Toxicity measurements in concentrated water samples - Rivm
Toxicity measurements in concentrated water samples - Rivm
Toxicity measurements in concentrated water samples - Rivm
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3.3.2 Elution from XAD<br />
Solvent selection<br />
In order to be extracted from the XAD, a substance must be desorbed from the res<strong>in</strong>s. The choice of<br />
solvent, or comb<strong>in</strong>ation of solvents, is a key factor <strong>in</strong> the effectiveness of elution. The choice of solvent<br />
for the purpose of substances concentration was based on solvent capacity, boil<strong>in</strong>g po<strong>in</strong>t, vapour<br />
pressure, toxicity <strong>in</strong> bioassays and health safety procedures.<br />
In pr<strong>in</strong>ciple, several solvents are suitable for elution of XAD, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g liquid carbon dioxide, us<strong>in</strong>g<br />
supercritical fluid extraction (Struijs et al., 1998). For several reasons, acetone proved to be most<br />
suitable for the purpose (Struijs and Van de Kamp, 2001). It was selected because of its general<br />
properties as a solvent – a wide range of chemicals are soluble <strong>in</strong> acetone – its volatility and its low<br />
boil<strong>in</strong>g po<strong>in</strong>t (56 °C), which make it easy to remove (see textbox on solvent properties). The solvent<br />
must be free of impurities to avoid addition of un<strong>in</strong>tentional toxicity.<br />
Solvent properties<br />
For desorption from XAD, the substance must be soluble <strong>in</strong> the solvent that is used to elute the<br />
XAD. Preferably, the substance should have more aff<strong>in</strong>ity for the solvent than for XAD. The<br />
aff<strong>in</strong>ity can be characterised by the Hildebrand solubility parameter δ, which is related to the<br />
polarity of a substance. The higher δ, the more polar a substance. For good desorption, δ of the<br />
substance should be closer to δ of the solvent than to δ of the XAD. Generally, compatibility<br />
between two materials can be expected when their solubility parameters are close <strong>in</strong> value.<br />
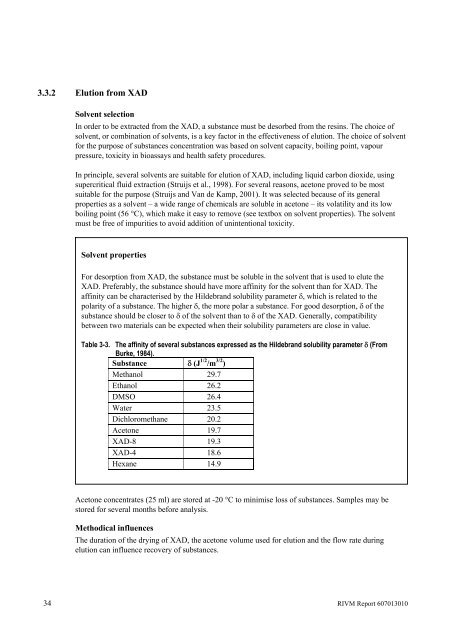
Table 3-3. The aff<strong>in</strong>ity of several substances expressed as the Hildebrand solubility parameter δ (From<br />
Burke, 1984).<br />
Substance δ (J 1/2 /m 3/2 )<br />
Methanol 29.7<br />
Ethanol 26.2<br />
DMSO 26.4<br />
Water 23.5<br />
Dichloromethane 20.2<br />
Acetone 19.7<br />
XAD-8 19.3<br />
XAD-4 18.6<br />
Hexane 14.9<br />
Acetone concentrates (25 ml) are stored at -20 °C to m<strong>in</strong>imise loss of substances. Samples may be<br />
stored for several months before analysis.<br />
Methodical <strong>in</strong>fluences<br />
The duration of the dry<strong>in</strong>g of XAD, the acetone volume used for elution and the flow rate dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
elution can <strong>in</strong>fluence recovery of substances.<br />
34 RIVM Report 607013010