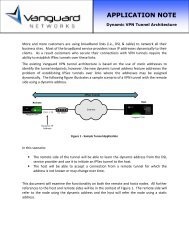
VPN - Vanguard Networks
VPN - Vanguard Networks
VPN - Vanguard Networks
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Vanguard</strong> <strong>VPN</strong> Tunneling<br />
Traffic Types<br />
Fragmentation and<br />
Reassembly<br />
Network Address<br />
Translation (NAT)<br />
Tunnel Source<br />
Address<br />
Access Control<br />
Policy Based<br />
Routing<br />
Quality of Service<br />
Grouped LCON<br />
<strong>Vanguard</strong> <strong>Networks</strong> Routers support tunneling for following traffic types:<br />
• IP<br />
• IPX<br />
• Routing protocols: RIP-v1, RIP-v2, OSPF and BGP<br />
• Broadcast packets such as local, directed and all subnet broadcasts<br />
• Bridge<br />
Fragmentation and Reassembly of the packet is done by the tunnel. If the packet size<br />
after adding the GRE header and Encryption header (if configured) exceeds the<br />
link’s MTU, then IP level fragmentation is done by the tunnel.<br />
On the remote side, when a fragmented packet is received by the tunnel, it waits for<br />
all the fragments before performing other tunnel operations like GRE header<br />
removal and Decryption.<br />
NAT static, external address can be used as a tunnel source address. NAT does not<br />
work on a tunnel/virtual interface. Do not configure tunnel/virtual interface as NAT<br />
internal or external interfaces. If Network Address Translation (NAT) is enabled and<br />
the LCON interface is external, then the tunnel source address should be configured<br />
as one of the external addresses configured for that LCON interface.<br />
The tunnel source address should be configured by the user. It is usually one of the<br />
numbered LCON physical interface addresses.<br />
<strong>Vanguard</strong> <strong>Networks</strong> routers do not support access control for tunneled packets. On<br />
the sending side, access control (if enabled) is performed before tunneling. On the<br />
receiving end, the tunnel is identified first (decapsulate tunnel header) and then<br />
access control is applied on the decapsulated packet.<br />
Policy Based Routing, along with tunneling, achieves flow based tunneling. In the<br />
Policy Based Routing configuration, you can choose the next hop address as the<br />
tunnel’s interface address. When a packet matches the flow, it is forwarded to the<br />
corresponding tunnel.<br />
Currently, Quality of Service (QoS) can be configured on LCONs. QoS cannot be<br />
configured on individual tunnels. The policy of the connected LCON is applied to<br />
the tunnel packets that travel over that LCON. Since QoS is not supported for LAN<br />
links/interfaces, Qos is not supported for LAN tunnels.<br />
The tunnel does not make any distinction between a Grouped or Point-to-Point<br />
LCON. Since only one LCON can be configured per tunnel, the tunnel simply<br />
forwards the packet to the configured LCON which can either be Grouped or <br />
Point-to-Point.<br />
Tunneling 2-7<br />
T0103-10, Revision L Release 7.3