3D DISCRETE DISLOCATION DYNAMICS APPLIED TO ... - NUMODIS
3D DISCRETE DISLOCATION DYNAMICS APPLIED TO ... - NUMODIS
3D DISCRETE DISLOCATION DYNAMICS APPLIED TO ... - NUMODIS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2.5 Acceleration of the DDD code 39<br />
[100]<br />
[001]<br />
Slip direction,<br />
[112]<br />
(1)<br />
(2)<br />
Slip plane,<br />
(11-1)<br />
Screw<br />
segment<br />
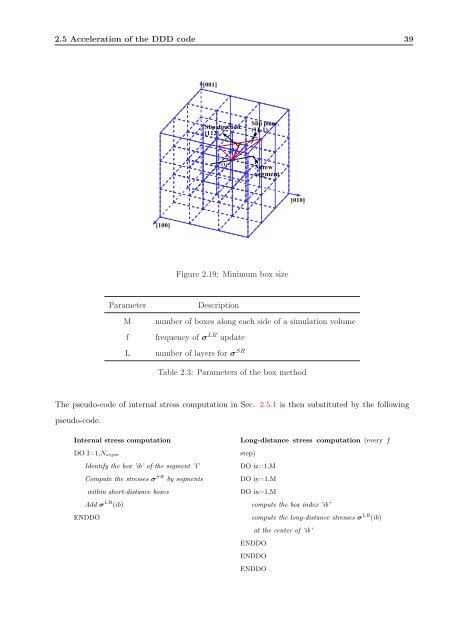
Figure 2.19: Minimum box size<br />
Parameter Description<br />
[010]<br />
M number of boxes along each side of a simulation volume<br />
f frequency of σ LR update<br />
L number of layers for σ SR<br />
Table 2.3: Parameters of the box method<br />
The pseudo-code of internal stress computation in Sec. 2.5.1 is then substituted by the following<br />
pseudo-code.<br />
Internal stress computation<br />
DO I=1,Nsegm<br />
Identify the box ’ib’ of the segment ’I’<br />
Compute the stresses σ SR by segments<br />
within short-distance boxes<br />
Add σ LR (ib)<br />
ENDDO<br />
Long-distance stress computation (every f<br />
step)<br />
DO iz=1,M<br />
DO iy=1,M<br />
DO ix=1,M<br />
compute the box index ’ib’<br />
compute the long-distance stresses σ LR (ib)<br />
ENDDO<br />
ENDDO<br />
ENDDO<br />
at the center of ’ib’