- Page 1 and 2:
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF B
- Page 3 and 4:
STATEMENT BY AUTHOR This dissertati
- Page 5 and 6:
DECLARATION I, hereby declare that
- Page 7 and 8:
Acknowledgements I would like to ex
- Page 9 and 10:
2. BLOCK COPOLYMER-MEDIATED SYNTHES
- Page 11 and 12:
5. CORRELATING BLOCK COPOLYMER SELF
- Page 13 and 14:
SYNOPSIS OF THE THESIS TO BE SUBMIT
- Page 15 and 16:
synthesis for its dependence on gol
- Page 17 and 18:
interactions between the templating
- Page 19 and 20:
utilized in the formation of nanopa
- Page 21 and 22: nanoparticle-protein conjugate conf
- Page 23 and 24: LIST OF FIGURES Figure 1.1. The len
- Page 25 and 26: Figure 4.2. UV-visible absorption s
- Page 27 and 28: Figure 5.9. (a) Absorbance (Abs max
- Page 29 and 30: Figure 7.5. Integrated absorbance o
- Page 31 and 32: Chapter 1 Synthesis, Characterizati
- Page 33 and 34: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 35 and 36: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 37 and 38: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 39 and 40: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
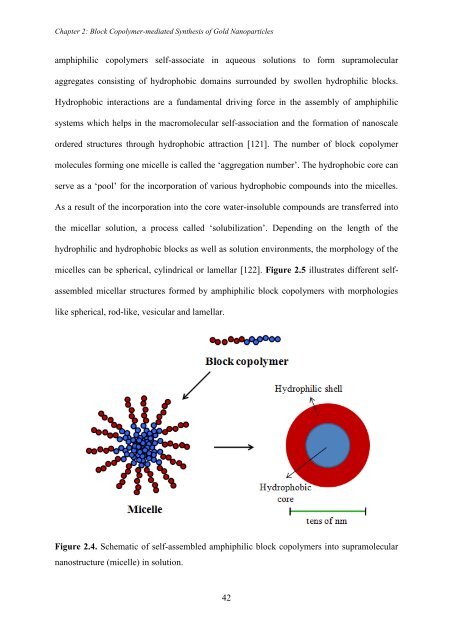
- Page 41 and 42: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 43 and 44: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 45 and 46: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 47 and 48: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 49 and 50: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 51 and 52: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 53 and 54: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 55 and 56: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 57 and 58: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 59 and 60: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 61 and 62: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 63 and 64: Chapter 1: Synthesis, Characterizat
- Page 65 and 66: Chapter 2 Block Copolymer-mediated
- Page 67 and 68: Chapter 2: Block Copolymer-mediated
- Page 69 and 70: Chapter 2: Block Copolymer-mediated
- Page 71: Chapter 2: Block Copolymer-mediated
- Page 75 and 76: Chapter 2: Block Copolymer-mediated
- Page 77 and 78: Chapter 2: Block Copolymer-mediated
- Page 79 and 80: Time-dependent Absorbance Chapter 2
- Page 81 and 82: Chapter 2: Block Copolymer-mediated
- Page 83 and 84: Chapter 2: Block Copolymer-mediated
- Page 85 and 86: Chapter 2: Block Copolymer-mediated
- Page 87 and 88: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 89 and 90: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 91 and 92: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 93 and 94: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 95 and 96: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 97 and 98: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 99 and 100: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 101 and 102: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 103 and 104: d/d (Q) (cm -1 ) S(Q) P(Q) Chapter
- Page 105 and 106: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 107 and 108: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 109 and 110: Chapter 3: Multi-Technique Approach
- Page 111 and 112: d/d (cm -1 ) P(Q) Chapter 3: Multi-
- Page 113 and 114: Chapter 4 Optimization of the Block
- Page 115 and 116: Chapter 4: Optimization of the Bloc
- Page 117 and 118: Chapter 4: Optimization of the Bloc
- Page 119 and 120: SPR Peak Absorbance Absorbance Chap
- Page 121 and 122: Absorbance Integrated Absorbance /
- Page 123 and 124:
Chapter 4: Optimization of the Bloc
- Page 125 and 126:
Chapter 4: Optimization of the Bloc
- Page 127 and 128:
Absorbance Chapter 4: Optimization
- Page 129 and 130:
SPR peak absorbance Chapter 4: Opti
- Page 131 and 132:
d/d (cm -1 ) Chapter 4: Optimizatio
- Page 133 and 134:
g I ()-1 Integrated Scattering Inte
- Page 135 and 136:
Relative number (%) Chapter 4: Opti
- Page 137 and 138:
Chapter 5 Correlating Block Copolym
- Page 139 and 140:
Chapter 5: Correlating Block Copoly
- Page 141 and 142:
d/d (cm -1 ) Chapter 5: Correlating
- Page 143 and 144:
Chapter 5: Correlating Block Copoly
- Page 145 and 146:
Chapter 5: Correlating Block Copoly
- Page 147 and 148:
Absorbance Absorbance Chapter 5: Co
- Page 149 and 150:
Integrated Absorbance / Yield Absor
- Page 151 and 152:
Chapter 5: Correlating Block Copoly
- Page 153 and 154:
Absorbance Absorbance Chapter 5: Co
- Page 155 and 156:
Chapter 5: Correlating Block Copoly
- Page 157 and 158:
Chapter 5: Correlating Block Copoly
- Page 159 and 160:
Chapter 6 High-Yield Synthesis of G
- Page 161 and 162:
Chapter 6: High-Yield Synthesis of
- Page 163 and 164:
Chapter 6: High-Yield Synthesis of
- Page 165 and 166:
Absorbance Chapter 6: High-Yield Sy
- Page 167 and 168:
Chapter 6: High-Yield Synthesis of
- Page 169 and 170:
Absorbance Chapter 6: High-Yield Sy
- Page 171 and 172:
d/d (cm -1 ) Chapter 6: High-Yield
- Page 173 and 174:
Chapter 6: High-Yield Synthesis of
- Page 175 and 176:
d/d (cm -1 ) Chapter 6: High-Yield
- Page 177 and 178:
Intensity (a.u.) Chapter 6: High-Yi
- Page 179 and 180:
g I ()-1 Chapter 6: High-Yield Synt
- Page 181 and 182:
Absorbance Integrated Absorbance /
- Page 183 and 184:
Chapter 6: High-Yield Synthesis of
- Page 185 and 186:
Chapter 7: Interaction of Gold Nano
- Page 187 and 188:
Chapter 7: Interaction of Gold Nano
- Page 189 and 190:
d/d (cm -1 ) Absorbance Chapter 7:
- Page 191 and 192:
Integrated Absorbance / Yield (a.u.
- Page 193 and 194:
Chapter 7: Interaction of Gold Nano
- Page 195 and 196:
Absorbance Absorbance Chapter 7: In
- Page 197 and 198:
d/d (cm -1 ) Chapter 7: Interaction
- Page 199 and 200:
d/d (cm -1 ) d/d (cm -1 ) Chapter 7
- Page 201 and 202:
Chapter 7: Interaction of Gold Nano
- Page 203 and 204:
Chapter 8: Summary Chapter 1 introd
- Page 205 and 206:
Chapter 8: Summary hence synthesis.
- Page 207 and 208:
Chapter 8: Summary irrespective of
- Page 209 and 210:
24. R. Elghanian, J.J. Storhoff, R.
- Page 211 and 212:
69. J.F. Hainfeld, D.N. Slatkin, T.
- Page 213 and 214:
119. N.S. Cameron, M.K. Corbierre a
- Page 215 and 216:
165. J.H. Lambert, Photometria sive
- Page 217 and 218:
210. D. Ray and V.K. Aswal, Confere
- Page 219 and 220:
9. SANS Studies of Temperature-depe
- Page 221:
14. Multi-technique Approach for th