quarterly statement - TIAA-CREF
quarterly statement - TIAA-CREF
quarterly statement - TIAA-CREF
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
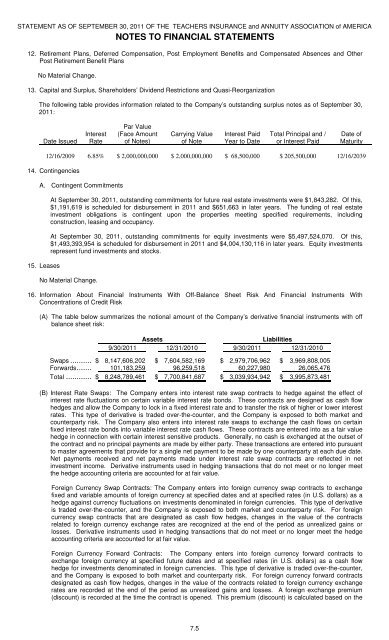
STATEMENT AS OF SEPTEMBER 30, 2011 OF THE TEACHERS INSURANCE and ANNUITY ASSOCIATION of AMERICA<br />
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS<br />
12. Retirement Plans, Deferred Compensation, Post Employment Benefits and Compensated Absences and Other<br />
Post Retirement Benefit Plans<br />
No Material Change.<br />
13. Capital and Surplus, Shareholders’ Dividend Restrictions and Quasi-Reorganization<br />
The following table provides information related to the Company’s outstanding surplus notes as of September 30,<br />
2011:<br />
Date Issued<br />
Interest<br />
Rate<br />
Par Value<br />
(Face Amount<br />
of Notes)<br />
Carrying Value<br />
of Note<br />
Interest Paid<br />
Year to Date<br />
Total Principal and /<br />
or Interest Paid<br />
Date of<br />
Maturity<br />
12/16/2009 6.85% $ 2,000,000,000 $ 2,000,000,000 $ 68,500,000 $ 205,500,000 12/16/2039<br />
14. Contingencies<br />
A. Contingent Commitments<br />
15. Leases<br />
At September 30, 2011, outstanding commitments for future real estate investments were $1,843,282. Of this,<br />
$1,191,619 is scheduled for disbursement in 2011 and $651,663 in later years. The funding of real estate<br />
investment obligations is contingent upon the properties meeting specified requirements, including<br />
construction, leasing and occupancy.<br />
At September 30, 2011, outstanding commitments for equity investments were $5,497,524,070. Of this,<br />
$1,493,393,954 is scheduled for disbursement in 2011 and $4,004,130,116 in later years. Equity investments<br />
represent fund investments and stocks.<br />
No Material Change.<br />
16. Information About Financial Instruments With Off-Balance Sheet Risk And Financial Instruments With<br />
Concentrations of Credit Risk<br />
(A) The table below summarizes the notional amount of the Company’s derivative financial instruments with off<br />
balance sheet risk:<br />
Assets<br />
Liabilities<br />
9/30/2011 12/31/2010 9/30/2011 12/31/2010<br />
Swaps .......... $ 8,147,606,202 $ 7,604,582,169 $ 2,979,706,962 $ 3,969,808,005<br />
Forwards....... 101,183,259 96,259,518 60,227,980 26,065,476<br />
Total ............ $ 8,248,789,461 $ 7,700,841,687 $ 3,039,934,942 $ 3,995,873,481<br />
(B) Interest Rate Swaps: The Company enters into interest rate swap contracts to hedge against the effect of<br />
interest rate fluctuations on certain variable interest rate bonds. These contracts are designed as cash flow<br />
hedges and allow the Company to lock in a fixed interest rate and to transfer the risk of higher or lower interest<br />
rates. This type of derivative is traded over-the-counter, and the Company is exposed to both market and<br />
counterparty risk. The Company also enters into interest rate swaps to exchange the cash flows on certain<br />
fixed interest rate bonds into variable interest rate cash flows. These contracts are entered into as a fair value<br />
hedge in connection with certain interest sensitive products. Generally, no cash is exchanged at the outset of<br />
the contract and no principal payments are made by either party. These transactions are entered into pursuant<br />
to master agreements that provide for a single net payment to be made by one counterparty at each due date.<br />
Net payments received and net payments made under interest rate swap contracts are reflected in net<br />
investment income. Derivative instruments used in hedging transactions that do not meet or no longer meet<br />
the hedge accounting criteria are accounted for at fair value.<br />
Foreign Currency Swap Contracts: The Company enters into foreign currency swap contracts to exchange<br />
fixed and variable amounts of foreign currency at specified dates and at specified rates (in U.S. dollars) as a<br />
hedge against currency fluctuations on investments denominated in foreign currencies. This type of derivative<br />
is traded over-the-counter, and the Company is exposed to both market and counterparty risk. For foreign<br />
currency swap contracts that are designated as cash flow hedges, changes in the value of the contracts<br />
related to foreign currency exchange rates are recognized at the end of the period as unrealized gains or<br />
losses. Derivative instruments used in hedging transactions that do not meet or no longer meet the hedge<br />
accounting criteria are accounted for at fair value.<br />
Foreign Currency Forward Contracts: The Company enters into foreign currency forward contracts to<br />
exchange foreign currency at specified future dates and at specified rates (in U.S. dollars) as a cash flow<br />
hedge for investments denominated in foreign currencies. This type of derivative is traded over-the-counter,<br />
and the Company is exposed to both market and counterparty risk. For foreign currency forward contracts<br />
designated as cash flow hedges, changes in the value of the contracts related to foreign currency exchange<br />
rates are recorded at the end of the period as unrealized gains and losses. A foreign exchange premium<br />
(discount) is recorded at the time the contract is opened. This premium (discount) is calculated based on the<br />
7.5