The Plant Vascular System: Evolution, Development and FunctionsF
The Plant Vascular System: Evolution, Development and FunctionsF
The Plant Vascular System: Evolution, Development and FunctionsF
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Insights into <strong>Plant</strong> <strong>Vascular</strong> Biology 303<br />
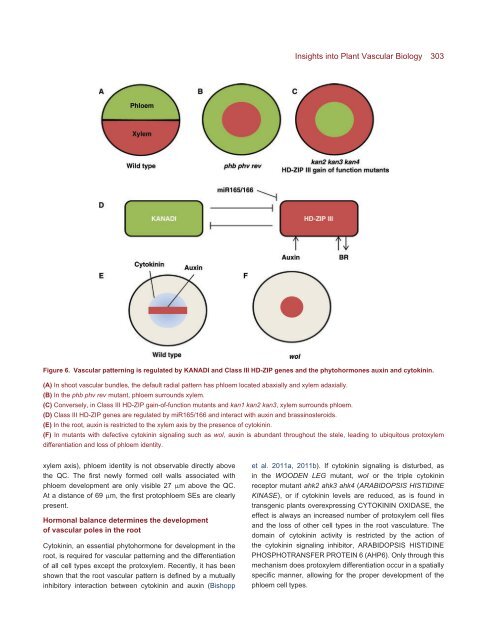
Figure 6. <strong>Vascular</strong> patterning is regulated by KANADI <strong>and</strong> Class III HD-ZIP genes <strong>and</strong> the phytohormones auxin <strong>and</strong> cytokinin.<br />
(A) In shoot vascular bundles, the default radial pattern has phloem located abaxially <strong>and</strong> xylem adaxially.<br />
(B) In the phb phv rev mutant, phloem surrounds xylem.<br />
(C) Conversely, in Class III HD-ZIP gain-of-function mutants <strong>and</strong> kan1 kan2 kan3, xylem surrounds phloem.<br />
(D) Class III HD-ZIP genes are regulated by miR165/166 <strong>and</strong> interact with auxin <strong>and</strong> brassinosteroids.<br />
(E) In the root, auxin is restricted to the xylem axis by the presence of cytokinin.<br />
(F) In mutants with defective cytokinin signaling such as wol, auxin is abundant throughout the stele, leading to ubiquitous protoxylem<br />
differentiation <strong>and</strong> loss of phloem identity.<br />
xylem axis), phloem identity is not observable directly above<br />
the QC. <strong>The</strong> first newly formed cell walls associated with<br />
phloem development are only visible 27 µm above the QC.<br />
At a distance of 69 µm, the first protophloem SEs are clearly<br />
present.<br />
Hormonal balance determines the development<br />
of vascular poles in the root<br />
Cytokinin, an essential phytohormone for development in the<br />
root, is required for vascular patterning <strong>and</strong> the differentiation<br />
of all cell types except the protoxylem. Recently, it has been<br />
shown that the root vascular pattern is defined by a mutually<br />
inhibitory interaction between cytokinin <strong>and</strong> auxin (Bishopp<br />
et al. 2011a, 2011b). If cytokinin signaling is disturbed, as<br />
in the WOODEN LEG mutant, wol or the triple cytokinin<br />
receptor mutant ahk2 ahk3 ahk4 (ARABIDOPSIS HISTIDINE<br />
KINASE), or if cytokinin levels are reduced, as is found in<br />
transgenic plants overexpressing CYTOKININ OXIDASE, the<br />
effect is always an increased number of protoxylem cell files<br />
<strong>and</strong> the loss of other cell types in the root vasculature. <strong>The</strong><br />
domain of cytokinin activity is restricted by the action of<br />
the cytokinin signaling inhibitor, ARABIDOPSIS HISTIDINE<br />
PHOSPHOTRANSFER PROTEIN 6 (AHP6). Only through this<br />
mechanism does protoxylem differentiation occur in a spatially<br />
specific manner, allowing for the proper development of the<br />
phloem cell types.