3D DISCRETE DISLOCATION DYNAMICS APPLIED TO ... - NUMODIS
3D DISCRETE DISLOCATION DYNAMICS APPLIED TO ... - NUMODIS
3D DISCRETE DISLOCATION DYNAMICS APPLIED TO ... - NUMODIS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
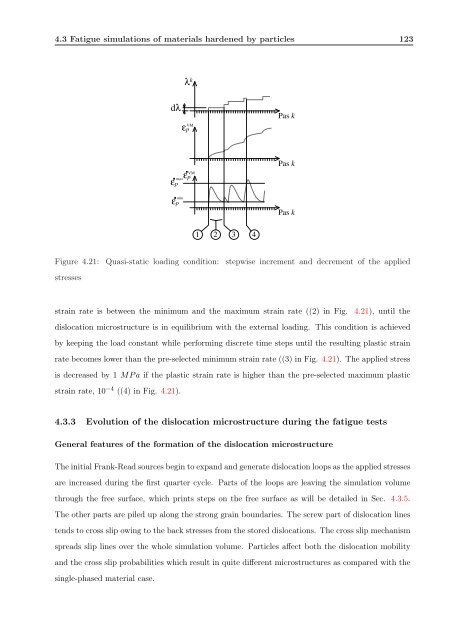
4.3 Fatigue simulations of materials hardened by particles 123<br />
dλ<br />
λ k<br />
εp VM<br />
εp VM<br />
εp max<br />
εp min<br />
1 2 3 4<br />
Figure 4.21: Quasi-static loading condition: stepwise increment and decrement of the applied<br />
stresses<br />
strain rate is between the minimum and the maximum strain rate ((2) in Fig. 4.21), until the<br />
dislocation microstructure is in equilibrium with the external loading. This condition is achieved<br />
by keeping the load constant while performing discrete time steps until the resulting plastic strain<br />
rate becomes lower than the pre-selected minimum strain rate ((3) in Fig. 4.21). The applied stress<br />
is decreased by 1 MP a if the plastic strain rate is higher than the pre-selected maximum plastic<br />
strain rate, 10 −4 ((4) in Fig. 4.21).<br />
4.3.3 Evolution of the dislocation microstructure during the fatigue tests<br />
Pas k<br />
Pas k<br />
Pas k<br />
General features of the formation of the dislocation microstructure<br />
The initial Frank-Read sources begin to expand and generate dislocation loops as the applied stresses<br />
are increased during the first quarter cycle. Parts of the loops are leaving the simulation volume<br />
through the free surface, which prints steps on the free surface as will be detailed in Sec. 4.3.5.<br />
The other parts are piled up along the strong grain boundaries. The screw part of dislocation lines<br />
tends to cross slip owing to the back stresses from the stored dislocations. The cross slip mechanism<br />
spreads slip lines over the whole simulation volume. Particles affect both the dislocation mobility<br />
and the cross slip probabilities which result in quite different microstructures as compared with the<br />
single-phased material case.