Instructions for Use - Glyco Kit MB-LAC AIA - Bruker
Instructions for Use - Glyco Kit MB-LAC AIA - Bruker
Instructions for Use - Glyco Kit MB-LAC AIA - Bruker
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Figure 1 exemplarily depictured possible experimental strategies to facilitate the identification of<br />
glyco-proteins, to enable the detection of N-glycosylation sites, to support the structural<br />
characterization of N-glycosylated peptides and to per<strong>for</strong>m glyco-profiling studies in the clinical<br />
context.<br />
General In<strong>for</strong>mation<br />
<strong>Glyco</strong>sylation is the most common post-translational modification of proteins, playing a key role in<br />
protein folding, stability, solubility, activity and molecular recognition. Altered glycosylation is known<br />
to act as an indicator or effector in pathologic mechanisms with potential impact on diagnosis and<br />
therapy of human diseases. Immunity to certain infectious diseases, prion diseases and cancer<br />
can all be associated with abnormal glycosylation patterns. As an example, increased branching<br />
and sialylation of N-linked glycans on cancer cells are potential tumor markers in molecular<br />
diagnostics.<br />
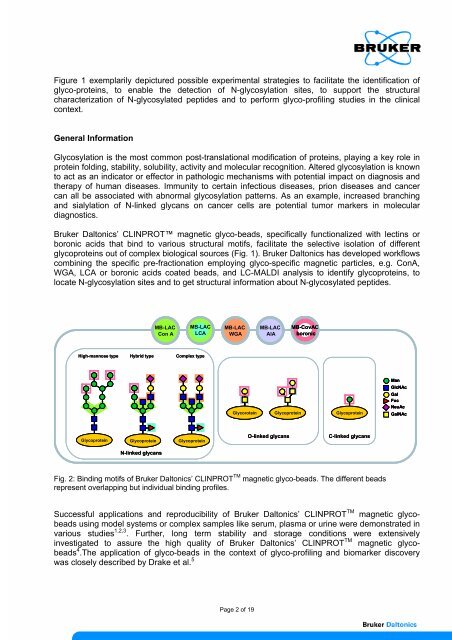
<strong>Bruker</strong> Daltonics’ CLINPROT magnetic glyco-beads, specifically functionalized with lectins or<br />
boronic acids that bind to various structural motifs, facilitate the selective isolation of different<br />
glycoproteins out of complex biological sources (Fig. 1). <strong>Bruker</strong> Daltonics has developed workflows<br />
combining the specific pre-fractionation employing glyco-specific magnetic particles, e.g. ConA,<br />
WGA, LCA or boronic acids coated beads, and LC-MALDI analysis to identify glycoproteins, to<br />
locate N-glycosylation sites and to get structural in<strong>for</strong>mation about N-glycosylated peptides.<br />
<strong>MB</strong>-<strong>LAC</strong><br />
Con A<br />
<strong>MB</strong>-<strong>LAC</strong><br />
LCA<br />
<strong>MB</strong>-<strong>LAC</strong><br />
WGA<br />
<strong>MB</strong>-<strong>LAC</strong><br />
<strong>AIA</strong><br />
<strong>MB</strong>-CovAC<br />
boronic<br />
High-mannose type Hybrid type Complex type<br />
<strong>Glyco</strong>rotein<br />
<strong>Glyco</strong>protein<br />
<strong>Glyco</strong>protein<br />
Man<br />
GlcNAc<br />
Gal<br />
Fuc<br />
NeuAc<br />
GalNAc<br />
<strong>Glyco</strong>protein<br />
<strong>Glyco</strong>protein<br />
<strong>Glyco</strong>protein<br />
O-linked glycans<br />
C-linked glycans<br />
N-linked glycans<br />
Fig. 2: Binding motifs of <strong>Bruker</strong> Daltonics’ CLINPROT TM magnetic glyco-beads. The different beads<br />
represent overlapping but individual binding profiles.<br />
Successful applications and reproducibility of <strong>Bruker</strong> Daltonics’ CLINPROT TM magnetic glycobeads<br />
using model systems or complex samples like serum, plasma or urine were demonstrated in<br />
various studies 1,2,3 . Further, long term stability and storage conditions were extensively<br />
investigated to assure the high quality of <strong>Bruker</strong> Daltonics’ CLINPROT TM magnetic glycobeads<br />
4 .The application of glyco-beads in the context of glyco-profiling and biomarker discovery<br />
was closely described by Drake et al. 5<br />
Page 2 of 19