Engineering geology of British rocks and soils Mudstones of the ...
Engineering geology of British rocks and soils Mudstones of the ...
Engineering geology of British rocks and soils Mudstones of the ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
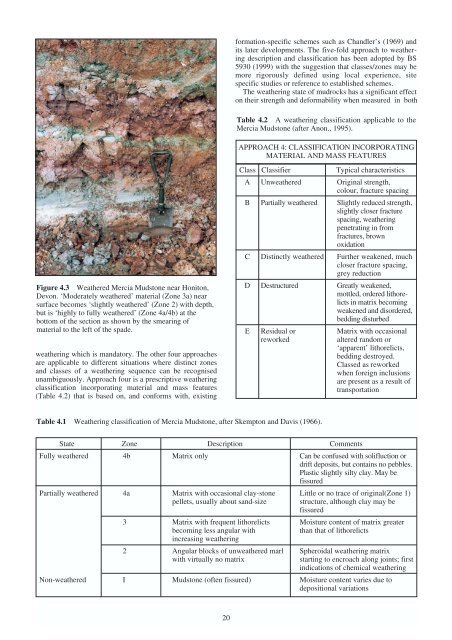
Figure 4.3 Wea<strong>the</strong>red Mercia Mudstone near Honiton,<br />
Devon. ‘Moderately wea<strong>the</strong>red’ material (Zone 3a) near<br />
surface becomes ‘slightly wea<strong>the</strong>red’ (Zone 2) with depth,<br />
but is ‘highly to fully wea<strong>the</strong>red’ (Zone 4a/4b) at <strong>the</strong><br />
bottom <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> section as shown by <strong>the</strong> smearing <strong>of</strong><br />
material to <strong>the</strong> left <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> spade.<br />
wea<strong>the</strong>ring which is m<strong>and</strong>atory. The o<strong>the</strong>r four approaches<br />
are applicable to different situations where distinct zones<br />
<strong>and</strong> classes <strong>of</strong> a wea<strong>the</strong>ring sequence can be recognised<br />
unambiguously. Approach four is a prescriptive wea<strong>the</strong>ring<br />
classification incorporating material <strong>and</strong> mass features<br />
(Table 4.2) that is based on, <strong>and</strong> conforms with, existing<br />
Table 4.1 Wea<strong>the</strong>ring classification <strong>of</strong> Mercia Mudstone, after Skempton <strong>and</strong> Davis (1966).<br />
20<br />
formation-specific schemes such as Ch<strong>and</strong>ler’s (1969) <strong>and</strong><br />
its later developments. The five-fold approach to wea<strong>the</strong>ring<br />
description <strong>and</strong> classification has been adopted by BS<br />
5930 (1999) with <strong>the</strong> suggestion that classes/zones may be<br />
more rigorously defined using local experience, site<br />
specific studies or reference to established schemes.<br />
The wea<strong>the</strong>ring state <strong>of</strong> mud<strong>rocks</strong> has a significant effect<br />
on <strong>the</strong>ir strength <strong>and</strong> deformability when measured in both<br />
Table 4.2 A wea<strong>the</strong>ring classification applicable to <strong>the</strong><br />
Mercia Mudstone (after Anon., 1995).<br />
APPROACH 4: CLASSIFICATION INCORPORATING<br />
MATERIAL AND MASS FEATURES<br />
Class Classifier Typical characteristics<br />
A Unwea<strong>the</strong>red Original strength,<br />
colour, fracture spacing<br />
B Partially wea<strong>the</strong>red Slightly reduced strength,<br />
slightly closer fracture<br />
spacing, wea<strong>the</strong>ring<br />
penetrating in from<br />
fractures, brown<br />
oxidation<br />
C Distinctly wea<strong>the</strong>red Fur<strong>the</strong>r weakened, much<br />
closer fracture spacing,<br />
grey reduction<br />
D Destructured Greatly weakened,<br />
mottled, ordered lithorelicts<br />
in matrix becoming<br />
weakened <strong>and</strong> disordered,<br />
bedding disturbed<br />
E Residual or Matrix with occasional<br />
reworked altered r<strong>and</strong>om or<br />
‘apparent’ lithorelicts,<br />
bedding destroyed.<br />
Classed as reworked<br />
when foreign inclusions<br />
are present as a result <strong>of</strong><br />
transportation<br />
State Zone Description Comments<br />
Fully wea<strong>the</strong>red 4b Matrix only Can be confused with solifluction or<br />
drift deposits, but contains no pebbles.<br />
Plastic slightly silty clay. May be<br />
fissured<br />
Partially wea<strong>the</strong>red 4a Matrix with occasional clay-stone Little or no trace <strong>of</strong> original(Zone 1)<br />
pellets, usually about s<strong>and</strong>-size structure, although clay may be<br />
fissured<br />
3 Matrix with frequent lithorelicts Moisture content <strong>of</strong> matrix greater<br />
becoming less angular with<br />
increasing wea<strong>the</strong>ring<br />
than that <strong>of</strong> lithorelicts<br />
2 Angular blocks <strong>of</strong> unwea<strong>the</strong>red marl Spheroidal wea<strong>the</strong>ring matrix<br />
with virtually no matrix starting to encroach along joints; first<br />
indications <strong>of</strong> chemical wea<strong>the</strong>ring<br />
Non-wea<strong>the</strong>red I Mudstone (<strong>of</strong>ten fissured) Moisture content varies due to<br />
depositional variations