Staff Members of the Institute of Biochemistry, TU Graz http://www ...
Staff Members of the Institute of Biochemistry, TU Graz http://www ...
Staff Members of the Institute of Biochemistry, TU Graz http://www ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Biophysical chemistry group<br />
Group leader: Albin Hermetter<br />
Post-docs: Heidrun Susani-Etzerodt, Jo-Anne Rasmussen<br />
Graduate students: Maria Morak, Jessica Schatte, Maximilian Schicher, Ute Stemmer<br />
Undergraduate students: Peter Krempl, Andreas Gasser, Martina Geier<br />
Technicians: Elfriede Zenzmaier<br />
General description<br />
Our research deals with <strong>the</strong> role <strong>of</strong> glycero(phospho)lipids and lipid modifying enzymes<br />
as components <strong>of</strong> membranes and lipoproteins, as mediators in cellular<br />
(patho)biochemistry, and <strong>the</strong>ir application as analytical tools in enzyme technology.<br />
Fluorescence spectroscopy is used as a main technique to investigate <strong>the</strong> behaviour <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong>se biomolecules in <strong>the</strong> respective supramolecular systems.<br />
Section 1 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> following report summarizes our studies on lipid oxidation, <strong>the</strong> effects<br />
<strong>of</strong> oxidized lipids on intracellular signalling, and <strong>the</strong> inhibition <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se processes by<br />
syn<strong>the</strong>tic and natural antioxidants.<br />
Section 2 describes <strong>the</strong> development <strong>of</strong> fluorescence and chip technology for functional<br />
proteomic analysis <strong>of</strong> lipolytic enzymes in microbial, animal and human cells.<br />
1. Lipid oxidation and a<strong>the</strong>rosclerosis – Lipotoxicity<br />
1.1. Interaction <strong>of</strong> oxidized phospholipids with vascular cells<br />
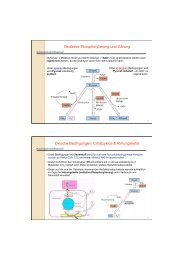
Sphingomyelin<br />
acid<br />
Sphingomyelinase<br />
Oxidized -<br />
Phospholipids<br />
O<br />
H<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O P O<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O P O<br />
OH<br />
+<br />
N<br />
N +<br />
Ceramide<br />
JNK<br />
p38 MAPK<br />
Caspase 3<br />
ERK<br />
AKT/PKB<br />
NFkB<br />
PROLIFERATION<br />
SURVIVAL<br />
Interactions <strong>of</strong> oxidized lipoproteins with<br />
<strong>the</strong> cells <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> arterial wall induce and<br />
influence <strong>the</strong> progress <strong>of</strong> a<strong>the</strong>rosclerosis.<br />
Accumulation <strong>of</strong> foam cells originating<br />
from macrophages and excessive intimal<br />
growth <strong>of</strong> vascular smooth muscle cells<br />
(SMC) alternating with focal massive cell<br />
death are characteristics typical <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> a<strong>the</strong>rosclerotic lesion. These phenomena are<br />
largely mediated by <strong>the</strong> oxidized phospholipid components <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> modified particles that<br />
are generated under <strong>the</strong> conditions <strong>of</strong> oxidative stress. In <strong>the</strong> framework <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> research<br />
consortium LIPOTOX, we investigate <strong>the</strong> “Toxicity <strong>of</strong> oxidized phospholipids in<br />
macrophages”. This study aims at identifying <strong>the</strong> molecular and cellular effects <strong>of</strong> an<br />
important subfamily <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> oxidized phospholipids containing long hydrocarbon chains<br />
in position sn-1 and short polar acyl residues in position sn-2 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> glycerol backbone.<br />
The respective compounds trigger an intracellular signaling network including<br />
sphingomyelinases, (MAP) kinases and transcription factors <strong>the</strong>reby inducing<br />
proliferation or apoptosis <strong>of</strong> vascular cells. Both phenomena largely depend on <strong>the</strong><br />
26