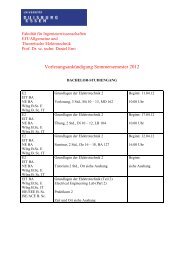
Computerorientierte Feldtheorie 1 Computational Electromagnetics ...
Computerorientierte Feldtheorie 1 Computational Electromagnetics ...
Computerorientierte Feldtheorie 1 Computational Electromagnetics ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Computerorientierte</strong> <strong>Feldtheorie</strong> 1<br />
<strong>Computational</strong> <strong>Electromagnetics</strong> 1<br />
Electromagnetic Simulation Software 1<br />
PoiSolve<br />
Introductory Lecture<br />
23.10.2009<br />
Andre Rennings, BA 345, andre.rennings@uni-due.de<br />
Outline<br />
2<br />
1
Why computer-aided methods are used?<br />
Why computer-aided methods are needed?<br />
3<br />
4<br />
2
Fundamentals of simulations<br />
As analytical solutions are difficult (or impossible), there exist many<br />
computational methods that are based on approximations of Maxwell’s<br />
equations and/or boundary conditions and/or material properties.<br />
”The power of analytical models over full-wave computational simulations is<br />
the significantly lower calculating time. With analytical models and modern<br />
mathematical software (like MATLAB or MAPLE), the solving time is decreased<br />
into seconds. The analytical result is always more or less an approximation,<br />
whereas the EM simulation is as exact as the user’s know-how with the<br />
simulator enables. However in practical design, the value of the saved<br />
calculation time is multiple times worth of the decreased accuracy when the<br />
limits of the model are acknowledged...”<br />
What do you think?<br />
Fundamentals of simulations<br />
5<br />
6<br />
3
Electromagnetic simulators<br />
Approaches to field solutions<br />
7<br />
8<br />
4
Fundamentals of simulations<br />
Fundamentals of simulations<br />
9<br />
10<br />
5
Fundamentals of simulations<br />
Important simulation parameters<br />
11<br />
12<br />
6
Checklist for accuracy<br />
Summary: Importance & place of numerical methods<br />
13<br />
14<br />
7
Various numerical methods<br />
Classification of numerical methods<br />
15<br />
16<br />
8
Frequency domain vs. time domain methods<br />
Advantages of FD modelling<br />
17<br />
18<br />
9
Advantages of TD modelling<br />
Finite Element Method, FEM<br />
19<br />
20<br />
10
Some features of FEM<br />
Finite Difference Time Domain, FDTD<br />
21<br />
22<br />
11
Some features of FDTD<br />
Method of Moments, MoM<br />
23<br />
24<br />
12
Some features of MoM<br />
Expansion functions<br />
25<br />
26<br />
13
MoM, FEM, FDTD – Comparison I<br />
MoM, FEM, FDTD – Comparison II<br />
27<br />
28<br />
14
Conclusions<br />
29<br />
15