Curved Beam - VTU e-Learning
Curved Beam - VTU e-Learning
Curved Beam - VTU e-Learning
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
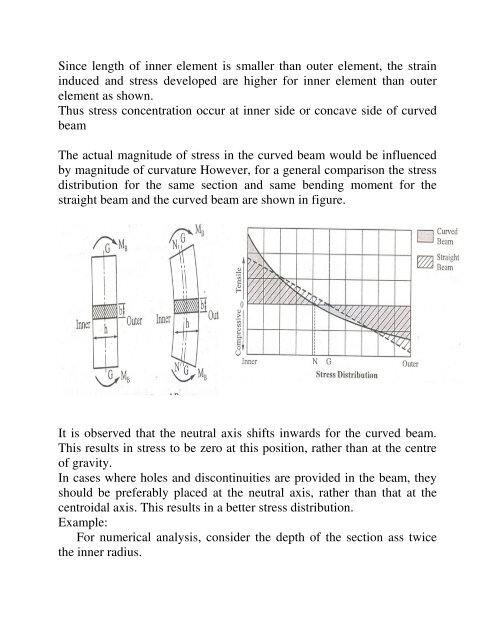
Since length of inner element is smaller than outer element, the strain<br />
induced and stress developed are higher for inner element than outer<br />
element as shown.<br />
Thus stress concentration occur at inner side or concave side of curved<br />
beam<br />
The actual magnitude of stress in the curved beam would be influenced<br />
by magnitude of curvature However, for a general comparison the stress<br />
distribution for the same section and same bending moment for the<br />
straight beam and the curved beam are shown in figure.<br />
It is observed that the neutral axis shifts inwards for the curved beam.<br />
This results in stress to be zero at this position, rather than at the centre<br />
of gravity.<br />
In cases where holes and discontinuities are provided in the beam, they<br />
should be preferably placed at the neutral axis, rather than that at the<br />
centroidal axis. This results in a better stress distribution.<br />
Example:<br />
For numerical analysis, consider the depth of the section ass twice<br />
the inner radius.