Guidelines for second generation HIV surveillance - World Health ...
Guidelines for second generation HIV surveillance - World Health ...
Guidelines for second generation HIV surveillance - World Health ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
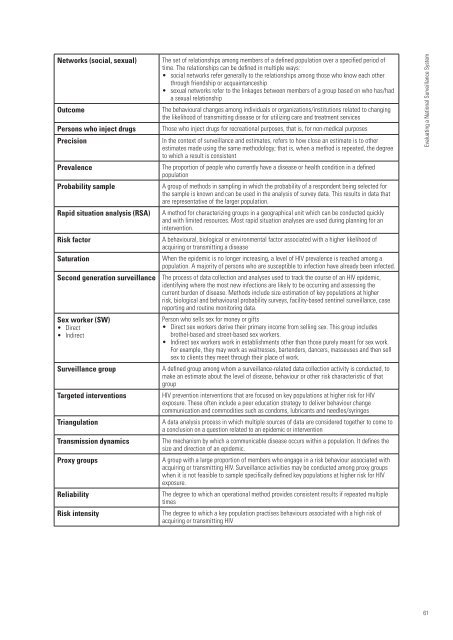
Networks (social, sexual)<br />
Outcome<br />
Persons who inject drugs<br />
Precision<br />
Prevalence<br />
Probability sample<br />
Rapid situation analysis (RSA)<br />
Risk factor<br />
Saturation<br />
Second <strong>generation</strong> <strong>surveillance</strong><br />
Sex worker (SW)<br />
• Direct<br />
• Indirect<br />
Surveillance group<br />
Targeted interventions<br />
Triangulation<br />
Transmission dynamics<br />
Proxy groups<br />
Reliability<br />
Risk intensity<br />
The set of relationships among members of a defined population over a specified period of<br />
time. The relationships can be defined in multiple ways:<br />
• social networks refer generally to the relationships among those who know each other<br />
through friendship or acquaintanceship<br />
• sexual networks refer to the linkages between members of a group based on who has/had<br />
a sexual relationship<br />
The behavioural changes among individuals or organizations/institutions related to changing<br />
the likelihood of transmitting disease or <strong>for</strong> utilizing care and treatment services<br />
Those who inject drugs <strong>for</strong> recreational purposes, that is, <strong>for</strong> non-medical purposes<br />
In the context of <strong>surveillance</strong> and estimates, refers to how close an estimate is to other<br />
estimates made using the same methodology; that is, when a method is repeated, the degree<br />
to which a result is consistent<br />
The proportion of people who currently have a disease or health condition in a defined<br />
population<br />
A group of methods in sampling in which the probability of a respondent being selected <strong>for</strong><br />
the sample is known and can be used in the analysis of survey data. This results in data that<br />
are representative of the larger population.<br />
A method <strong>for</strong> characterizing groups in a geographical unit which can be conducted quickly<br />
and with limited resources. Most rapid situation analyses are used during planning <strong>for</strong> an<br />
intervention.<br />
A behavioural, biological or environmental factor associated with a higher likelihood of<br />
acquiring or transmitting a disease<br />
When the epidemic is no longer increasing, a level of <strong>HIV</strong> prevalence is reached among a<br />
population. A majority of persons who are susceptible to infection have already been infected.<br />
The process of data collection and analyses used to track the course of an <strong>HIV</strong> epidemic,<br />
identifying where the most new infections are likely to be occurring and assessing the<br />
current burden of disease. Methods include size estimation of key populations at higher<br />
risk, biological and behavioural probability surveys, facility-based sentinel <strong>surveillance</strong>, case<br />
reporting and routine monitoring data.<br />
Person who sells sex <strong>for</strong> money or gifts<br />
• Direct sex workers derive their primary income from selling sex. This group includes<br />
brothel-based and street-based sex workers.<br />
• Indirect sex workers work in establishments other than those purely meant <strong>for</strong> sex work.<br />
For example, they may work as waitresses, bartenders, dancers, masseuses and then sell<br />
sex to clients they meet through their place of work.<br />
A defined group among whom a <strong>surveillance</strong>-related data collection activity is conducted, to<br />
make an estimate about the level of disease, behaviour or other risk characteristic of that<br />
group<br />
<strong>HIV</strong> prevention interventions that are focused on key populations at higher risk <strong>for</strong> <strong>HIV</strong><br />
exposure. These often include a peer education strategy to deliver behaviour change<br />
communication and commodities such as condoms, lubricants and needles/syringes<br />
A data analysis process in which multiple sources of data are considered together to come to<br />
a conclusion on a question related to an epidemic or intervention<br />
The mechanism by which a communicable disease occurs within a population. It defines the<br />
size and direction of an epidemic.<br />
A group with a large proportion of members who engage in a risk behaviour associated with<br />
acquiring or transmitting <strong>HIV</strong>. Surveillance activities may be conducted among proxy groups<br />
when it is not feasible to sample specifically defined key populations at higher risk <strong>for</strong> <strong>HIV</strong><br />
exposure.<br />
The degree to which an operational method provides consistent results if repeated multiple<br />
times<br />
The degree to which a key population practises behaviours associated with a high risk of<br />
acquiring or transmitting <strong>HIV</strong><br />
Evaluating a National Surveillance System<br />
61