Environmentally Degradation of r-PMMA/PMMA-Blend-PU/Ecoflex ...
Environmentally Degradation of r-PMMA/PMMA-Blend-PU/Ecoflex ...
Environmentally Degradation of r-PMMA/PMMA-Blend-PU/Ecoflex ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1038<br />
<strong>Environmentally</strong> <strong>Degradation</strong> <strong>of</strong> r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-<strong>Blend</strong>-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex Sheet<br />
where :<br />
W a is weight <strong>of</strong> sample after extraction;<br />
W b is weight <strong>of</strong> sample before extraction.<br />
2.3.2 Mechanical Tests<br />
The impact strength both Izod and Charpy types<br />
were determined according to ASTM D256 [9] and<br />
ASTM D6110 [10] respectively. The specimens were<br />
tested by using impact strength machine and the energy<br />
<strong>of</strong> hammer was 7.5 J (Impact tester: Italy Cast Type<br />
695700).<br />
2.3.3 The Ultraviolet <strong>Degradation</strong><br />
The ultraviolet degradation was examined according<br />
to QUV-A cabinet from PAN ASIA Industry Co., Ltd.<br />
Thailand standard by detecting the total change in color<br />
from Gretag Macbeth Model COLOR iMATCH,<br />
before and after located in QUV test for 14 days<br />
(according to PAN Asia Industrial Co. Ltd., the 7 days<br />
in QUV-A cabinet was equal to one year). After<br />
ultraviolet degradation r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/<br />
Ec<strong>of</strong>lex sheet was determined the impact strength to<br />
compare the r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex sheet<br />
before testing.<br />
2.3.4 <strong>Degradation</strong> <strong>of</strong> r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-<strong>Blend</strong>-<strong>PU</strong>/<br />
Ec<strong>of</strong>lex Sheet by Landfills<br />
The specimens <strong>of</strong> r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/<br />
Ec<strong>of</strong>lex sheet were taken landfills for six months. The<br />
specimens were buried in covered soil under naturally<br />
condition for biodegradability. After the expiry <strong>of</strong> the<br />
time, the specimens used methods for monitoring in<br />
vitro such as the percentage <strong>of</strong> weight loss and the<br />
surface morphology <strong>of</strong> SEM micrographs. The results<br />
are discussed in more detail below.<br />
2.3.5 Surface Morphology <strong>of</strong> r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-<br />
<strong>Blend</strong>-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex Sheet<br />
A JEOL JSM-5410LV scanning electron<br />
microscope was used to examine the surface<br />
morphology <strong>of</strong> r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex<br />
sheet. The specimens were prepared by fracture in<br />
cryogenically in liquid nitrogen.<br />
3. Results and Discussion<br />
3.1 Mechanical Properties <strong>of</strong> r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-<strong>Blend</strong>-<br />
<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex Sheet<br />
The impact strength property <strong>of</strong> the<br />
r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex sheet were<br />
modified poly (methyl methacrylate) sheet with<br />
polyurethane by using IPNs technique (by Izod and<br />
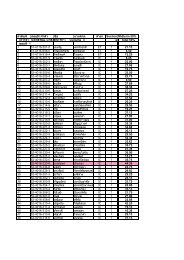
Charpy type) are shown in Table 1. It shows that the<br />
highest impact was observed at MMA:r-<strong>PMMA</strong>:<strong>PU</strong><br />
(72:3:25)/3 EF and (71:4:25)/3 EF, but the impact<br />
strength <strong>of</strong> MMA:r-<strong>PMMA</strong>:<strong>PU</strong> (71:4:25)/3 EF is<br />
higher than MMA:r-<strong>PMMA</strong>:<strong>PU</strong> (72:3:25)/3 EF. This is<br />
probably due to structure <strong>of</strong> EF was ester bond that was<br />
interacted with -NHCOO group on <strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PU</strong><br />
polymer networks. This behavior was led EF particle<br />
embedded between polymer networks <strong>of</strong> <strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PU</strong><br />
[4]. However, the comparing impact strength <strong>of</strong><br />
r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex sheet without EF<br />
was slightly more than r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/<br />
Ec<strong>of</strong>lex sheet with EF. It can be concluded that<br />
r-<strong>PMMA</strong> did not affect impact strength <strong>of</strong> <strong>PMMA</strong>.<br />
Hence, r-<strong>PMMA</strong> has been possible to recycle into<br />
production process, by dissolves within MMA.<br />
3.2 Surface Morphology and Percentage <strong>of</strong> IPNs <strong>of</strong><br />
Impact Modified <strong>PMMA</strong> Sheet<br />
The percentage <strong>of</strong> IPNs that were estimated by<br />
solvent extraction to determine grafted MMA<br />
monomer and uncross-linking <strong>PMMA</strong> in the final<br />
product are shown in Table 1, shown<br />
MMA:r-<strong>PMMA</strong>:<strong>PU</strong> (71:4:25)/3 EF was the highest<br />
percentage <strong>of</strong> IPNs when compared with other amount<br />
<strong>of</strong> EF monomer in casting process.<br />
The results <strong>of</strong> surface morphology by SEM<br />
(scanning electron microscope) <strong>of</strong> r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>blend-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex<br />
sheet were shown in Fig. 2.<br />
The r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex sheet<br />
consists <strong>of</strong> the previously polymer from r-<strong>PMMA</strong>