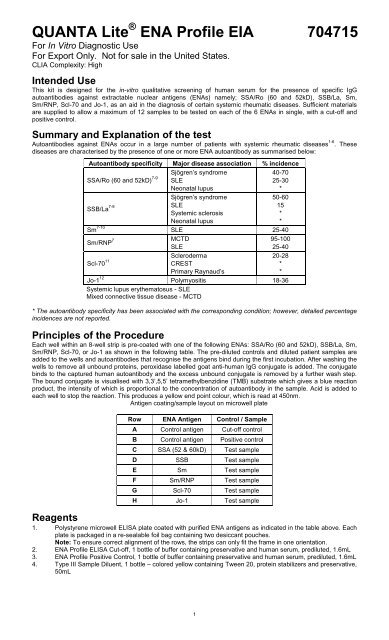
QUANTA Lite ENA Profile EIA - inova
QUANTA Lite ENA Profile EIA - inova
QUANTA Lite ENA Profile EIA - inova
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
ProcedureMaterials provided• Instruction Leaflet: Giving full assay details.• QC Certificate: Indicating the expected performance of the batch.• <strong>ENA</strong> <strong>Profile</strong> Coated Wells: 12 x 8 well strips in which each of the wells is coated with purified <strong>ENA</strong> antigens asindicated in the table in Principles of the Procedure. Each plate is packaged in a re-sealable foil bag containingtwo desiccant pouches.Note: To ensure correct alignment of the rows, the strips can only fit the frame in oneorientation.• Type III Sample Diluent: 1 bottle containing 50mL of buffer for diluting the samples. Ready to use.• HRP Wash Concentrate: 1 bottle containing 25mL of a 40x concentrated buffer for washing the wells.• <strong>ENA</strong> <strong>Profile</strong> ELISA Cut-off: 1 bottle containing 1.6mL of diluted human serum. The expected <strong>ENA</strong> result isgiven on the QC certificate. Ready to use.• <strong>ENA</strong> <strong>Profile</strong> Positive Control: 1 bottle containing 1.6mL of diluted human serum. The expected <strong>ENA</strong> result isgiven on the QC certificate. Ready to use.• HRP <strong>ENA</strong> <strong>Profile</strong> IgG Conjugate: 1 bottle containing 10mL of peroxidase labelled antibody to human IgG.Coloured blue, ready to use.• TMB Chromogen: 1 bottle containing 10mL TMB substrate. Ready to use.• HRP Stop Solution: 1 bottle containing 10mL of 0.344M Sulfuric Acid. Ready to use.Additional materials required but not provided• Automatic microplate plate washer: This is recommended, however, plate washing can be performedmanually.• Plate reader: Capable of measuring optical densities at 450nm referenced on air.• Distilled or deionised water: This should be of the highest quality available.• Calibrated micropipettes: For dispensing 10-1000µL.• Multichannel pipette: Recommended for dispensing 100µL volumes of conjugate, substrate and stop solution.• Glass/plastic tubes: For sample dilution.MethodBefore you start1. Bring the kit to room temperature• The kit is designed for room temperature operation (20-24°C).• Remove the kit from storage and stand at room temperature for approximately 60 minutes. Wellsmust not be removed from the foil bag until they have reached room temperature.Note: The kits maybe maintained at room temperature for up to 1 week.2. Kit componentsGently mix each kit component before use.3. Wash buffer (40X concentrate) dilutionDilute the HRP Wash Concentrate 1:40 by adding the contents of the HRP Wash Concentrate bottle to975mL of distilled or deionized water. If the entire plate will not be run within this period, a smaller quantitycan be prepared by adding 2.0mL of the concentrate to 78mL of distilled or deionized water for every 16wells that will be used. The diluted buffer is stable for 1 week at 2-8°C. If the entire kit is not likely to beused within this time, smaller volumes can be made as appropriate. If the buffer shows any signs ofmicrobial contamination or turns cloudy, discard and prepare a fresh dilution.4. Strip and frame handlingRemembering that each patient sample to be tested requires a single micro-well strip, place the requirednumber of strips in the frame of the plate. Position from well A1, filling columns from left to right across theplate. When handling the plate, squeeze the long edges of the frame to prevent the wells falling out.Note: Return unused wells to the foil bag immediately with the two desiccant pouches and re-seal tightly tominimise exposure to moisture. Take care not to puncture or tear the foil bag, see below.WARNING:Exposure of wells to moisture or contamination by dust or other particulate matter will result inantigen degradation, leading to poor assay precision and potentially false results.5. Sample dilutionDilute 10µL of each sample with 1000µL of sample diluent (1:101) and mix well.Note: Diluted samples must be used within 8 hours.Note: The positive and cut-off controls are ready to use and require no dilution.Assay procedureMaintain the same dispensing sequence throughout the assay.1. Sample additionUsing one whole strip per test sample, dispense 100µL of the ready to use cut-off control into row A andpositive control into row B of all the strips. Add 100µL of diluted (1:101) test sample to the remaining 6 wellsin each of the strips. Note: Samples must be added to the plate as quickly as possible to minimise assaydrift, and the timer started after the addition of the last sample.Incubate at room temperature for 30minutes.2. WashingThe washing procedure is critical and requires special attention. An improperly washed plate will giveinaccurate results, with poor precision and high backgrounds. After incubation remove the plate and washwells 3 times with 200-300µL wash buffer per well. Wash the plate either by using an automatic platewasher or manually as indicated below. After the final automated wash, invert the plate and tap the wellsdry on absorbent paper.Plates can be washed manually as follows:3
a. Flick out the contents of the plate into a sink.b. Tap the wells dry on absorbent paper.c. Fill each well with 200-300µL of wash buffer using a multichannel pipette.d. Gently shake the plate on a flat surface.e. Repeat a-d twice.f. Repeat a and b.3. Conjugate additionDispense 100µL of conjugate into each well, blot the top of the wells with a tissue to remove any splashes.Note: To avoid contamination, never return excess conjugate to the reagent bottle. Incubate at roomtemperature for 30 minutes.4. WashingRepeat step 2.5. Substrate (TMB) additionDispense 100µL of TMB substrate into each well, blot the top of the wells with a tissue to remove anysplashes. Note: To avoid contamination, never return excess TMB to the reagent bottle. Incubate at roomtemperature in the dark for 30 minutes.6. StoppingDispense 100 µL of stop solution into each well. This causes a change in colour from blue to yellow.7. Optical density measurementRead the optical density (OD) of each well at 450nm on a microplate reader, within 30 minutes of stoppingthe reaction.Quality Control1. Quality controlIn order for an assay to be valid, all the following criteria must be met:• Cut-off and positive controls must be included in each run.• The OD of the cut-off and the <strong>ENA</strong> result of the positive controls should be in the ranges specified onthe QC Certificate. If the above criteria are not met, the assay is invalid and the test should berepeated.2. Calculation of the sample and positive control resultUse the following formula to calculate the <strong>ENA</strong> result for each sample:Sample orpositive controlODCut-off controlODx10=Sample or control value(U/mL)Samples giving results in the equivocal range should be confirmed on the relevant specific <strong>ENA</strong> ELISA.3. Assay calibrationThe assay is calibrated against an arbitrary reference. The <strong>ENA</strong> results are semi-quantitative and aredefined by the formula given above.4. Interpretation of Sm and RNP valuesIf a sample is negative for Sm antibodies but positive in the RNP ELISA, then the reactivity is due to thepresence of anti-RNP antibodies alone. If the value of the Sm ELISA is positive and equivalent to the RNPELISA value, then the activity is largely due to the presence of anti-Sm antibodies. An Sm sample that ispositive, but gives a value of less than 80% of the RNP value should be reported as positive for both Smand RNP antibodies. It is difficult to estimate the specific RNP activity of samples giving ODs higher thancan be measured by the ELISA plate reader. Diluting the sample further at 1:200 or 1:400 may help toascertain if the RNP activity is higher than the Sm.Limitations of the Procedure• This kit is used as an aid to diagnosis only. A positive result suggests certain diseases that should be confirmedby clinical findings.• The results obtained from this assay are not diagnostic proof of the presence or absence of disease.Expected ValuesThe cut-off control has been set at a point equivalent to the upper normal limit resulting in 3 different samples beingfound positive for SSB, RNP and Scl-70. The results for all 120 samples were confirmed using the respectiveBINDAZYME single specificity <strong>EIA</strong> kits. The ranges are provided as a guide only. ELISA assays are very sensitiveand capable of detecting small differences in sample populations. It is recommended that each laboratorydetermine its own normal range, based on the population techniques and equipment employed.<strong>ENA</strong> Result Interpretation12.0 Positive4
Performance CharacteristicsPrecisionThe intra-assay precision was measured by adding 12 replicates of a medium value sample for each specificityacross the appropriate row of a single plate.INTRA-ASSAY PRECISIONSpecificityMean value (OpticalDensity)% C.V.SSA 3.10 1.8SSB 1.31 5.9Sm 2.41 3.8Sm/RNP 2.16 3.0Scl-70 2.19 2.9Jo-1 1.44 2.6The inter-assay precision was measured by adding a negative, low positive and a strong positive sample for eachspecificity in singlicate on three kit lots.INTER-ASSAY PRECISIONAssaySample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3U/mL %C.V. U/mL %C.V. U/mL %C.V.SSA/Ro 3.3 6.1 15.5 7.1 29.3 6.1SSB/La 1.9 15.8 23.6 12.7 27.9 19.0Sm 3.7 8.1 19.4 8.3 37.5 10.7Sm/RNP 7.7 5.2 19.3 5.2 46.3 11.9Scl-70 2.6 15.4 18.2 5.0 31.8 4.4Jo-1 3.1 16.1 19.5 6.7 45.3 9.1Relative Specificity, Sensitivity, AgreementThe relative specificity, sensitivity and agreement have been determined by assaying 139 <strong>ENA</strong> positive samples(141 Scl-70) in the profile and each of the BINDAZYME single specificity <strong>EIA</strong> kits.BINDAZYMEELISASSA/RoSSBSmSm/RNPScl-70Jo-1SingleRelative correlations (%)specificity kit+ - Sensitivity Specificity Agreement+ 66 3100 95.9 97.8- 0 70+ 26 0- 1 112+ 18 0- 2 119+ 63 2- 2 72+ 13 5- 0 123+ 21 2- 0 11696.3 100 99.390 100 98.696.9 97.3 97.1100 96.1 96.5100 98.3 98.614 of the 17 discrepant readings were considered equivocal, with all specific assay results being close to the cut-offvalue of the assay (highest value obtained was 12.6 U/mL and the majority 61) pos. (42.7) neg. neg.Sm pos. (20.6) neg. pos. (19.9) neg. pos. (>61)Sm/RNP pos. (28.9) neg. pos. (>61) pos. (>61) pos. (>61)Scl-70 neg. neg. neg. neg. neg.Jo-1 neg. neg. neg. neg. neg.5
AntigenCDC-6nucleolarCDC-7SSACDC-8centromereCDC-9Scl-70CDC-10Jo-1SSA neg. pos. (46.4) neg. neg. pos. (24.0)SSB neg. neg. neg. neg. neg.Sm neg. neg. neg. neg. neg.Sm/RNP neg. neg. neg. neg. neg.Scl-70 neg. neg. neg. pos. (>61) neg.Jo-1 neg. neg. neg. neg. pos. (>61)All sera were correctly identified according to Table 2 in the above reference.Note: Samples CDC-6 and -8 contain antibodies to fibrillarin and centromere antigens, respectively and thuswould not be detected by this kit.Reports indicate the majority of Jo-1 positive sera also contain antibodies to SSA 52kD. This appears the case forCDC-10, which was SSA positive in the profile assay but negative when tested in an SSA/Ro 60kD only kit.Interfering SubstancesA range of interfering substances was spiked into <strong>ENA</strong> negative and positive samples, which have then beensubsequently assayed. The method used to check these substances was based on the Interference Check A pluskit - Kokusai Shiyaku, Japan.SubstanceBilirubin F (Free)Bilirubin C (Conjugate)Haemolysed HaemoglobinChyleConcentration18.3mg/dL19.0mg/dL490mg/dL1930 UnitsNo interference was observed.Plate template1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12ABCDEFGHSummary of procedure1. Add 100µL of each calibrator, control and 1:101 diluted sample to the appropriate wells.Incubate for 30 minutes. Wash.2. Add 100µL of conjugate to each well.Incubate for 30 minutes. Wash.3. Add 100µL of substrate to each well.Incubate for 30 minutes.4. Add 100µL of stop solution to each well.Measure the absorbance at 450nm.6
References1. Mongey AB, Hess EV. Antinuclear Antibodies and Disease Specificity. Adv Intern Med, 1991. 36:151-169.2. Moore TL et al. Extractable Nuclear Antigens. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 1981. 10 No.2: 309-318.3. Nakamura et al. Advances in Laboratory Tests for Autoantibodies to Nuclear Antigens in SystemicRheumatic Diseases. Laboratory Medicine. 1984. 15 No.3:190-198.4. White RH, Robbins DL. Clinical Significance and Interpretation of Antinuclear Antibodies. West J Med,1987. 147: 210-213.5. Nakamura RM, Tan M. Recent Progress in the Study of Autoantibodies to Nuclear Antigens. HumanPathology. 1978. 9 No.1:85-91.6. Hardin JA et al. The Molecular Biology of Autoantibodies. Arthritis Foundation Atlanta GA. 1987. Chapter 7:32-36.7. Maddison PJ et al. Antibodies to nRNP, Sm, Ro(SSA), and La(SSB) detected by ELISA: their specificityand inter-relations in connective tissue disease sera. Clin Exp Immunol, 1985. 62: 337-345.8. Harley JB, Yamagata H, Reuchlin M. Anti-La/SSA Antibody is Present in Some Normal Sera and isCoincident with Anti-Ro/SSA Precipitins in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Rheumatol, 1984. 11: 309-314.9. Reichlin M. Clinical and Immunological Significance of Antibodies to Ro and La in Systemic LupusErythematosus. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 1982. 25, No.7: 767-772.10. Mitsuhiko Yasuma et al. Clinical Significance of IgG Anti-Sm Antibodies in Patients with Systemic LupusErythematosus. J Rheumatol, 1990. 17:4: 469-475.11. Aeschlimann A et al. Anti-Scl-70 antibodies detected by immunoblotting in progressive systemic sclerosis:specificity and clinical correlations. Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1989. 48: 992-997.12. Cornin ME, Miller FW, Plotz PH. Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis. Arthritis Foundation Atlanta GA. 1988.Chapter 21: 120-123.13. Protein Reference Unit Handbook of Autoimmunity (3rd Edition) 2004 Ed A Milford Ward. J. Sheldon, GDWild. Publ. PRU Publications, Sheffield. 14.14. Tan EM et al. A critical evaluation of enzyme immunoassays for the detection of antinuclear antibodies ofdefined specificities. Arthritis and Rheum. 1999; 42 (3): 455-464.15. Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories. Center for Disease Control/National Institute ofHealth, 2007, Fifth Edition.Manufactured By:INOVA Diagnostics, Inc.9900 Old Grove RoadSan Diego, CA 92131United States of AmericaTechnical Service (U.S. & Canada Only) : 877-829-4745Technical Service (Outside the U.S.) :00+ 1 858-805-7950support@<strong>inova</strong>dx.comAuthorized Representative in the EU:Medical Technology Promedt Consulting GmbHAltenhofstrasse 80D-66386 St. Ingbert, GermanyTel.: +49-6894-581020Fax.: +49-6894-581021www.mt-procons.com624715USA July 2012Revision 1<strong>QUANTA</strong> <strong>Lite</strong> and INOVA Diagnostics are registered trademarks Copyright 2011 All Rights Reserved©7