Download the full report (112 p.) - KCE
Download the full report (112 p.) - KCE
Download the full report (112 p.) - KCE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
20 Interventions in Alzheimer’s Disease <strong>KCE</strong> Reports 111<br />
3.2.2 Interventions addressing <strong>the</strong> patient<br />
3.2.2.1 Studies focussing on specific interventions<br />
In <strong>the</strong> following table we have mentioned <strong>the</strong> level of evidence supporting <strong>the</strong> various<br />
interventions targeting <strong>the</strong> person with dementia, describing studies focussing on <strong>the</strong><br />
intervention itself. Included are interventions addressing patient cognition, patient<br />
emotion, patient sensory enhancement; physical activity interventions; functional<br />
performance interventions; communication/interaction/relationship interventions;<br />
environmental interventions.<br />
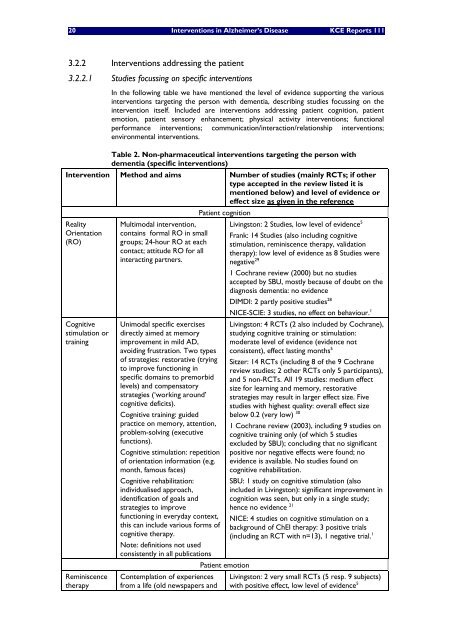
Table 2. Non-pharmaceutical interventions targeting <strong>the</strong> person with<br />
dementia (specific interventions)<br />
Intervention Method and aims Number of studies (mainly RCTs; if o<strong>the</strong>r<br />
type accepted in <strong>the</strong> review listed it is<br />
mentioned below) and level of evidence or<br />
effect size as given in <strong>the</strong> reference<br />
Patient cognition<br />
Reality<br />
Orientation<br />
(RO)<br />
Cognitive<br />
stimulation or<br />
training<br />
Reminiscence<br />
<strong>the</strong>rapy<br />
Multimodal intervention,<br />
contains formal RO in small<br />
groups; 24-hour RO at each<br />
contact; attitude RO for all<br />
interacting partners.<br />
Unimodal specific exercises<br />
directly aimed at memory<br />
improvement in mild AD,<br />
avoiding frustration. Two types<br />
of strategies: restorative (trying<br />
to improve functioning in<br />
specific domains to premorbid<br />
levels) and compensatory<br />
strategies (‘working around’<br />
cognitive deficits).<br />
Cognitive training: guided<br />
practice on memory, attention,<br />
problem-solving (executive<br />
functions).<br />
Cognitive stimulation: repetition<br />
of orientation information (e.g.<br />
month, famous faces)<br />
Cognitive rehabilitation:<br />
individualised approach,<br />
identification of goals and<br />
strategies to improve<br />
functioning in everyday context,<br />
this can include various forms of<br />
cognitive <strong>the</strong>rapy.<br />
Note: definitions not used<br />
consistently in all publications<br />
Contemplation of experiences<br />
from a life (old newspapers and<br />
Patient emotion<br />
Livingston: 2 Studies, low level of evidence 5<br />
Frank: 14 Studies (also including cognitive<br />
stimulation, reminiscence <strong>the</strong>rapy, validation<br />
<strong>the</strong>rapy): low level of evidence as 8 Studies were<br />
negative 29<br />
1 Cochrane review (2000) but no studies<br />
accepted by SBU, mostly because of doubt on <strong>the</strong><br />
diagnosis dementia: no evidence<br />
DIMDI: 2 partly positive studies 28<br />
NICE-SCIE: 3 studies, no effect on behaviour. 1<br />
Livingston: 4 RCTs (2 also included by Cochrane),<br />
studying cognitive training or stimulation:<br />
moderate level of evidence (evidence not<br />
consistent), effect lasting months 5<br />
Sitzer: 14 RCTs (including 8 of <strong>the</strong> 9 Cochrane<br />
review studies; 2 o<strong>the</strong>r RCTs only 5 participants),<br />
and 5 non-RCTs. All 19 studies: medium effect<br />
size for learning and memory, restorative<br />
strategies may result in larger effect size. Five<br />
studies with highest quality: overall effect size<br />
below 0.2 (very low) 30<br />
1 Cochrane review (2003), including 9 studies on<br />
cognitive training only (of which 5 studies<br />
excluded by SBU); concluding that no significant<br />
positive nor negative effects were found; no<br />
evidence is available. No studies found on<br />
cognitive rehabilitation.<br />
SBU: 1 study on cognitive stimulation (also<br />
included in Livingston): significant improvement in<br />
cognition was seen, but only in a single study;<br />
hence no evidence 21<br />
NICE: 4 studies on cognitive stimulation on a<br />
background of ChEI <strong>the</strong>rapy: 3 positive trials<br />
(including an RCT with n=13), 1 negative trial. 1<br />
Livingston: 2 very small RCTs (5 resp. 9 subjects)<br />
with positive effect, low level of evidence 5