Environmentally Degradation of r-PMMA/PMMA-Blend-PU/Ecoflex ...
Environmentally Degradation of r-PMMA/PMMA-Blend-PU/Ecoflex ...
Environmentally Degradation of r-PMMA/PMMA-Blend-PU/Ecoflex ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1042<br />
<strong>Environmentally</strong> <strong>Degradation</strong> <strong>of</strong> r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-<strong>Blend</strong>-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex Sheet<br />
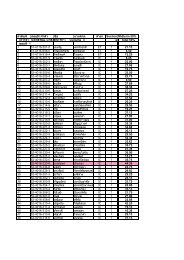
mechanical properties was observed at ratio <strong>of</strong><br />
MMA:r-<strong>PMMA</strong>:<strong>PU</strong> (71:4:25)/3 EF. According to the<br />
percentage <strong>of</strong> IPNs, it showed the maximum value in<br />
this condition. When considered the results as potential<br />
<strong>of</strong> biodegradation, it showed that r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<br />
<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex sheet from this research<br />
could be degraded in soil by landfills method. Towards,<br />
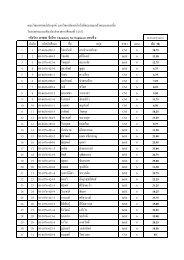
after landfills for 6 months, percentages <strong>of</strong> weight loss<br />
were increased upon to amount <strong>of</strong> Ec<strong>of</strong>lex. In addition<br />
to this, the SEMs image shown the surface morphology<br />
<strong>of</strong> specimens were damaged. That illustrated Ec<strong>of</strong>lex<br />
had an effect on r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex<br />
sheet in potential biodegradation due to swelled by<br />
humidity and microbial enzymatic activity in soil.<br />
However, the impact strength <strong>of</strong><br />
r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex sheet from this<br />
research was better than the GP<strong>PMMA</strong> from industry.<br />
Hence, the r-<strong>PMMA</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong>-blend-<strong>PU</strong>/Ec<strong>of</strong>lex sheet<br />
can be utilized as the impact materials for variable<br />
application with potential in biodegradation and<br />
r-<strong>PMMA</strong> can reduce the costs <strong>of</strong> raw material in<br />
<strong>PMMA</strong> casting process.<br />
Acknowledgments<br />
The authors acknowledge with thanks for financial<br />
support from the iTAP (Industrial Technology<br />
Assistance Program), NSTDA (National Science and<br />
Technology Development Agency). Special thanks to<br />
the National Metal and Materials Technology Center<br />
(MTEC) and Pan ASIA Industrial Co., Ltd., Bangkok,<br />
Thailand for supplying the materials and equipment<br />
were used in this research.<br />
References<br />
[1] N. Kreua-ongarjnukool, K. Charmorndusit, S.<br />
Pankumnead, J. Rotpradit, The impact modification <strong>of</strong><br />
poly(methyl methacrylate) sheet by using polyurethane,<br />
Thai Patent 0701001014, 2007.<br />
[2] K. Chamondusit, C. Sriprachuabwong, S. Pongchaloen, S.<br />
Rodium, A study and preparation <strong>of</strong> transparent impact<br />
styrene—methyl methacrylate by casting process, Thai<br />
Patent 0601102635, 2006.<br />
[3] L.H. Sperling, Interpenetrating Polymer Networks, 1st ed.,<br />
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 2004, pp. 288-306.<br />
[4] T. Jeevananda, I. Siddaramaiah, Synthesis and<br />
characterization <strong>of</strong> polyaniline filled <strong>PU</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong><br />
interpenetrating polymer network, European Polymer<br />
Journal 39 (2003) 569-578.<br />
[5] U. Witt, T. Einig, M. Yamamoto, I. Kleeberg, W.D.<br />
Deckwer, R.J. Műller, Biodegradation <strong>of</strong><br />
aliphatic-aromatic copolyester: Evalution <strong>of</strong> the final<br />
biodegradable and ecotoxological impact <strong>of</strong> degradation<br />
intermediate, Chemosphere 44 (2001) 289-299.<br />
[6] S. Panyadee, Recycling <strong>PMMA</strong> scrap in casting process,<br />
B.Sc. Special Project, Department <strong>of</strong> Industrial Chemistry,<br />
Faculty <strong>of</strong> Applied Science, KMUTNB (King Mongkut’s<br />
University <strong>of</strong> Technology North Bangkok), Bangkok,<br />
2008.<br />
[7] C. Vancaeyzeele, O. Ficheta, S. Boileaub, D. Teyssie,<br />
Polyisobutene-poly (methyl methacrylate)<br />
interpenetrating polymer network: Synthesis and<br />
characterization, Journal <strong>of</strong> Polymer 46 (2005)<br />
6888-6896.<br />
[8] P.S.O. Patricio, Effect <strong>of</strong> blend composition on<br />
microstructure, morphology, and gas permeability in<br />
<strong>PU</strong>/<strong>PMMA</strong> blends, Journal <strong>of</strong> Membrane Science 271<br />
(2006) 177-185.<br />
[9] ASTM D 256, Standard Test Methods for Determining the<br />
Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance <strong>of</strong> Plastics, West<br />
Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.<br />
[10] ASTM D 6110, Standard Test Methods for Determining<br />
the Charpy Pendulum Impact Resistance <strong>of</strong> Plastics, West<br />
Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.<br />
[11] M.R. Timmins, D.F. Gilmore, R.C. Fuller, R.W. Lenz,<br />
Bacterial polyesters and their biodegradation,<br />
Biodegradable Polymer and Packaging 11 (1993) 119-130.<br />
[12] E. Marten, R.J. Műller, W.D. Deckwer, Studies on the<br />
enzymatic hydrolysis <strong>of</strong> polyesters II aliphatic-aromatic<br />
copolyester, Polymer <strong>Degradation</strong> and Stability 88 (2005)<br />
371-381.<br />
[13] J.P. Eubeler, M. Bernhard, S. Zok, T.P. Knepper,<br />
Environmental biodegradation <strong>of</strong> synthetic polymer I. test<br />
methodologies and procedures, Trends in Analytical<br />
Chemistry 28 (2009) 1057-1072.