00 Contents - Hilti Svenska AB
00 Contents - Hilti Svenska AB
00 Contents - Hilti Svenska AB
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
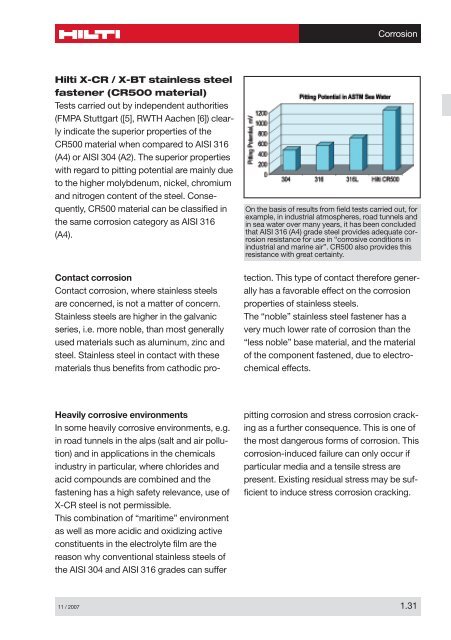
<strong>Hilti</strong> X-CR / X-BT stainless steel<br />
fastener (CR5<strong>00</strong> material)<br />
Tests carried out by independent authorities<br />
(FMPA Stuttgart ([5], RWTH Aachen [6]) clearly<br />
indicate the superior properties of the<br />
CR5<strong>00</strong> material when compared to AISI 316<br />
(A4) or AISI 304 (A2). The superior properties<br />
with regard to pitting potential are mainly due<br />
to the higher molybdenum, nickel, chromium<br />
and nitrogen content of the steel. Consequently,<br />
CR5<strong>00</strong> material can be classified in<br />
the same corrosion category as AISI 316<br />
(A4).<br />
Contact corrosion<br />
Contact corrosion, where stainless steels<br />
are concerned, is not a matter of concern.<br />
Stainless steels are higher in the galvanic<br />
series, i.e. more noble, than most generally<br />
used materials such as aluminum, zinc and<br />
steel. Stainless steel in contact with these<br />
materials thus benefits from cathodic pro-<br />
Heavily corrosive environments<br />
In some heavily corrosive environments, e.g.<br />
in road tunnels in the alps (salt and air pollution)<br />
and in applications in the chemicals<br />
industry in particular, where chlorides and<br />
acid compounds are combined and the<br />
fastening has a high safety relevance, use of<br />
X-CR steel is not permissible.<br />
This combination of “maritime” environment<br />
as well as more acidic and oxidizing active<br />
constituents in the electrolyte film are the<br />
reason why conventional stainless steels of<br />
the AISI 304 and AISI 316 grades can suffer<br />
Corrosion<br />
On the basis of results from field tests carried out, for<br />
example, in industrial atmospheres, road tunnels and<br />
in sea water over many years, it has been concluded<br />
that AISI 316 (A4) grade steel provides adequate corrosion<br />
resistance for use in “corrosive conditions in<br />
industrial and marine air”. CR5<strong>00</strong> also provides this<br />
resistance with great certainty.<br />
tection. This type of contact therefore generally<br />
has a favorable effect on the corrosion<br />
properties of stainless steels.<br />
The “noble” stainless steel fastener has a<br />
very much lower rate of corrosion than the<br />
“less noble” base material, and the material<br />
of the component fastened, due to electrochemical<br />
effects.<br />
pitting corrosion and stress corrosion cracking<br />
as a further consequence. This is one of<br />
the most dangerous forms of corrosion. This<br />
corrosion-induced failure can only occur if<br />
particular media and a tensile stress are<br />
present. Existing residual stress may be sufficient<br />
to induce stress corrosion cracking.<br />
11 / 2<strong>00</strong>7 1.31