsUoUV02 5 10 30 35 Y [V]∆UwU O∆U (max. 30 V)3)2)4634D01U2 101630 24Uo0 12Ys Plage <strong>de</strong> réglage (100 % = angle <strong>de</strong> rotation 90°)Y Signal <strong>de</strong> comman<strong>de</strong>Uo Plage du point <strong>de</strong> départ∆U Plage <strong>de</strong> travail pour Ys = 100 %(plage <strong>de</strong> travail virtuelle, si Y > 10 V)∆Uw Plage <strong>de</strong> travail active = 10 V − Uo543Exemples selonPoint <strong>de</strong> départ Plage <strong>de</strong> travail ∆U Plage <strong>de</strong> réglagediagrammeUo réglé réglée activeYs1) Plage <strong>de</strong> travail min. 0 V– 2 V– 2 V– 100 % / 90°2) Angle <strong>de</strong> rotation min. 5 V– 30 V– 5 V– 16,7 % / 15°3) Angle <strong>de</strong> rotation min. 0 V– 30 V– 10 V– 33,3 % / 30°4) Réglage d'usine 0 V– 10 V– 10 V– 100 % / 90°Remarque :• L'entrée Y est limitée à 10 V– maximum, c'est-à-dire que les signaux > 10 V– sontécrêtés.• La plage <strong>de</strong> travail réglable ∆U est <strong>de</strong> 30 V maximum.• La plage <strong>de</strong> travail effective ∆Uw = 10 V − Uo se situe entre 0 V et 10 VExempleFormule <strong>de</strong> calculRéglages <strong>de</strong>s potentiomètresCaractéristique pourl'exempleOn cherche la plage <strong>de</strong> travail à régler ∆U, si le servomoteur doit s'ouvrir <strong>de</strong> 0...50 %(0…45°). Le point <strong>de</strong> départ Uo est 2 V.Calcul <strong>de</strong> la valeur <strong>de</strong> réglage pour ∆U :∆ U=Plage <strong>de</strong> réglage max Ys maxPlage <strong>de</strong> réglageUo = 2 V, ∆U = 16 VY S[%]100<strong>de</strong> travail Ys[%][%]⋅100 %( 10 [ V] − Uo[ V]) = ⋅ ( 10 V −2 V) = 16 V50 %504634D020Uo2 10 18∆Uw (8 V)∆U (16 V)Y [V]Plage <strong>de</strong> réglage max. Ysmax = 100 % (90°)Plage <strong>de</strong> réglage <strong>de</strong> travail Ys = 50 % (45,5°)Plage <strong>de</strong> travail virtuelle ∆U = 16 VPlage <strong>de</strong> travail active ∆Uw = 8 V13/36Building Technologies <strong>Servomoteurs</strong> <strong>rotatifs</strong> <strong>sans</strong> <strong>ressort</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>rappel</strong> GDB...1... / GLB...1... / GSF...1 CE1Z4634frHVAC Products 04.2005