animal production - CSK Himachal Pradesh Agricultural University ...
animal production - CSK Himachal Pradesh Agricultural University ...
animal production - CSK Himachal Pradesh Agricultural University ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
the lambs and kids during second week after birth, with red hot iron and apply antiseptic cream to the wound. Provide<br />
legume hay, concentrate mixture and milk, as given in the following table:<br />
Adult stock<br />
Female<br />
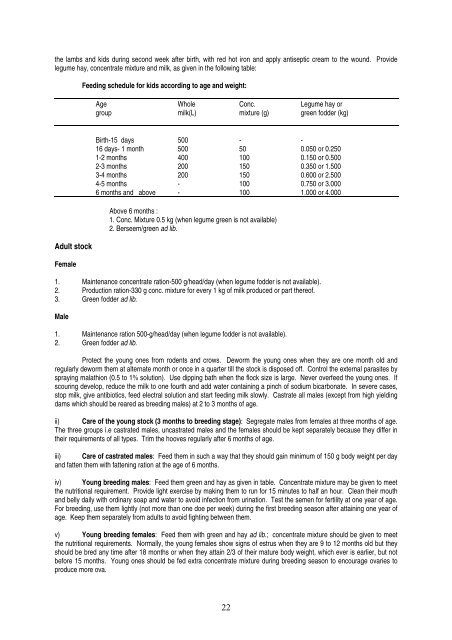
Feeding schedule for kids according to age and weight:<br />
Age Whole Conc. Legume hay or<br />
group milk(L) mixture (g) green fodder (kg)<br />
Birth-15 days 500 - -<br />
16 days- 1 month 500 50 0.050 or 0.250<br />
1-2 months 400 100 0.150 or 0.500<br />
2-3 months 200 150 0.350 or 1.500<br />
3-4 months 200 150 0.600 or 2.500<br />
4-5 months - 100 0.750 or 3.000<br />
6 months and above - 100 1.000 or 4.000<br />
Above 6 months :<br />
1. Conc. Mixture 0.5 kg (when legume green is not available)<br />
2. Berseem/green ad lib.<br />
1. Maintenance concentrate ration-500 g/head/day (when legume fodder is not available).<br />
2. Production ration-330 g conc. mixture for every 1 kg of milk produced or part thereof.<br />
3. Green fodder ad lib.<br />
Male<br />
1. Maintenance ration 500-g/head/day (when legume fodder is not available).<br />
2. Green fodder ad lib.<br />
Protect the young ones from rodents and crows. Deworm the young ones when they are one month old and<br />
regularly deworm them at alternate month or once in a quarter till the stock is disposed off. Control the external parasites by<br />
spraying malathion (0.5 to 1% solution). Use dipping bath when the flock size is large. Never overfeed the young ones. If<br />
scouring develop, reduce the milk to one fourth and add water containing a pinch of sodium bicarbonate. In severe cases,<br />
stop milk, give antibiotics, feed electral solution and start feeding milk slowly. Castrate all males (except from high yielding<br />
dams which should be reared as breeding males) at 2 to 3 months of age.<br />
ii) Care of the young stock (3 months to breeding stage): Segregate males from females at three months of age.<br />
The three groups i.e castrated males, uncastrated males and the females should be kept separately because they differ in<br />
their requirements of all types. Trim the hooves regularly after 6 months of age.<br />
iii) Care of castrated males: Feed them in such a way that they should gain minimum of 150 g body weight per day<br />
and fatten them with fattening ration at the age of 6 months.<br />
iv) Young breeding males: Feed them green and hay as given in table. Concentrate mixture may be given to meet<br />
the nutritional requirement. Provide light exercise by making them to run for 15 minutes to half an hour. Clean their mouth<br />
and belly daily with ordinary soap and water to avoid infection from urination. Test the semen for fertility at one year of age.<br />
For breeding, use them lightly (not more than one doe per week) during the first breeding season after attaining one year of<br />
age. Keep them separately from adults to avoid fighting between them.<br />
v) Young breeding females: Feed them with green and hay ad lib.; concentrate mixture should be given to meet<br />
the nutritional requirements. Normally, the young females show signs of estrus when they are 9 to 12 months old but they<br />
should be bred any time after 18 months or when they attain 2/3 of their mature body weight, which ever is earlier, but not<br />
before 15 months. Young ones should be fed extra concentrate mixture during breeding season to encourage ovaries to<br />
produce more ova.<br />
22