Dingee Reservoir Final Seismic Report - East Bay Municipal Utility ...
Dingee Reservoir Final Seismic Report - East Bay Municipal Utility ...
Dingee Reservoir Final Seismic Report - East Bay Municipal Utility ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
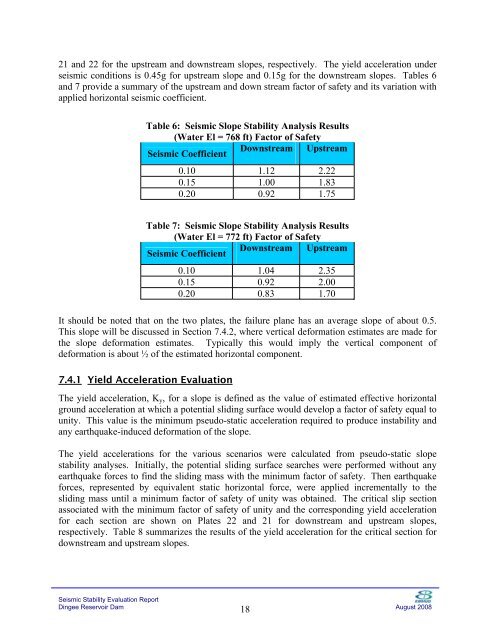
21 and 22 for the upstream and downstream slopes, respectively. The yield acceleration under<br />
seismic conditions is 0.45g for upstream slope and 0.15g for the downstream slopes. Tables 6<br />
and 7 provide a summary of the upstream and down stream factor of safety and its variation with<br />
applied horizontal seismic coefficient.<br />
Table 6: <strong>Seismic</strong> Slope Stability Analysis Results<br />
(Water El = 768 ft) Factor of Safety<br />
Downstream Upstream<br />
<strong>Seismic</strong> Coefficient<br />
0.10 1.12 2.22<br />
0.15 1.00 1.83<br />
0.20 0.92 1.75<br />
Table 7: <strong>Seismic</strong> Slope Stability Analysis Results<br />
(Water El = 772 ft) Factor of Safety<br />
Downstream Upstream<br />
<strong>Seismic</strong> Coefficient<br />
0.10 1.04 2.35<br />
0.15 0.92 2.00<br />
0.20 0.83 1.70<br />
It should be noted that on the two plates, the failure plane has an average slope of about 0.5.<br />
This slope will be discussed in Section 7.4.2, where vertical deformation estimates are made for<br />
the slope deformation estimates. Typically this would imply the vertical component of<br />
deformation is about ½ of the estimated horizontal component.<br />
7.4.1 Yield Acceleration Evaluation<br />
The yield acceleration, K y , for a slope is defined as the value of estimated effective horizontal<br />
ground acceleration at which a potential sliding surface would develop a factor of safety equal to<br />
unity. This value is the minimum pseudo-static acceleration required to produce instability and<br />
any earthquake-induced deformation of the slope.<br />
The yield accelerations for the various scenarios were calculated from pseudo-static slope<br />
stability analyses. Initially, the potential sliding surface searches were performed without any<br />
earthquake forces to find the sliding mass with the minimum factor of safety. Then earthquake<br />
forces, represented by equivalent static horizontal force, were applied incrementally to the<br />
sliding mass until a minimum factor of safety of unity was obtained. The critical slip section<br />
associated with the minimum factor of safety of unity and the corresponding yield acceleration<br />
for each section are shown on Plates 22 and 21 for downstream and upstream slopes,<br />
respectively. Table 8 summarizes the results of the yield acceleration for the critical section for<br />
downstream and upstream slopes.<br />
<strong>Seismic</strong> Stability Evaluation <strong>Report</strong><br />
<strong>Dingee</strong> <strong>Reservoir</strong> Dam<br />
18<br />
August 2008