Curved Beam - VTU e-Learning
Curved Beam - VTU e-Learning
Curved Beam - VTU e-Learning
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
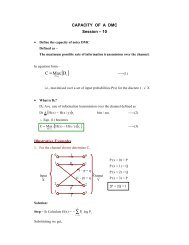
c = Radius of centroidal axis<br />
r n = Radius of neutral axis<br />
CL= Centre line of curvature<br />
Summation of forces over the whole cross section<br />
i.e. dF 0<br />
As θ<br />
θ<br />
∴ θ<br />
θ<br />
<br />
=0<br />
is not equal to zero,<br />
∴ <br />
<br />
= 0 ..... (ii)<br />
The neutral axis radius 'rn' can be determined from the above equation.<br />
If the moments are taken about the neutral axis,<br />
M b = – ydF<br />
Substituting the value of dF, we get<br />
M b = θ<br />
θ<br />
<br />
dA<br />
= θ<br />
θ y dA<br />
= θ<br />
θ<br />
ydA <br />
<br />
0<br />
Since ydA represents the statical moment of area, it may be replaced<br />
by A.e., the product of total area A and the distance 'e' from the<br />
centroidal axis to the neutral axis.