Toxicity measurements in concentrated water samples - Rivm
Toxicity measurements in concentrated water samples - Rivm
Toxicity measurements in concentrated water samples - Rivm
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
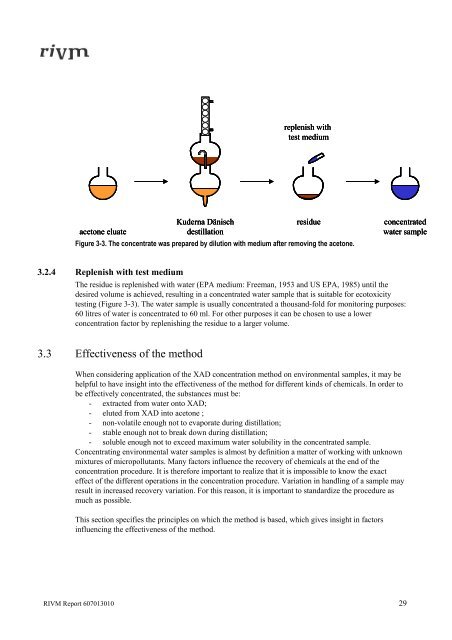
acetone eluate<br />
Kuderna Dänisch<br />
destillation<br />
replenish with<br />
test medium<br />
Figure 3-3. The concentrate was prepared by dilution with medium after remov<strong>in</strong>g the acetone.<br />
3.2.4 Replenish with test medium<br />
residue <strong>concentrated</strong><br />
<strong>water</strong> sample<br />
The residue is replenished with <strong>water</strong> (EPA medium: Freeman, 1953 and US EPA, 1985) until the<br />
desired volume is achieved, result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> a <strong>concentrated</strong> <strong>water</strong> sample that is suitable for ecotoxicity<br />
test<strong>in</strong>g (Figure 3-3). The <strong>water</strong> sample is usually <strong>concentrated</strong> a thousand-fold for monitor<strong>in</strong>g purposes:<br />
60 litres of <strong>water</strong> is <strong>concentrated</strong> to 60 ml. For other purposes it can be chosen to use a lower<br />
concentration factor by replenish<strong>in</strong>g the residue to a larger volume.<br />
3.3 Effectiveness of the method<br />
When consider<strong>in</strong>g application of the XAD concentration method on environmental <strong>samples</strong>, it may be<br />
helpful to have <strong>in</strong>sight <strong>in</strong>to the effectiveness of the method for different k<strong>in</strong>ds of chemicals. In order to<br />
be effectively <strong>concentrated</strong>, the substances must be:<br />
- extracted from <strong>water</strong> onto XAD;<br />
- eluted from XAD <strong>in</strong>to acetone ;<br />
- non-volatile enough not to evaporate dur<strong>in</strong>g distillation;<br />
- stable enough not to break down dur<strong>in</strong>g distillation;<br />
- soluble enough not to exceed maximum <strong>water</strong> solubility <strong>in</strong> the <strong>concentrated</strong> sample.<br />
Concentrat<strong>in</strong>g environmental <strong>water</strong> <strong>samples</strong> is almost by def<strong>in</strong>ition a matter of work<strong>in</strong>g with unknown<br />
mixtures of micropollutants. Many factors <strong>in</strong>fluence the recovery of chemicals at the end of the<br />
concentration procedure. It is therefore important to realize that it is impossible to know the exact<br />
effect of the different operations <strong>in</strong> the concentration procedure. Variation <strong>in</strong> handl<strong>in</strong>g of a sample may<br />
result <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>creased recovery variation. For this reason, it is important to standardize the procedure as<br />
much as possible.<br />
This section specifies the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples on which the method is based, which gives <strong>in</strong>sight <strong>in</strong> factors<br />
<strong>in</strong>fluenc<strong>in</strong>g the effectiveness of the method.<br />
RIVM Report 607013010 29