Longan production in Asia - United Nations in Indonesia
Longan production in Asia - United Nations in Indonesia
Longan production in Asia - United Nations in Indonesia
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
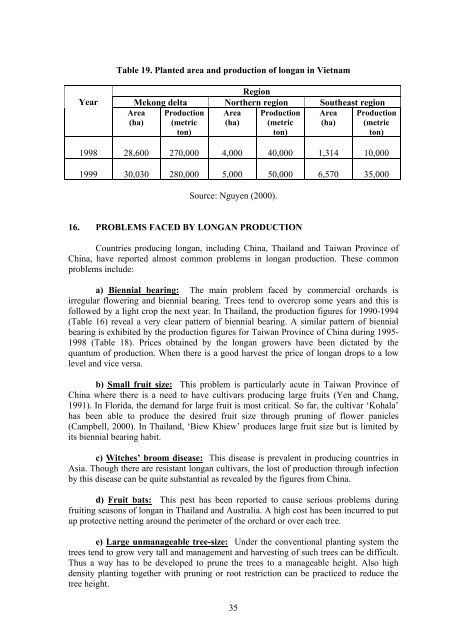
Table 19. Planted area and <strong>production</strong> of longan <strong>in</strong> Vietnam<br />
Year<br />
Region<br />
Mekong delta Northern region Southeast region<br />
Area Production Area Production Area Production<br />
(ha) (metric (ha) (metric (ha) (metric<br />
ton)<br />
ton)<br />
ton)<br />
1998 28,600 270,000 4,000 40,000 1,314 10,000<br />
1999 30,030 280,000 5,000 50,000 6,570 35,000<br />
Source: Nguyen (2000).<br />
16. PROBLEMS FACED BY LONGAN PRODUCTION<br />
Countries produc<strong>in</strong>g longan, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g Ch<strong>in</strong>a, Thailand and Taiwan Prov<strong>in</strong>ce of<br />
Ch<strong>in</strong>a, have reported almost common problems <strong>in</strong> longan <strong>production</strong>. These common<br />
problems <strong>in</strong>clude:<br />
a) Biennial bear<strong>in</strong>g: The ma<strong>in</strong> problem faced by commercial orchards is<br />
irregular flower<strong>in</strong>g and biennial bear<strong>in</strong>g. Trees tend to overcrop some years and this is<br />
followed by a light crop the next year. In Thailand, the <strong>production</strong> figures for 1990-1994<br />
(Table 16) reveal a very clear pattern of biennial bear<strong>in</strong>g. A similar pattern of biennial<br />
bear<strong>in</strong>g is exhibited by the <strong>production</strong> figures for Taiwan Prov<strong>in</strong>ce of Ch<strong>in</strong>a dur<strong>in</strong>g 1995-<br />
1998 (Table 18). Prices obta<strong>in</strong>ed by the longan growers have been dictated by the<br />
quantum of <strong>production</strong>. When there is a good harvest the price of longan drops to a low<br />
level and vice versa.<br />
b) Small fruit size: This problem is particularly acute <strong>in</strong> Taiwan Prov<strong>in</strong>ce of<br />
Ch<strong>in</strong>a where there is a need to have cultivars produc<strong>in</strong>g large fruits (Yen and Chang,<br />
1991). In Florida, the demand for large fruit is most critical. So far, the cultivar ‘Kohala’<br />
has been able to produce the desired fruit size through prun<strong>in</strong>g of flower panicles<br />
(Campbell, 2000). In Thailand, ‘Biew Khiew’ produces large fruit size but is limited by<br />
its biennial bear<strong>in</strong>g habit.<br />
c) Witches’ broom disease: This disease is prevalent <strong>in</strong> produc<strong>in</strong>g countries <strong>in</strong><br />
<strong>Asia</strong>. Though there are resistant longan cultivars, the lost of <strong>production</strong> through <strong>in</strong>fection<br />
by this disease can be quite substantial as revealed by the figures from Ch<strong>in</strong>a.<br />
d) Fruit bats: This pest has been reported to cause serious problems dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
fruit<strong>in</strong>g seasons of longan <strong>in</strong> Thailand and Australia. A high cost has been <strong>in</strong>curred to put<br />
up protective nett<strong>in</strong>g around the perimeter of the orchard or over each tree.<br />
e) Large unmanageable tree-size: Under the conventional plant<strong>in</strong>g system the<br />
trees tend to grow very tall and management and harvest<strong>in</strong>g of such trees can be difficult.<br />
Thus a way has to be developed to prune the trees to a manageable height. Also high<br />
density plant<strong>in</strong>g together with prun<strong>in</strong>g or root restriction can be practiced to reduce the<br />
tree height.<br />
35