The Plant Vascular System: Evolution, Development and FunctionsF
The Plant Vascular System: Evolution, Development and FunctionsF
The Plant Vascular System: Evolution, Development and FunctionsF
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
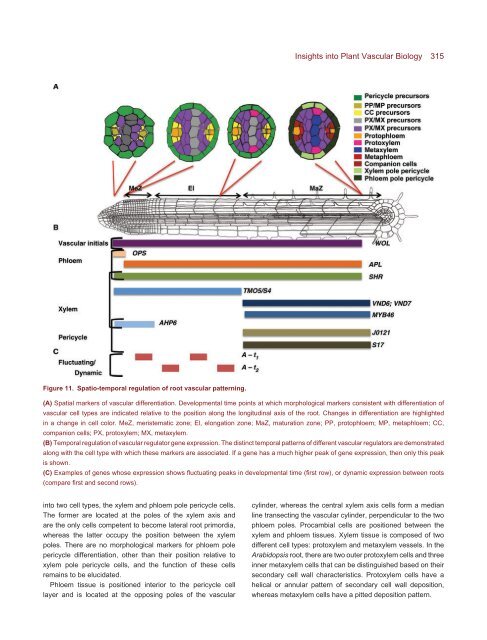
Figure 11. Spatio-temporal regulation of root vascular patterning.<br />
Insights into <strong>Plant</strong> <strong>Vascular</strong> Biology 315<br />
(A) Spatial markers of vascular differentiation. <strong>Development</strong>al time points at which morphological markers consistent with differentiation of<br />
vascular cell types are indicated relative to the position along the longitudinal axis of the root. Changes in differentiation are highlighted<br />
in a change in cell color. MeZ, meristematic zone; El, elongation zone; MaZ, maturation zone; PP, protophloem; MP, metaphloem; CC,<br />
companion cells; PX, protoxylem; MX, metaxylem.<br />
(B) Temporal regulation of vascular regulator gene expression. <strong>The</strong> distinct temporal patterns of different vascular regulators are demonstrated<br />
along with the cell type with which these markers are associated. If a gene has a much higher peak of gene expression, then only this peak<br />
is shown.<br />
(C) Examples of genes whose expression shows fluctuating peaks in developmental time (first row), or dynamic expression between roots<br />
(compare first <strong>and</strong> second rows).<br />
into two cell types, the xylem <strong>and</strong> phloem pole pericycle cells.<br />
<strong>The</strong> former are located at the poles of the xylem axis <strong>and</strong><br />
are the only cells competent to become lateral root primordia,<br />
whereas the latter occupy the position between the xylem<br />
poles. <strong>The</strong>re are no morphological markers for phloem pole<br />
pericycle differentiation, other than their position relative to<br />
xylem pole pericycle cells, <strong>and</strong> the function of these cells<br />
remains to be elucidated.<br />
Phloem tissue is positioned interior to the pericycle cell<br />
layer <strong>and</strong> is located at the opposing poles of the vascular<br />
cylinder, whereas the central xylem axis cells form a median<br />
line transecting the vascular cylinder, perpendicular to the two<br />
phloem poles. Procambial cells are positioned between the<br />
xylem <strong>and</strong> phloem tissues. Xylem tissue is composed of two<br />
different cell types: protoxylem <strong>and</strong> metaxylem vessels. In the<br />
Arabidopsis root, there are two outer protoxylem cells <strong>and</strong> three<br />
inner metaxylem cells that can be distinguished based on their<br />
secondary cell wall characteristics. Protoxylem cells have a<br />
helical or annular pattern of secondary cell wall deposition,<br />
whereas metaxylem cells have a pitted deposition pattern.