Biennial Report 2011â2012
Biennial Report 2011â2012
Biennial Report 2011â2012
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Department of Eukaryote Genetic Engineering<br />
HBoV1-4 antigens in yeast expression system has not yet been<br />
reported. , In the current study, the capsid proteins VP1 and<br />
VP2 of HBoV1were expressed in yeast S.cerevisiae. Electron<br />
microscopy demonstrated that both purified recombinant proteins<br />
self assembled into virus-like particles (VLPs) exhibiting<br />
the typical icosahedral appearance of parvoviruses with a<br />
diameter of approximately 20 nm. The yield and stability of<br />
HBoV1 VP2 protein was significantly higher in comparison to<br />
VP1, therefore VP2 was chosen for the developing of an immunoassay<br />
and generation of monoclonal antibodies. HBoV1<br />
VP2 VLPs were stable in yeast and were easily purified by caesium<br />
chloride gradient ultracentrifugation. Therefore, yeast<br />
expression system proved to be simple, efficient and cost-effective,<br />
suitable for high-level production of HBoV1 VP2 as<br />
VLPs. Four monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) of IgG1 subtype<br />
were generated by immunization of mouse with recombinant<br />
HBoV1 VP2 VLPs. Three of them specifically recognized<br />
only HBoV1 VP2 protein; one MAb was cross-reactive with<br />
HBoV2 and HBoV4 VP2 proteins. Recombinant HBoV1<br />
VP2 VLPs and VP2-specific MAbs were employed to develop<br />
serological assays to detect virus-specific IgG antibodies in human<br />
serum specimens.<br />
Human PARV4<br />
Human parvovirus 4 (PARV4) is a recently discovered new<br />
member of the Parvoviridea family not closely related to any<br />
of the known human parvoviruses. PARV4 is widely distributed<br />
in intravenous drug users, particularly in those co-infected<br />
with human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C. PARV4<br />
has been isolated from plasma of individuals with symptoms<br />
of acute viral infection, however, till now PARV4 has not been<br />
associated with any disease and its prevalence in human population<br />
is not yet clearly established. In the current study, the<br />
major capsid protein VP2 of PARV4 was generated in yeast<br />
Sacharomyces cerevisiae and used for serological detection of virus-specific<br />
IgG and IgM in the sera of low risk individuals.<br />
One-hundred seventy serum specimens obtained from patients<br />
with acute respiratory diseases were tested for PARV4-specific<br />
IgG and IgM antibodies. Sixteen (9.4%) seropositive individuals<br />
were diagnosed, including 10 IgG positive, 12 IgM positive<br />
and 6 both IgG and IgM positive. Six of 16 sero-positive<br />
A<br />
B<br />
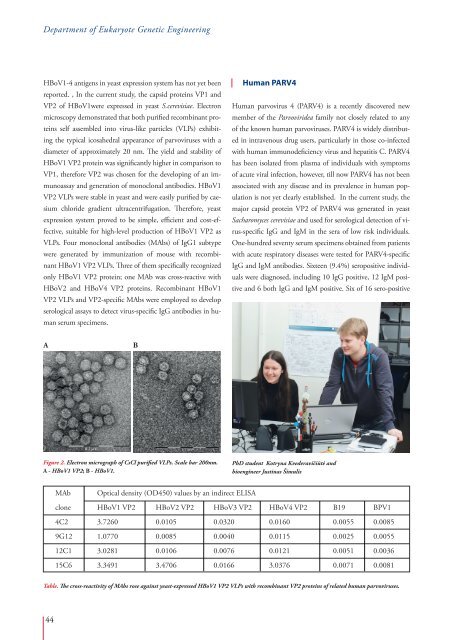
Figure 2. Electron micrograph of CsCl purified VLPs. Scale bar 200nm.<br />
A - HBoV1 VP2; B - HBoV1.<br />
PhD student Kotryna Kvederavičiūtė and<br />
bioengineer Justinas Šimulis<br />
MAb<br />
Optical density (OD450) values by an indirect ELISA<br />
clone HBoV1 VP2 HBoV2 VP2 HBoV3 VP2 HBoV4 VP2 B19 BPV1<br />
4C2 3.7260 0.0105 0.0320 0.0160 0.0055 0.0085<br />
9G12 1.0770 0.0085 0.0040 0.0115 0.0025 0.0055<br />
12C1 3.0281 0.0106 0.0076 0.0121 0.0051 0.0036<br />
15C6 3.3491 3.4706 0.0166 3.0376 0.0071 0.0081<br />
Table. The cross-reactivity of MAbs rose against yeast-expressed HBoV1 VP2 VLPs with recombinant VP2 proteins of related human parvoviruses.<br />
44