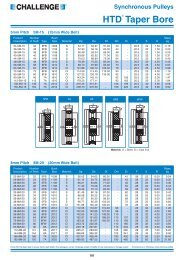
TORQUE LIMITERS
TORQUE LIMITERS
TORQUE LIMITERS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
single-position<br />
multi-position<br />
load holding<br />
full disengagement<br />
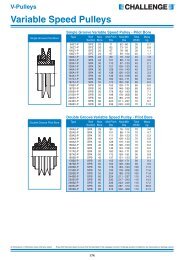
SELECTION<br />
BACKLASH FREE <strong>TORQUE</strong> <strong>LIMITERS</strong> FROM R+W<br />
According to disengagement torque<br />
As a rule torque limiters are rated according<br />
to the required disengagement torque,<br />
which must be greater than the torque that<br />
is necessary for regular machine operation.<br />
T KN<br />
1.5 · T AS (Nm)<br />
T KN = rated torque of coupling<br />
T AS = peak torque of motor<br />
(Nm)<br />
(Nm)<br />
The disengagement torque of the torque<br />
limiters is determined as a rule in accordance<br />
with the drive specifications.<br />
The following calcucation has proven itself<br />
as a good rule of thumb:<br />
or<br />
T KN<br />
P<br />
9550 · –— AN<br />
n<br />
· 1.5 (Nm)<br />
T KN = rated torque of coupling<br />
(Nm)<br />
P AN = drive power<br />
(kw)<br />
n = speed of drive (rpm))<br />
According to acceleration torque (start-up at no load)<br />
S A = shock or load factor<br />
S A = 1 (uniform load)<br />
S A = 2 (non-uniform load)<br />
S A = 3 (high dynamic load)<br />
Values for S A = 2-3 are usual for servo drives on machine-tools<br />
J<br />
T KN · J L ––––– L<br />
· T AS · S A (Nm)<br />
J A + J L<br />
T KN = rated torque of coupling<br />
α = angular acceleration<br />
= ––<br />
t<br />
= –––––<br />
· n<br />
t · 30<br />
(Nm)<br />
–––<br />
1 s 2<br />
t = acceleration time (s)<br />
ω = angular speed in (s- 1 )<br />
n = speed of drive (rpm)<br />
J L = moment of inertia on load side (kgm 2 )<br />
J A = moment of inertia on driving side (kgm 2 )<br />
T AS = peak torque of motor<br />
(Nm)<br />
According to acceleration and load torque (start with load)<br />
J<br />
T KN · J L + T AN –––––<br />
L<br />
· (T AS - T AN ) + T AN · S A (Nm)<br />
J A + J L<br />
S A = shock or load factor<br />
S A = 1 (uniform load)<br />
S A = 2 (non-uniform load)<br />
S A = 3 (high dynamic load)<br />
Values for S A = 2-3 are usual for servo drives on machine-tools<br />
T KN = rated torque of coupling<br />
α = angular acceleration<br />
= ––<br />
t<br />
= –––––<br />
· n<br />
t · 30<br />
(Nm)<br />
–––<br />
1 s 2<br />
t = acceleration time (s)<br />
ω = angular speed in (s- 1 )<br />
n = speed of drive (rpm)<br />
J L = moment of inertia on load side (kgm 2 )<br />
T AN = load torque<br />
(Nm)<br />
J A = moment of inertia on driving side (kgm 2 )<br />
T AS = peak torque of motor<br />
(Nm)<br />
www.rwcouplings.com<br />
R+W<br />
27