Guidelines for second generation HIV surveillance - World Health ...
Guidelines for second generation HIV surveillance - World Health ...
Guidelines for second generation HIV surveillance - World Health ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
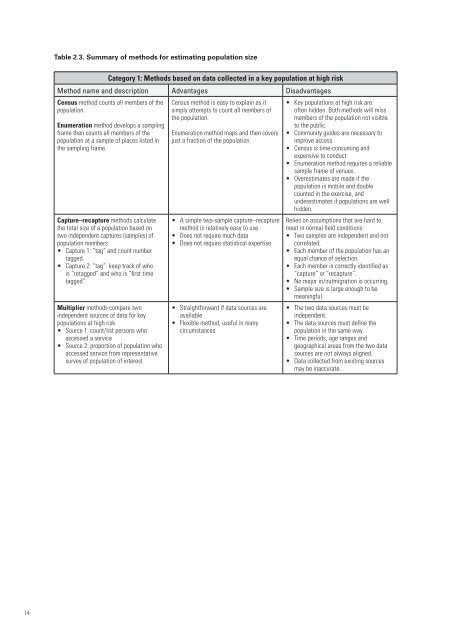
Table 2.3. Summary of methods <strong>for</strong> estimating population size<br />
Category 1: Methods based on data collected in a key population at high risk<br />
Method name and description Advantages Disadvantages<br />
Census method counts all members of the<br />
population.<br />
Enumeration method develops a sampling<br />
frame then counts all members of the<br />
population at a sample of places listed in<br />
the sampling frame.<br />
Capture–recapture methods calculate<br />
the total size of a population based on<br />
two independent captures (samples) of<br />
population members:<br />
• Capture 1: “tag” and count number<br />
tagged.<br />
• Capture 2: “tag”: keep track of who<br />
is “retagged” and who is “first time<br />
tagged”.<br />
Multiplier methods compare two<br />
independent sources of data <strong>for</strong> key<br />
populations at high risk.<br />
• Source 1: count/list persons who<br />
accessed a service<br />
• Source 2: proportion of population who<br />
accessed service from representative<br />
survey of population of interest<br />
Census method is easy to explain as it<br />
simply attempts to count all members of<br />
the population.<br />
Enumeration method maps and then covers<br />
just a fraction of the population.<br />
• A simple two-sample capture–recapture<br />
method is relatively easy to use.<br />
• Does not require much data<br />
• Does not require statistical expertise<br />
• Straight<strong>for</strong>ward if data sources are<br />
available<br />
• Flexible method, useful in many<br />
circumstances<br />
• Key populations at high risk are<br />
often hidden. Both methods will miss<br />
members of the population not visible<br />
to the public.<br />
• Community guides are necessary to<br />
improve access.<br />
• Census is time-consuming and<br />
expensive to conduct<br />
• Enumeration method requires a reliable<br />
sample frame of venues.<br />
• Overestimates are made if the<br />
population is mobile and double<br />
counted in the exercise, and<br />
underestimates if populations are well<br />
hidden.<br />
Relies on assumptions that are hard to<br />
meet in normal field conditions:<br />
• Two samples are independent and not<br />
correlated.<br />
• Each member of the population has an<br />
equal chance of selection.<br />
• Each member is correctly identified as<br />
“capture” or “recapture”.<br />
• No major in/outmigration is occurring.<br />
• Sample size is large enough to be<br />
meaningful.<br />
• The two data sources must be<br />
independent.<br />
• The data sources must define the<br />
population in the same way.<br />
• Time periods, age ranges and<br />
geographical areas from the two data<br />
sources are not always aligned.<br />
• Data collected from existing sources<br />
may be inaccurate.<br />
14