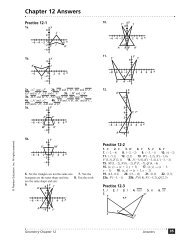
Chapter 12 Sequences; Induction; the Binomial Theorem
Chapter 12 Sequences; Induction; the Binomial Theorem
Chapter 12 Sequences; Induction; the Binomial Theorem
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Chapter</strong> <strong>12</strong>: <strong>Sequences</strong>; <strong>Induction</strong>; <strong>the</strong> <strong>Binomial</strong> <strong>Theorem</strong><br />
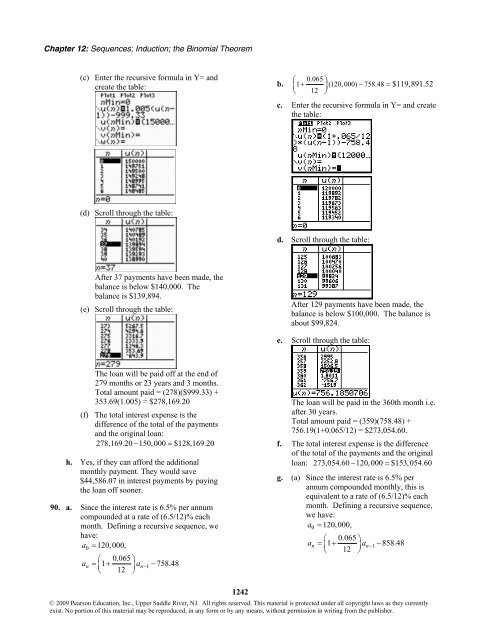
(c) Enter <strong>the</strong> recursive formula in Y= and<br />
create <strong>the</strong> table:<br />
b.<br />
⎛ 0.065 ⎞<br />
⎜1 + ⎟(<strong>12</strong>0,000) −758.48<br />
= $119,891.52<br />
⎝ <strong>12</strong> ⎠<br />
c. Enter <strong>the</strong> recursive formula in Y= and create<br />
<strong>the</strong> table:<br />
(d) Scroll through <strong>the</strong> table:<br />
d. Scroll through <strong>the</strong> table:<br />
After 37 payments have been made, <strong>the</strong><br />
balance is below $140,000. The<br />
balance is $139,894.<br />
(e) Scroll through <strong>the</strong> table:<br />
After <strong>12</strong>9 payments have been made, <strong>the</strong><br />
balance is below $100,000. The balance is<br />
about $99,824.<br />
e. Scroll through <strong>the</strong> table:<br />
The loan will be paid off at <strong>the</strong> end of<br />
279 months or 23 years and 3 months.<br />
Total amount paid = (278)($999.33) +<br />
353.69(1.005) = $278,169.20<br />
(f) The total interest expense is <strong>the</strong><br />
difference of <strong>the</strong> total of <strong>the</strong> payments<br />
and <strong>the</strong> original loan:<br />
278,169.20 − 150,000 = $<strong>12</strong>8,169.20<br />
h. Yes, if <strong>the</strong>y can afford <strong>the</strong> additional<br />
monthly payment. They would save<br />
$44,586.07 in interest payments by paying<br />
<strong>the</strong> loan off sooner.<br />
90. a. Since <strong>the</strong> interest rate is 6.5% per annum<br />
compounded at a rate of (6.5/<strong>12</strong>)% each<br />
month. Defining a recursive sequence, we<br />
have:<br />
a0<br />
= <strong>12</strong>0,000,<br />
⎛ 0.065 ⎞<br />
an<br />
= ⎜1+ ⎟an<br />
− 1 −758.48<br />
⎝ <strong>12</strong> ⎠<br />
The loan will be paid in <strong>the</strong> 360th month i.e.<br />
after 30 years.<br />
Total amount paid = (359)(758.48) +<br />
756.19(1+0.065/<strong>12</strong>) = $273,054.60.<br />
f. The total interest expense is <strong>the</strong> difference<br />
of <strong>the</strong> total of <strong>the</strong> payments and <strong>the</strong> original<br />
loan: 273,054.60 − <strong>12</strong>0,000 = $153,054.60<br />
g. (a) Since <strong>the</strong> interest rate is 6.5% per<br />
annum compounded monthly, this is<br />
equivalent to a rate of (6.5/<strong>12</strong>)% each<br />
month. Defining a recursive sequence,<br />
we have:<br />
a0<br />
= <strong>12</strong>0,000,<br />
⎛ 0.065 ⎞<br />
an<br />
= ⎜1+ ⎟an<br />
− 1 −858.48<br />
⎝ <strong>12</strong> ⎠<br />
<strong>12</strong>42<br />
© 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as <strong>the</strong>y currently<br />
exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from <strong>the</strong> publisher.