The Plant Vascular System: Evolution, Development and FunctionsF
The Plant Vascular System: Evolution, Development and FunctionsF
The Plant Vascular System: Evolution, Development and FunctionsF
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
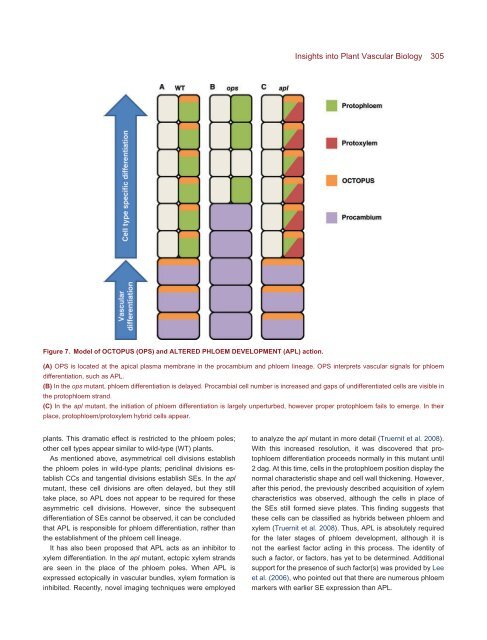
Figure 7. Model of OCTOPUS (OPS) <strong>and</strong> ALTERED PHLOEM DEVELOPMENT (APL) action.<br />
Insights into <strong>Plant</strong> <strong>Vascular</strong> Biology 305<br />
(A) OPS is located at the apical plasma membrane in the procambium <strong>and</strong> phloem lineage. OPS interprets vascular signals for phloem<br />
differentiation, such as APL.<br />
(B) In the ops mutant, phloem differentiation is delayed. Procambial cell number is increased <strong>and</strong> gaps of undifferentiated cells are visible in<br />
the protophloem str<strong>and</strong>.<br />
(C) In the apl mutant, the initiation of phloem differentiation is largely unperturbed, however proper protophloem fails to emerge. In their<br />
place, protophloem/protoxylem hybrid cells appear.<br />
plants. This dramatic effect is restricted to the phloem poles;<br />
other cell types appear similar to wild-type (WT) plants.<br />
As mentioned above, asymmetrical cell divisions establish<br />
the phloem poles in wild-type plants; periclinal divisions establish<br />
CCs <strong>and</strong> tangential divisions establish SEs. In the apl<br />
mutant, these cell divisions are often delayed, but they still<br />
take place, so APL does not appear to be required for these<br />
asymmetric cell divisions. However, since the subsequent<br />
differentiation of SEs cannot be observed, it can be concluded<br />
that APL is responsible for phloem differentiation, rather than<br />
the establishment of the phloem cell lineage.<br />
It has also been proposed that APL acts as an inhibitor to<br />
xylem differentiation. In the apl mutant, ectopic xylem str<strong>and</strong>s<br />
are seen in the place of the phloem poles. When APL is<br />
expressed ectopically in vascular bundles, xylem formation is<br />
inhibited. Recently, novel imaging techniques were employed<br />
to analyze the apl mutant in more detail (Truernit et al. 2008).<br />
With this increased resolution, it was discovered that protophloem<br />
differentiation proceeds normally in this mutant until<br />
2 dag. At this time, cells in the protophloem position display the<br />
normal characteristic shape <strong>and</strong> cell wall thickening. However,<br />
after this period, the previously described acquisition of xylem<br />
characteristics was observed, although the cells in place of<br />
the SEs still formed sieve plates. This finding suggests that<br />
these cells can be classified as hybrids between phloem <strong>and</strong><br />
xylem (Truernit et al. 2008). Thus, APL is absolutely required<br />
for the later stages of phloem development, although it is<br />
not the earliest factor acting in this process. <strong>The</strong> identity of<br />
such a factor, or factors, has yet to be determined. Additional<br />
support for the presence of such factor(s) was provided by Lee<br />
et al. (2006), who pointed out that there are numerous phloem<br />
markers with earlier SE expression than APL.