CARB® toroidal roller bearings â a revolutionary ... - Acorn Bearings
CARB® toroidal roller bearings â a revolutionary ... - Acorn Bearings
CARB® toroidal roller bearings â a revolutionary ... - Acorn Bearings
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
1 Product information 2 Recommendations 3 Product data<br />
Page ............. 3 Radial location Page ............. 37<br />
Design of bearing arrangements<br />
Two <strong>bearings</strong> are generally required to<br />
support, guide and locate a shaft in<br />
the radial and axial directions. To do<br />
this, one bearing is designated the<br />
locating bearing and the other is the<br />
non-locating bearing.<br />
In traditional self-aligning bearing<br />
systems, the locating bearing locates<br />
the shaft axially in its housing while<br />
the non-locating bearing typically<br />
moves in its housing to accommodate<br />
axial expansion of the shaft.<br />
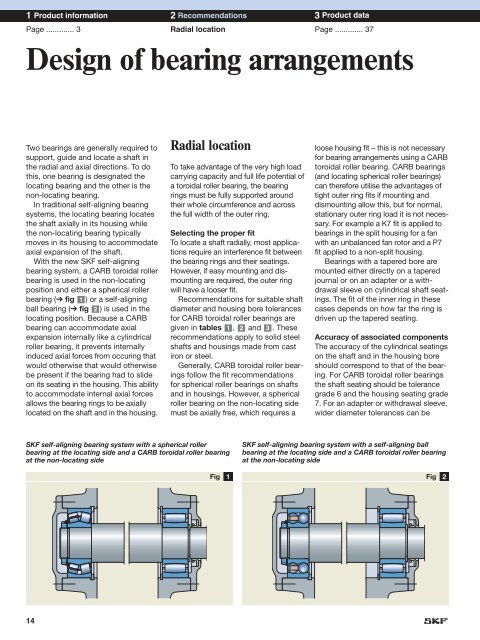
With the new SKF self-aligning<br />
bearing system, a CARB <strong>toroidal</strong> <strong>roller</strong><br />
bearing is used in the non-locating<br />
position and either a spherical <strong>roller</strong><br />
bearing (➔ fig 1 ) or a self-aligning<br />
ball bearing (➔ fig 2 ) is used in the<br />
locating position. Because a CARB<br />
bearing can accommodate axial<br />
expansion internally like a cylindrical<br />
<strong>roller</strong> bearing, it prevents internally<br />
induced axial forces from occuring that<br />
would otherwise that would otherwise<br />
be present if the bearing had to slide<br />
on its seating in the housing. This ability<br />
to accommodate internal axial forces<br />
allows the bearing rings to be axially<br />
located on the shaft and in the housing.<br />
Radial location<br />
To take advantage of the very high load<br />
carrying capacity and full life potential of<br />
a <strong>toroidal</strong> <strong>roller</strong> bearing, the bearing<br />
rings must be fully supported around<br />
their whole circumference and across<br />
the full width of the outer ring.<br />
Selecting the proper fit<br />
To locate a shaft radially, most applications<br />
require an interference fit between<br />
the bearing rings and their seatings.<br />
However, if easy mounting and dismounting<br />
are required, the outer ring<br />
will have a looser fit.<br />
Recommendations for suitable shaft<br />
diameter and housing bore tolerances<br />
for CARB <strong>toroidal</strong> <strong>roller</strong> <strong>bearings</strong> are<br />
given in tables 1 , 2 and 3 . These<br />
recommendations apply to solid steel<br />
shafts and housings made from cast<br />
iron or steel.<br />
Generally, CARB <strong>toroidal</strong> <strong>roller</strong> <strong>bearings</strong><br />
follow the fit recommendations<br />
for spherical <strong>roller</strong> <strong>bearings</strong> on shafts<br />
and in housings. However, a spherical<br />
<strong>roller</strong> bearing on the non-locating side<br />
must be axially free, which requires a<br />
loose housing fit – this is not necessary<br />
for bearing arrangements using a CARB<br />
<strong>toroidal</strong> <strong>roller</strong> bearing. CARB <strong>bearings</strong><br />
(and locating spherical <strong>roller</strong> <strong>bearings</strong>)<br />
can therefore utilise the advantages of<br />
tight outer ring fits if mounting and<br />
dismounting allow this, but for normal,<br />
stationary outer ring load it is not necessary.<br />
For example a K7 fit is applied to<br />
<strong>bearings</strong> in the split housing for a fan<br />
with an unbalanced fan rotor and a P7<br />
fit applied to a non-split housing.<br />
<strong>Bearings</strong> with a tapered bore are<br />
mounted either directly on a tapered<br />
journal or on an adapter or a withdrawal<br />
sleeve on cylindrical shaft seatings.<br />
The fit of the inner ring in these<br />
cases depends on how far the ring is<br />
driven up the tapered seating.<br />
Accuracy of associated components<br />
The accuracy of the cylindrical seatings<br />
on the shaft and in the housing bore<br />
should correspond to that of the bearing.<br />
For CARB <strong>toroidal</strong> <strong>roller</strong> <strong>bearings</strong><br />
the shaft seating should be tolerance<br />
grade 6 and the housing seating grade<br />
7. For an adapter or withdrawal sleeve,<br />
wider diameter tolerances can be<br />
SKF self-aligning bearing system with a spherical <strong>roller</strong><br />
bearing at the locating side and a CARB <strong>toroidal</strong> <strong>roller</strong> bearing<br />
at the non-locating side<br />
SKF self-aligning bearing system with a self-aligning ball<br />
bearing at the locating side and a CARB <strong>toroidal</strong> <strong>roller</strong> bearing<br />
at the non-locating side<br />
Fig 1<br />
Fig 2<br />
14