Journal of Applied Science Studies - Ozean Publications
Journal of Applied Science Studies - Ozean Publications
Journal of Applied Science Studies - Ozean Publications
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
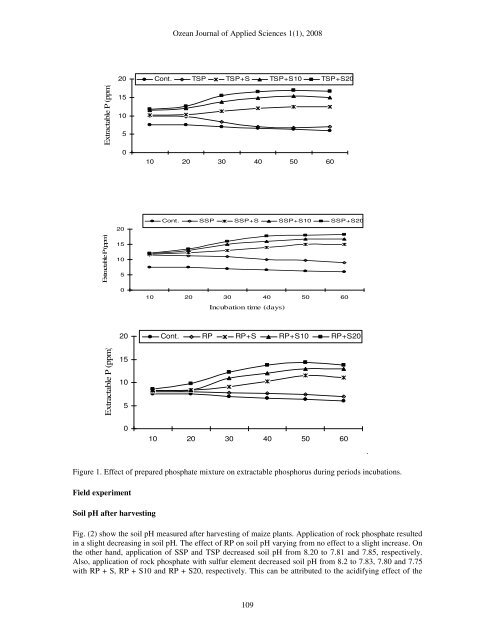
<strong>Ozean</strong> <strong>Journal</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Applied</strong> <strong>Science</strong>s 1(1), 2008<br />
Extractable P (ppm)<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
Cont. TSP TSP+S TSP+S10 TSP+S20<br />
10 20 30 40 50 60<br />
Extractable P (ppm)<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
Cont. SSP SSP+S SSP+S10 SSP+S20<br />
10 20 30 40 50 60<br />
Incubation time (days)<br />
Extractable P (ppm)<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
Cont. RP RP+S RP+S10 RP+S20<br />
0<br />
10 20 30 40 50 60<br />
.<br />
Figure 1. Effect <strong>of</strong> prepared phosphate mixture on extractable phosphorus during periods incubations.<br />
Field experiment<br />
Soil pH after harvesting<br />
Fig. (2) show the soil pH measured after harvesting <strong>of</strong> maize plants. Application <strong>of</strong> rock phosphate resulted<br />
in a slight decreasing in soil pH. The effect <strong>of</strong> RP on soil pH varying from no effect to a slight increase. On<br />
the other hand, application <strong>of</strong> SSP and TSP decreased soil pH from 8.20 to 7.81 and 7.85, respectively.<br />
Also, application <strong>of</strong> rock phosphate with sulfur element decreased soil pH from 8.2 to 7.83, 7.80 and 7.75<br />
with RP + S, RP + S10 and RP + S20, respectively. This can be attributed to the acidifying effect <strong>of</strong> the<br />
109