Primer on Automobile Fuel Efficiency and Emissions - Pollution Probe
Primer on Automobile Fuel Efficiency and Emissions - Pollution Probe
Primer on Automobile Fuel Efficiency and Emissions - Pollution Probe
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Envir<strong>on</strong>mental Problems Associated with the <strong>Automobile</strong><br />
If emissi<strong>on</strong>s were of no health or envir<strong>on</strong>mental c<strong>on</strong>sequence, then we would not be c<strong>on</strong>cerned about them.<br />
However, as detailed previously in Table 1-1, automobile emissi<strong>on</strong>s need to be taken very seriously. Of great c<strong>on</strong>cern<br />
are the greenhouse gas emissi<strong>on</strong>s that trap heat in our atmosphere <strong>and</strong> c<strong>on</strong>tribute to climate change. Other emissi<strong>on</strong>s<br />
combine to form smog that threatens the quality of our air <strong>and</strong> the health of our envir<strong>on</strong>ment. Even the<br />
health of our lakes <strong>and</strong> oceans is threatened<br />
by automobile emissi<strong>on</strong>s: NOx <strong>and</strong><br />
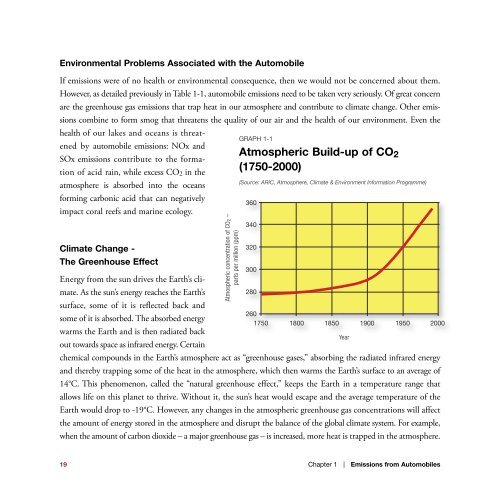
GRAPH 1-1<br />
Atmospheric Build-up of CO<br />
SOx emissi<strong>on</strong>s c<strong>on</strong>tribute to the formati<strong>on</strong><br />
of acid rain, while excess CO2 in the<br />
2<br />
(1750-2000)<br />
(Source: ARIC, Atmosphere, Climate & Envir<strong>on</strong>ment Informati<strong>on</strong> Programme)<br />
atmosphere is absorbed into the oceans<br />
forming carb<strong>on</strong>ic acid that can negatively<br />
360<br />
impact coral reefs <strong>and</strong> marine ecology.<br />
Climate Change -<br />
The Greenhouse Effect<br />
Atmospheric c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> of CO2 –<br />
parts per milli<strong>on</strong> (ppm)<br />
340<br />
320<br />
300<br />
Energy from the sun drives the Earth’s climate.<br />
As the sun’s energy reaches the Earth’s<br />
280<br />
surface, some of it is reflected back <strong>and</strong><br />
260<br />
some of it is absorbed. The absorbed energy<br />
warms the Earth <strong>and</strong> is then radiated back<br />
Year<br />
out towards space as infrared energy. Certain<br />
chemical compounds in the Earth’s atmosphere act as “greenhouse gases,” absorbing the radiated infrared energy<br />
<strong>and</strong> thereby trapping some of the heat in the atmosphere, which then warms the Earth’s surface to an average of<br />
14°C. This phenomen<strong>on</strong>, called the “natural greenhouse effect,” keeps the Earth in a temperature range that<br />
allows life <strong>on</strong> this planet to thrive. Without it, the sun’s heat would escape <strong>and</strong> the average temperature of the<br />
Earth would drop to -19°C. However, any changes in the atmospheric greenhouse gas c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s will affect<br />
the amount of energy stored in the atmosphere <strong>and</strong> disrupt the balance of the global climate system. For example,<br />
when the amount of carb<strong>on</strong> dioxide – a major greenhouse gas – is increased, more heat is trapped in the atmosphere.<br />
1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000<br />
19<br />
Chapter 1 | Emissi<strong>on</strong>s from <strong>Automobile</strong>s