- Page 1: Reproduction prohibited without per
- Page 4 and 5: Contents CONTENTS .................
- Page 6 and 7: vi Contents 4.21 EXERCISES.........
- Page 8 and 9: viii Contents 10.1 INTRODUCTION ...
- Page 10 and 11: x Contents 16.8.1 Converting a base
- Page 12 and 13: xii Contents 23.6.3 The specificati
- Page 14 and 15: Preface This book is aimed at stude
- Page 16 and 17: xvi Actual parameter Preface The ph
- Page 18 and 19: xviii Elaboration Preface At run-ti
- Page 20 and 21: xx Object Preface An instance of a
- Page 23: 1 Introduction to programming 1 Int
- Page 27 and 28: Introduction to programming 5 • T
- Page 29 and 30: Introduction to programming 7 The s
- Page 31 and 32: Introduction to programming 9 Line
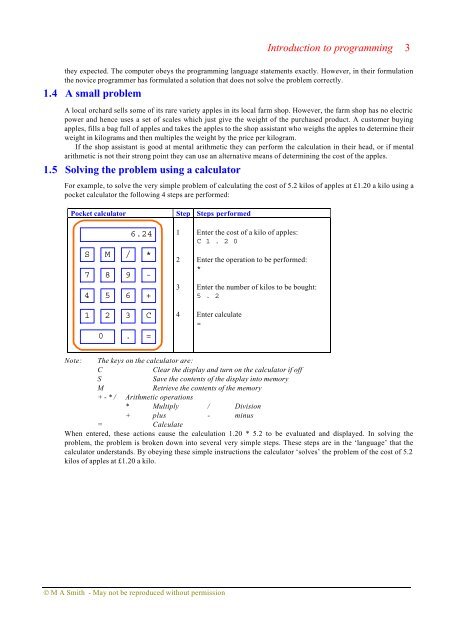
- Page 33 and 34: Introduction to programming 11 Cost
- Page 35 and 36: Introduction to programming 13 In t
- Page 37 and 38: Introduction to programming 15 For
- Page 39 and 40: Introduction to programming 17 •
- Page 41 and 42: Software design 19 In software the
- Page 43 and 44: Software design 21 2.4 The class In
- Page 45 and 46: Software design 23 Inheritance diag
- Page 47 and 48: 25 Ada introduction: Part 1 3 Ada i
- Page 49 and 50: Ada introduction: Part 1 27 3.3.2 C
- Page 51 and 52: Ada introduction: Part 1 29 can be
- Page 53 and 54: Ada introduction: Part 1 31 with Ad
- Page 55 and 56: Ada introduction: Part 1 33 To inpu
- Page 57 and 58: Ada introduction: Part 1 35 Functio
- Page 59 and 60: Ada introduction: Part 1 37 3.14 Ex
- Page 61 and 62: Note: In reality the floating point
- Page 63 and 64: Ada introduction: Part 2 41 4.4 Mod
- Page 65 and 66: Ada introduction: Part 2 43 4.7.2 I
- Page 67 and 68: Ada introduction: Part 2 45 For exa
- Page 69 and 70: Ada introduction: Part 2 47 When pe
- Page 71 and 72: Ada introduction: Part 2 49 4.12 Co
- Page 73 and 74: Ada introduction: Part 2 51 4.13.1
- Page 75 and 76:
Ada introduction: Part 2 53 Note 3
- Page 77 and 78:
Ada introduction: Part 2 55 if Ch i
- Page 79 and 80:
Ada introduction: Part 2 57 For exa
- Page 81 and 82:
Ada introduction: Part 2 59 type Mi
- Page 83 and 84:
Procedures and functions 61 The fun
- Page 85 and 86:
Procedures and functions 63 The maj
- Page 87 and 88:
Procedures and functions 65 Mode Al
- Page 89 and 90:
Procedures and functions 67 The pro
- Page 91 and 92:
Procedures and functions 69 5.8 Dif
- Page 93 and 94:
Procedures and functions 71 Note: T
- Page 95 and 96:
6 Packages as classes This chapter
- Page 97 and 98:
Packages as classes 75 6.3.1 An obj
- Page 99 and 100:
Packages as classes 77 package Clas
- Page 101 and 102:
Packages as classes 79 The body of
- Page 103 and 104:
Packages as classes 81 Thus without
- Page 105 and 106:
Packages as classes 83 6.9 Type pri
- Page 107 and 108:
Packages as classes 85 which when r
- Page 109 and 110:
Packages as classes 87 The Ada spec
- Page 111 and 112:
The main body of the program proces
- Page 113 and 114:
Packages as classes 91 The procedur
- Page 115 and 116:
Packages as classes 93 Construct th
- Page 117 and 118:
Data structures 95 This initializat
- Page 119 and 120:
Data structures 97 Then an assignme
- Page 121 and 122:
Data structures 99 In Ada a variant
- Page 123 and 124:
Data structures 101 7.10 Exercises
- Page 125 and 126:
which when combined with appropriat
- Page 127 and 128:
Arrays 105 with Ada.Text_Io, Class_
- Page 129 and 130:
Arrays 107 8.3.1 Putting it all tog
- Page 131 and 132:
Arrays 109 8.4.1 The class Board Th
- Page 133 and 134:
Arrays 111 8.4.4 The class Board Th
- Page 135 and 136:
Arrays 113 8.4.5 Putting it all tog
- Page 137 and 138:
Arrays 115 8.5.2 Attributes of mult
- Page 139 and 140:
Arrays 117 The following code would
- Page 141 and 142:
Arrays 119 This type is defined in
- Page 143 and 144:
Arrays 121 In the implementation of
- Page 145 and 146:
Arrays 123 The Ada specification of
- Page 147 and 148:
Arrays 125 The function valid check
- Page 149 and 150:
9 Case study: Design of a game This
- Page 151 and 152:
Case study: Design of a game 129 A
- Page 153 and 154:
Case study: Design of a game 131 Co
- Page 155 and 156:
Case study: Design of a game 133 Cu
- Page 157 and 158:
Case study: Design of a game 135 --
- Page 159 and 160:
The specification for the class Cel
- Page 161 and 162:
Case study: Design of a game 139 pr
- Page 163 and 164:
Case study: Design of a game 141 Th
- Page 165 and 166:
Case study: Design of a game 143 Th
- Page 167 and 168:
Case study: Design of a game 145 In
- Page 169 and 170:
10 Inheritance This chapter introdu
- Page 171 and 172:
Two instances of the class Interest
- Page 173 and 174:
Inheritance 151 The two classes Acc
- Page 175 and 176:
Inheritance 153 which when run, wou
- Page 177 and 178:
Inheritance 155 The specialization
- Page 179 and 180:
Inheritance 157 Note: The methods o
- Page 181 and 182:
Inheritance 159 10.7.1 Putting it a
- Page 183 and 184:
Inheritance 161 10.8.1 Implementati
- Page 185 and 186:
10.9 Hiding the base class methods
- Page 187 and 188:
Inheritance 165 • For an object o
- Page 189 and 190:
Exceptions 167 11.1.1 Putting it al
- Page 191 and 192:
Exceptions 169 11.3 Private child A
- Page 193 and 194:
12 Defining new operators This chap
- Page 195 and 196:
Exceptions 173 Using the above pack
- Page 197 and 198:
Exceptions 175 The function Rat_Con
- Page 199 and 200:
Exceptions 177 12.3.1 Overloading =
- Page 201 and 202:
Exceptions 179 The overloaded defin
- Page 203 and 204:
Exceptions 181 12.3.5 use type A mo
- Page 205 and 206:
13 Exceptions This chapter looks at
- Page 207 and 208:
Exceptions 185 Note: The object Eve
- Page 209 and 210:
Exceptions 187 A program to demonst
- Page 211 and 212:
Exceptions 189 package body Class_S
- Page 213 and 214:
14 Generics This chapter looks at g
- Page 215 and 216:
Exceptions 193 The above generic pr
- Page 217 and 218:
Exceptions 195 14.3 Generic stack T
- Page 219 and 220:
Exceptions 197 14.3.1 Putting it al
- Page 221 and 222:
Thus, an instantiation of a procedu
- Page 223 and 224:
Exceptions 201 14.5 Sorting Some of
- Page 225 and 226:
14.6.1 Putting it all together Exce
- Page 227 and 228:
Exceptions 205 An efficient impleme
- Page 229 and 230:
Exceptions 207 The implementation o
- Page 231 and 232:
15 Dynamic memory allocation This c
- Page 233 and 234:
Dynamic memory allocation 211 In a
- Page 235 and 236:
Dynamic memory allocation 213 One w
- Page 237 and 238:
Dynamic memory allocation 215 15.2.
- Page 239 and 240:
Dynamic memory allocation 217 The p
- Page 241 and 242:
Dynamic memory allocation 219 15.4.
- Page 243 and 244:
Dynamic memory allocation 221 A ben
- Page 245 and 246:
Dynamic memory allocation 223 15.5.
- Page 247 and 248:
15.7 Attributes 'Access and 'Unchec
- Page 249 and 250:
16 Polymorphism In the processes de
- Page 251 and 252:
Polymorphism 229 This can be implem
- Page 253 and 254:
Polymorphism 231 16.2.1 Putting it
- Page 255 and 256:
Polymorphism 233 Figure 16.3 Hetero
- Page 257 and 258:
Polymorphism 235 16.5 A building in
- Page 259 and 260:
Polymorphism 237 An example interac
- Page 261 and 262:
Polymorphism 239 The conversion fro
- Page 263 and 264:
Polymorphism 241 Screen Observed Ob
- Page 265 and 266:
Polymorphism 243 The method Add_Obs
- Page 267 and 268:
Polymorphism 245 The functions vali
- Page 269 and 270:
Polymorphism 247 The driver program
- Page 271 and 272:
17 Containers This chapter describe
- Page 273 and 274:
Containers 251 This mirrors closely
- Page 275 and 276:
Containers 253 will produce the fol
- Page 277 and 278:
Containers 255 When an instance of
- Page 279 and 280:
Containers 257 When the iterator Co
- Page 281 and 282:
Containers 259 In the implementatio
- Page 283 and 284:
Containers 261 A deep copy of this
- Page 285 and 286:
Containers 263 • If the objects o
- Page 287 and 288:
Containers 265 17.6.1 Ada specifica
- Page 289 and 290:
Containers 267 The procedure Adjust
- Page 291 and 292:
17.7 A set Containers 269 Using as
- Page 293 and 294:
Containers 271 17.7.1 Putting it al
- Page 295 and 296:
18 Input and output This chapter de
- Page 297 and 298:
Input and output 275 18.2 Reading a
- Page 299 and 300:
Input and output 277 Then the follo
- Page 301 and 302:
Input and output 279 18.5 Self-asse
- Page 303 and 304:
Persistence 281 A program to implem
- Page 305 and 306:
Persistence 283 with Ada.Strings.Un
- Page 307 and 308:
Persistence 285 The process to add
- Page 309 and 310:
Persistence 287 The procedure Add u
- Page 311 and 312:
20 Tasks This chapter describes the
- Page 313 and 314:
Tasks 291 The execution of the abov
- Page 315 and 316:
Tasks 293 Likewise, the task Task_I
- Page 317 and 318:
Tasks 295 20.4 Protected type In es
- Page 319 and 320:
Tasks 297 The implementation of the
- Page 321 and 322:
Tasks 299 to the entry prevents the
- Page 323 and 324:
Note: 20.7.1 Accept alternative Tas
- Page 325 and 326:
Tasks 303 the implementation of whi
- Page 327 and 328:
Tasks 305 • How can a task select
- Page 329 and 330:
System programming 307 21.1.1 Putti
- Page 331 and 332:
System programming 309 The followin
- Page 333 and 334:
22 A text user interface This chapt
- Page 335 and 336:
A Text user interface 313 Note: The
- Page 337 and 338:
A Text user interface 315 with Clas
- Page 339 and 340:
A Text user interface 317 Window_St
- Page 341 and 342:
A Text user interface 319 The follo
- Page 343 and 344:
A Text user interface 321 package C
- Page 345 and 346:
A Text user interface 323 with Clas
- Page 347 and 348:
A Text user interface 325 function
- Page 349 and 350:
A Text user interface 327 • What
- Page 351 and 352:
TUI the implementation 329 23.1.1 S
- Page 353 and 354:
TUI the implementation 331 package
- Page 355 and 356:
TUI the implementation 333 23.2.4 T
- Page 357 and 358:
TUI the implementation 335 with Ada
- Page 359 and 360:
TUI the implementation 337 The Inpu
- Page 361 and 362:
TUI the implementation 339 procedur
- Page 363 and 364:
TUI the implementation 341 New_Line
- Page 365 and 366:
TUI the implementation 343 private
- Page 367 and 368:
TUI the implementation 345 The proc
- Page 369 and 370:
TUI the implementation 347 procedur
- Page 371 and 372:
TUI the implementation 349 with Pac
- Page 373 and 374:
TUI the implementation 351 Method S
- Page 375 and 376:
TUI the implementation 353 procedur
- Page 377 and 378:
TUI the implementation 355 The proc
- Page 379 and 380:
24 Scope of declared objects This c
- Page 381 and 382:
Proc_2_2 Proc_1_1 Proc_2_1 Proc_2_2
- Page 383 and 384:
25 Mixed language programming This
- Page 385 and 386:
Mixed language programming 363 3 Tr
- Page 387 and 388:
Mixed language programming 365 /* *
- Page 389 and 390:
Appendix A 367 if Temp < 15 then Pu
- Page 391 and 392:
Appendix A 369 package body Class_I
- Page 393 and 394:
Appendix B: Components of Ada B.1 R
- Page 395 and 396:
T'Digits The decimal precision. Uni
- Page 397 and 398:
Appendix B 375 access enumeration E
- Page 399 and 400:
Appendix B 377 B.8.2Ada information
- Page 401 and 402:
Appendix C 379 package Standard is
- Page 403 and 404:
Appendix C 381 type Character is (n
- Page 405 and 406:
Appendix C 383 package Ada.IO_Excep
- Page 407 and 408:
Appendix C 385 --Specification of l
- Page 409 and 410:
Appendix C 387 procedure Get(File :
- Page 411 and 412:
Appendix C 389 procedure Get(Item :
- Page 413 and 414:
Appendix C 391 package Ada.Characte
- Page 415 and 416:
Appendix C 393 --Conversion, Concat
- Page 417 and 418:
Appendix C 395 return Natural; Goin
- Page 419 and 420:
Appendix C 397 Right : in Bounded_S
- Page 421 and 422:
Appendix C 399 Count : out size_t;
- Page 423 and 424:
Appendix C 401 C.14 The Package Ada
- Page 425 and 426:
Appendix C 403 --Storage-related De
- Page 427 and 428:
Appendix D 405 with Ada.Text_Io; us
- Page 429 and 430:
Appendix D 407 with Ada.Text_Io, Ad
- Page 431 and 432:
Appendix D 409 package Class_Perfor
- Page 433 and 434:
Appendix D 411 declare Kb : constan
- Page 435 and 436:
Appendix D 413 package body Class_B
- Page 437 and 438:
Appendix D 415 The instantiation of
- Page 439 and 440:
Appendix D 417 with Ada.Text_Io, Ad
- Page 441 and 442:
References Intermetrics (1995) Ada
- Page 443 and 444:
Index 421 'class, 233 Class attribu
- Page 445 and 446:
Index 423 + dyadic, 53 monadic, 54