Frontier Tanzania Environmental Research REPORT 110 ...
Frontier Tanzania Environmental Research REPORT 110 ...
Frontier Tanzania Environmental Research REPORT 110 ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Kazimzumbwi Forest Reserve<br />
54<br />
KEY TO ABBREVIATIONS IN ZOOLOGICAL TABLES<br />
NEW RECORDS<br />
* Species not previously recorded in Kazimzumbwi FR<br />
** Species not previously recorded in Coastal Forests<br />
ECOLOGICAL (ECOL.) TYPE<br />
F - Forest dependent species (primary forest only, not including forest edge or secondary forest)<br />
f - Forest dwelling but not forest dependent species<br />
O - Non-forest species<br />
ENDEMIC (END.) STATUS<br />
E - Endemic species (occurring only in the Pugu Hills)<br />
N - Near endemic species (a - range limited to Coastal Forests, b – range limited to Coastal Forests and the Eastern Arc<br />
Mountains, c – range limited to Coastal Forests, the Eastern Arc Mountains and a few other East African forests)<br />
W - Widespread distribution species<br />
IUCN STATUS (1996)<br />
EN – Endangered, VU – Vulnerable, LR – Lower Risk (cd – Conservation Dependent, nt – Near Threatened)<br />
(CITES classification is given as the Appendix in which the species appears)<br />
Nine species listed in Table 16 have not previously been recorded in Kazimzumbwi FR; mainly<br />
antelope (including the near-endemic Cephalophus adersi) and Cricetomyidae (including the<br />
near-endemic Beamys hindei). Two of these species also represent new records for Coastal<br />
Forests (in general). One species; Lepus saxatalis, is a non-forest species however and it may be<br />
for this reason that it has not been listed in previous Coastal Forest mammal fauna.<br />
Of the 32 mammal species recorded in Kazimzumbwi FR, 7 (22%) are forest dependent, 11<br />
(34%) forest dwelling and 3 (9%) non-forest species (Table 17). The greatest forest dependency<br />
is within the ungulates, notably Cephalophus species. There are no mammal species endemic to<br />
the Pugu Hills, although 4 species recorded (13%) are near-endemics. One has a range restricted<br />
to Coastal Forests alone, two have ranges restricted to Coastal Forests and Eastern Arc Mountains<br />
and one has a range of Coastal Forests, Eastern Arc Mountains and a few other East African<br />
forests (Table 17 and 18). The majority of species recorded (17 or 53%) have wide distributions.<br />
Three species were recorded which are listed as Threatened (Endangered or Vulnerable) by the<br />
IUCN and two that are listed as at Lower Risk. Four species were recorded which appear in<br />
CITES Appendix II.<br />
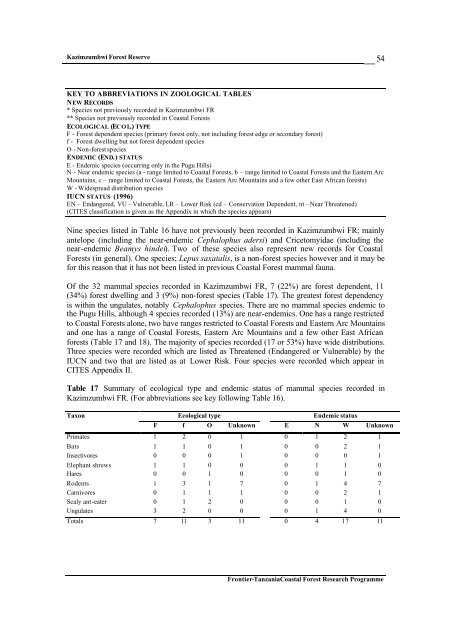
Table 17 Summary of ecological type and endemic status of mammal species recorded in<br />
Kazimzumbwi FR. (For abbreviations see key following Table 16).<br />
Taxon Ecological type Endemic status<br />
F f O Unknown E N W Unknown<br />
Primates 1 2 0 1 0 1 2 1<br />
Bats 1 1 0 1 0 0 2 1<br />
Insectivores 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1<br />
Elephant shrews 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0<br />
Hares 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0<br />
Rodents 1 3 1 7 0 1 4 7<br />
Carnivores 0 1 1 1 0 0 2 1<br />
Scaly ant-eater 0 1 2 0 0 0 1 0<br />
Ungulates 3 2 0 0 0 1 4 0<br />
Totals 7 11 3 11 0 4 17 11<br />
<strong>Frontier</strong>-<strong>Tanzania</strong>Coastal Forest <strong>Research</strong> Programme