Role of glycated LDL in diabetic atherosclerosis
Role of glycated LDL in diabetic atherosclerosis
Role of glycated LDL in diabetic atherosclerosis
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
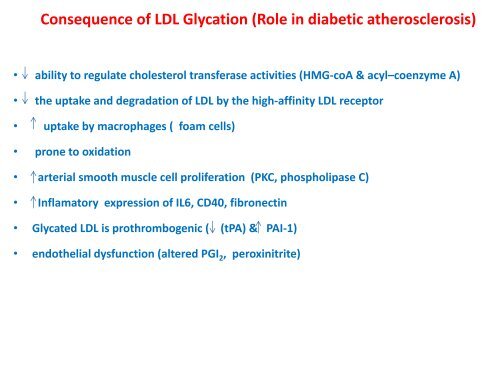
Consequence <strong>of</strong> <strong>LDL</strong> Glycation (<strong>Role</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>atherosclerosis</strong>)<br />
• ability to regulate cholesterol transferase activities (HMG-coA & acyl–coenzyme A)<br />
• the uptake and degradation <strong>of</strong> <strong>LDL</strong> by the high-aff<strong>in</strong>ity <strong>LDL</strong> receptor<br />
• uptake by macrophages ( foam cells)<br />
• prone to oxidation<br />
• arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation (PKC, phospholipase C)<br />
• Inflamatory expression <strong>of</strong> IL6, CD40, fibronect<strong>in</strong><br />
• Glycated <strong>LDL</strong> is prothrombogenic ( (tPA) & PAI-1)<br />
• endothelial dysfunction (altered PGI 2 , perox<strong>in</strong>itrite)<br />
L.