An overview of vis-nir-swir field spectroscopy - Spectral International
An overview of vis-nir-swir field spectroscopy - Spectral International
An overview of vis-nir-swir field spectroscopy - Spectral International
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
________________________________________________________________<br />
This assemblage also contains adularia. The chemical bonds for feldspars are<br />
not detectable in the SWIR range. This varies from alteration around veins,<br />
fractures and permeable zones to selective replacement <strong>of</strong> plagioclase in<br />
alteration envelopes.<br />
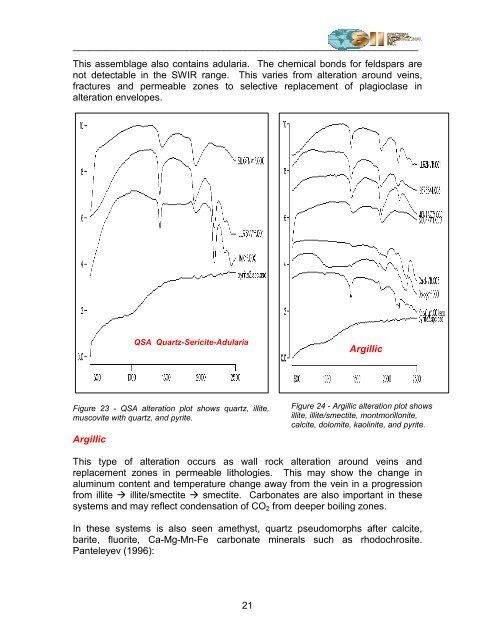
Figure 23 - QSA alteration plot shows quartz, illite,<br />
muscovite with quartz, and pyrite.<br />
Argillic<br />
QSA Quartz-Sericite-Adularia<br />
This type <strong>of</strong> alteration occurs as wall rock alteration around veins and<br />
replacement zones in permeable lithologies. This may show the change in<br />
aluminum content and temperature change away from the vein in a progression<br />
from illite illite/smectite smectite. Carbonates are also important in these<br />
systems and may reflect condensation <strong>of</strong> CO2 from deeper boiling zones.<br />
In these systems is also seen amethyst, quartz pseudomorphs after calcite,<br />
barite, fluorite, Ca-Mg-Mn-Fe carbonate minerals such as rhodochrosite.<br />
Panteleyev (1996):<br />
21<br />
Argillic<br />
Figure 24 - Argillic alteration plot shows<br />
illite, illite/smectite, montmorillonite,<br />
calcite, dolomite, kaolinite, and pyrite.