Guidelines for second generation HIV surveillance - World Health ...
Guidelines for second generation HIV surveillance - World Health ...
Guidelines for second generation HIV surveillance - World Health ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
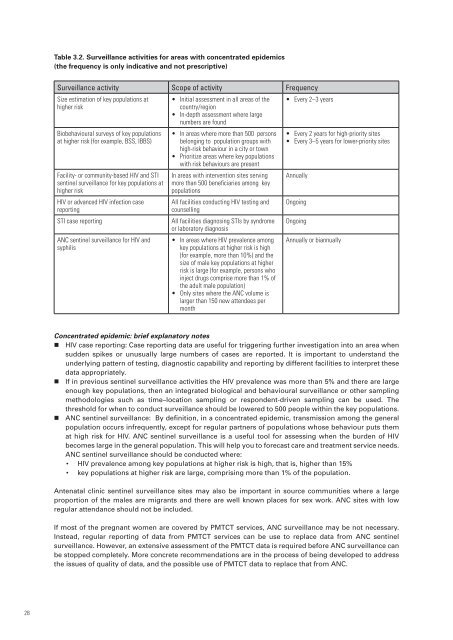
Table 3.2. Surveillance activities <strong>for</strong> areas with concentrated epidemics<br />
(the frequency is only indicative and not prescriptive)<br />
Surveillance activity Scope of activity Frequency<br />
Size estimation of key populations at<br />
higher risk<br />
• Initial assessment in all areas of the<br />
country/region<br />
• In-depth assessment where large<br />
numbers are found<br />
• Every 2–3 years<br />
Biobehavioural surveys of key populations<br />
at higher risk (<strong>for</strong> example, BSS, IBBS)<br />
Facility- or community-based <strong>HIV</strong> and STI<br />
sentinel <strong>surveillance</strong> <strong>for</strong> key populations at<br />
higher risk<br />
<strong>HIV</strong> or advanced <strong>HIV</strong> infection case<br />
reporting<br />
STI case reporting<br />
ANC sentinel <strong>surveillance</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>HIV</strong> and<br />
syphilis<br />
• In areas where more than 500 persons<br />
belonging to population groups with<br />
high-risk behaviour in a city or town<br />
• Prioritize areas where key populations<br />
with risk behaviours are present<br />
In areas with intervention sites serving<br />
more than 500 beneficiaries among key<br />
populations<br />
All facilities conducting <strong>HIV</strong> testing and<br />
counselling<br />
All facilities diagnosing STIs by syndrome<br />
or laboratory diagnosis<br />
• In areas where <strong>HIV</strong> prevalence among<br />
key populations at higher risk is high<br />
(<strong>for</strong> example, more than 10%) and the<br />
size of male key populations at higher<br />
risk is large (<strong>for</strong> example, persons who<br />
inject drugs comprise more than 1% of<br />
the adult male population)<br />
• Only sites where the ANC volume is<br />
larger than 150 new attendees per<br />
month<br />
• Every 2 years <strong>for</strong> high-priority sites<br />
• Every 3–5 years <strong>for</strong> lower-priority sites<br />
Annually<br />
Ongoing<br />
Ongoing<br />
Annually or biannually<br />
Concentrated epidemic: brief explanatory notes<br />
• <strong>HIV</strong> case reporting: Case reporting data are useful <strong>for</strong> triggering further investigation into an area when<br />
sudden spikes or unusually large numbers of cases are reported. It is important to understand the<br />
underlying pattern of testing, diagnostic capability and reporting by different facilities to interpret these<br />
data appropriately.<br />
• If in previous sentinel <strong>surveillance</strong> activities the <strong>HIV</strong> prevalence was more than 5% and there are large<br />
enough key populations, then an integrated biological and behavioural <strong>surveillance</strong> or other sampling<br />
methodologies such as time–location sampling or respondent-driven sampling can be used. The<br />
threshold <strong>for</strong> when to conduct <strong>surveillance</strong> should be lowered to 500 people within the key populations.<br />
• ANC sentinel <strong>surveillance</strong>: By definition, in a concentrated epidemic, transmission among the general<br />
population occurs infrequently, except <strong>for</strong> regular partners of populations whose behaviour puts them<br />
at high risk <strong>for</strong> <strong>HIV</strong>. ANC sentinel <strong>surveillance</strong> is a useful tool <strong>for</strong> assessing when the burden of <strong>HIV</strong><br />
becomes large in the general population. This will help you to <strong>for</strong>ecast care and treatment service needs.<br />
ANC sentinel <strong>surveillance</strong> should be conducted where:<br />
• <strong>HIV</strong> prevalence among key populations at higher risk is high, that is, higher than 15%<br />
• key populations at higher risk are large, comprising more than 1% of the population.<br />
Antenatal clinic sentinel <strong>surveillance</strong> sites may also be important in source communities where a large<br />
proportion of the males are migrants and there are well known places <strong>for</strong> sex work. ANC sites with low<br />
regular attendance should not be included.<br />
If most of the pregnant women are covered by PMTCT services, ANC <strong>surveillance</strong> may be not necessary.<br />
Instead, regular reporting of data from PMTCT services can be use to replace data from ANC sentinel<br />
<strong>surveillance</strong>. However, an extensive assessment of the PMTCT data is required be<strong>for</strong>e ANC <strong>surveillance</strong> can<br />
be stopped completely. More concrete recommendations are in the process of being developed to address<br />
the issues of quality of data, and the possible use of PMTCT data to replace that from ANC.<br />
28