final .cdr
final .cdr
final .cdr
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
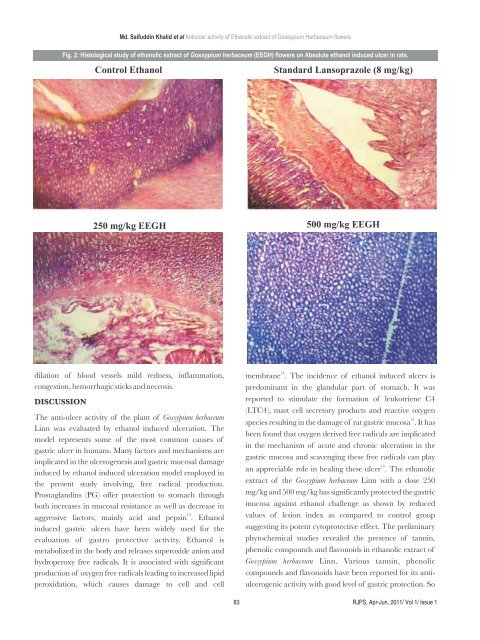
dilation of blood vessels mild redness, inflammation,<br />
congestion, hemorrhagic sticks and necrosis.<br />
DISCUSSION<br />
Md. Saifuddin Khalid et al Antiulcer activity of Ethanolic extract of Gossypium Harbaceum flowers<br />
Fig. 2: Histological study of ethanolic extract of Gossypium herbaceum (EEGH) flowers on Absolute ethanol induced ulcer in rats.<br />
Control Ethanol Standard Lansoprazole (8 mg/kg)<br />
250 mg/kg EEGH<br />
The anti-ulcer activity of the plant of Gossypium herbaceum<br />
Linn was evaluated by ethanol induced ulceration. The<br />
model represents some of the most common causes of<br />
gastric ulcer in humans. Many factors and mechanisms are<br />
implicated in the ulcerogenesis and gastric mucosal damage<br />
induced by ethanol induced ulceration model employed in<br />
the present study involving, free radical production.<br />
Prostaglandins (PG) offer protection to stomach through<br />
both increases in mucosal resistance as well as decrease in<br />
13<br />
aggressive factors, mainly acid and pepsin . Ethanol<br />
induced gastric ulcers have been widely used for the<br />
evaluation of gastro protective activity. Ethanol is<br />
metabolized in the body and releases superoxide anion and<br />
hydroperoxy free radicals. It is associated with significant<br />
production of oxygen free radicals leading to increased lipid<br />
peroxidation, which causes damage to cell and cell<br />
83<br />
500 mg/kg EEGH<br />
14<br />
membrane . The incidence of ethanol induced ulcers is<br />
predominant in the glandular part of stomach. It was<br />
reported to stimulate the formation of leukotriene C4<br />
(LTC4), mast cell secretory products and reactive oxygen<br />
15<br />
species resulting in the damage of rat gastric mucosa . It has<br />
been found that oxygen derived free radicals are implicated<br />
in the mechanism of acute and chronic ulceration in the<br />
gastric mucosa and scavenging these free radicals can play<br />
16<br />
an appreciable role in healing these ulcer . The ethanolic<br />
extract of the Gossypium herbaceum Linn with a dose 250<br />
mg/kg and 500 mg/kg has significantly protected the gastric<br />
mucosa against ethanol challenge as shown by reduced<br />
values of lesion index as compared to control group<br />
suggesting its potent cytoprotective effect. The preliminary<br />
phytochemical studies revealed the presence of tannin,<br />
phenolic compounds and flavonoids in ethanolic extract of<br />
Gossypium herbaceum Linn. Various tannin, phenolic<br />
compounds and flavonoids have been reported for its antiulcerogenic<br />
activity with good level of gastric protection. So<br />
RJPS, Apr-Jun, 2011/ Vol 1/ Issue 1