arc-flash analysis of utility power systems - Michigan Technological ...
arc-flash analysis of utility power systems - Michigan Technological ...
arc-flash analysis of utility power systems - Michigan Technological ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
the test system. When the voltage is at 900 volts, the l g I a is equal to 3.55 kA when<br />
using equation (3.1) and 3.76 kA when using equation (3.2). When the voltage is at<br />
1.1 kV, the l g I a is equal to 3.92 kA when using equation (3.1) and 3.68 kA when using<br />
equation (3.2). If the voltage was to be applied in the equation (3.1), there would be a<br />
multiplying factor anywhere from 1.1 to 15 times and the incident energy would<br />
continue to increase.<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
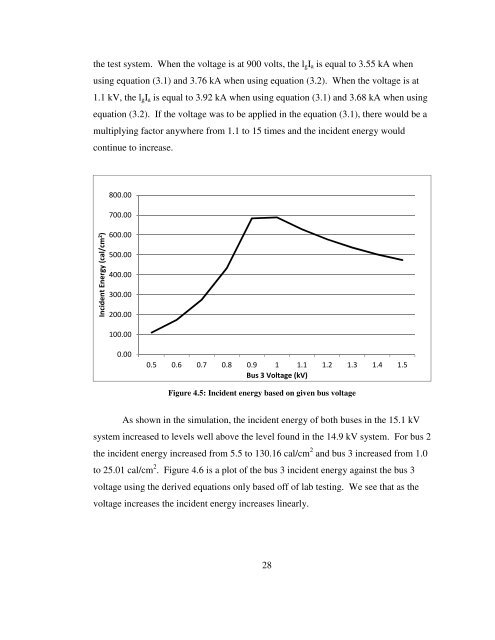
Figure 4.5: Incident energy based on given bus voltage<br />
As shown in the simulation, the incident energy <strong>of</strong> both buses in the 15.1 kV<br />
system increased to levels well above the level found in the 14.9 kV system. For bus 2<br />
the incident energy increased from 5.5 to 130.16 cal/cm 2 and bus 3 increased from 1.0<br />
to 25.01 cal/cm 2 . Figure 4.6 is a plot <strong>of</strong> the bus 3 incident energy against the bus 3<br />
voltage using the derived equations only based <strong>of</strong>f <strong>of</strong> lab testing. We see that as the<br />
voltage increases the incident energy increases linearly.<br />
28