market analysis final report v1.1 - ESA Space Weather Web Server
market analysis final report v1.1 - ESA Space Weather Web Server
market analysis final report v1.1 - ESA Space Weather Web Server
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>ESA</strong> SW Programme Study Market Analysis<br />
Final Report<br />
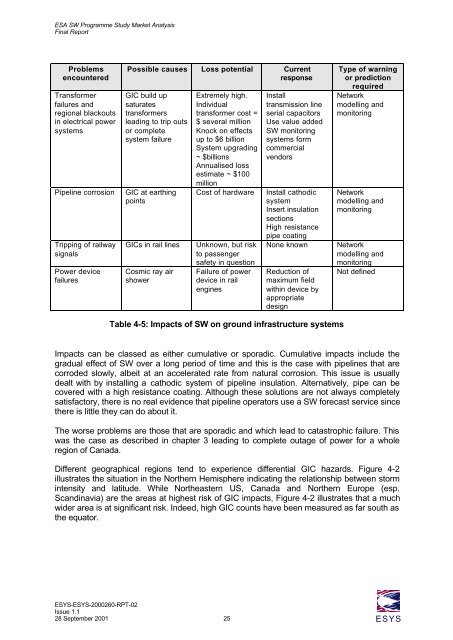
Problems<br />
encountered<br />
Transformer<br />
failures and<br />
regional blackouts<br />
in electrical power<br />
systems<br />
Possible causes Loss potential Current<br />
response<br />
GIC build up<br />
saturates<br />
transformers<br />
leading to trip outs<br />
or complete<br />
system failure<br />
Pipeline corrosion GIC at earthing<br />
points<br />
Tripping of railway<br />
signals<br />
Power device<br />
failures<br />
Extremely high.<br />
Individual<br />
transformer cost =<br />
$ several million<br />
Knock on effects<br />
up to $6 billion<br />
System upgrading<br />
~ $billions<br />
Annualised loss<br />
estimate ~ $100<br />
million<br />
GICs in rail lines Unknown, but risk<br />
to passenger<br />
Cosmic ray air<br />
shower<br />
Install<br />
transmission line<br />
serial capacitors<br />
Use value added<br />
SW monitoring<br />
systems form<br />
commercial<br />
vendors<br />
Cost of hardware Install cathodic<br />
system<br />
Insert insulation<br />
sections<br />
High resistance<br />
safety in question<br />
Failure of power<br />
device in rail<br />
engines<br />
pipe coating<br />
Type of warning<br />
or prediction<br />
required<br />
Network<br />
modelling and<br />
monitoring<br />
Network<br />
modelling and<br />
monitoring<br />
None known Network<br />
modelling and<br />
Reduction of<br />
maximum field<br />
within device by<br />
appropriate<br />
design<br />
Table 4-5: Impacts of SW on ground infrastructure systems<br />
monitoring<br />
Not defined<br />
Impacts can be classed as either cumulative or sporadic. Cumulative impacts include the<br />
gradual effect of SW over a long period of time and this is the case with pipelines that are<br />
corroded slowly, albeit at an accelerated rate from natural corrosion. This issue is usually<br />
dealt with by installing a cathodic system of pipeline insulation. Alternatively, pipe can be<br />
covered with a high resistance coating. Although these solutions are not always completely<br />
satisfactory, there is no real evidence that pipeline operators use a SW forecast service since<br />
there is little they can do about it.<br />
The worse problems are those that are sporadic and which lead to catastrophic failure. This<br />
was the case as described in chapter 3 leading to complete outage of power for a whole<br />
region of Canada.<br />
Different geographical regions tend to experience differential GIC hazards. Figure 4-2<br />
illustrates the situation in the Northern Hemisphere indicating the relationship between storm<br />
intensity and latitude. While Northeastern US, Canada and Northern Europe (esp.<br />
Scandinavia) are the areas at highest risk of GIC impacts, Figure 4-2 illustrates that a much<br />
wider area is at significant risk. Indeed, high GIC counts have been measured as far south as<br />
the equator.<br />
ESYS-ESYS-2000260-RPT-02<br />
Issue 1.1<br />
28 September 2001 25 ESYS