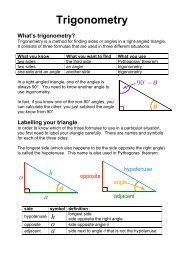
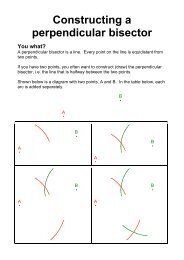
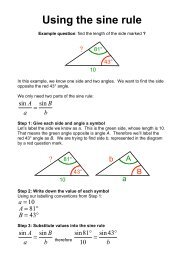
Section 1.1 Section 1.2 Section 1.3 - The Student Room
Section 1.1 Section 1.2 Section 1.3 - The Student Room
Section 1.1 Section 1.2 Section 1.3 - The Student Room
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
SECTION 13<br />
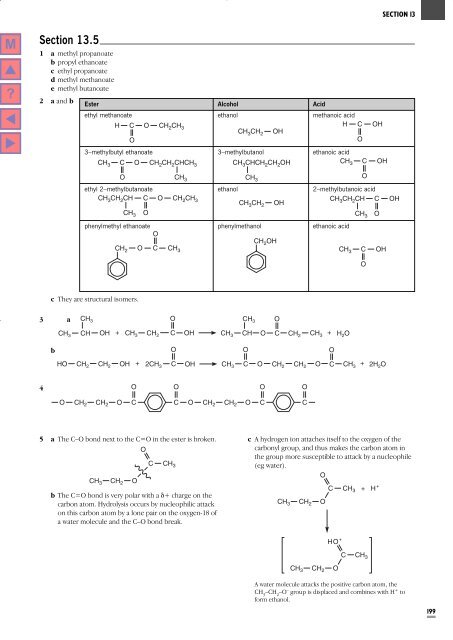
<strong>Section</strong> 13.5<br />
CH 3 C OH<br />
CH 3 CH 2 OH<br />
1 a methyl propanoate<br />
b propyl ethanoate<br />
c ethyl propanoate<br />
d methyl methanoate<br />
e methyl butanoate<br />
2 a and b<br />
Ester Alcohol Acid<br />
ethyl methanoate ethanol methanoic acid<br />
H C O CH 2 CH 3<br />
H C OH<br />
CH 3 CH 2 OH<br />
O<br />
O<br />
3–methylbutyl ethanoate 3–methylbutanol ethanoic acid<br />
CH 3 C O CH 2 CH 2 CHCH 3<br />
CH 3 CHCH 2 CH 2 OH<br />
O<br />
CH 3<br />
CH 3<br />
O<br />
ethyl 2–methylbutanoate ethanol 2–methylbutanoic acid<br />
CH 3 CH 2 CH C O CH 2 CH 3<br />
CH 3 CH 2 CH C OH<br />
CH 3 O<br />
CH 3 O<br />
phenylmethyl ethanoate phenylmethanol ethanoic acid<br />
O<br />
CH 2 OH<br />
CH 2 O C CH 3<br />
CH 3 C OH<br />
O<br />
c <strong>The</strong>y are structural isomers.<br />
3 a<br />
CH 3<br />
CH<br />
CH 3<br />
CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 CH<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
+<br />
C<br />
OH<br />
CH 3<br />
C CH 2<br />
CH 3 H 2 O<br />
O<br />
+<br />
b<br />
HO<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
CH 2 CH 2 OH + 2CH 3 C OH CH 3 C O CH 2 CH 2 O C CH 3<br />
+ 2H 2 O<br />
4<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O CH 2 CH 2 O C<br />
C O<br />
CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
O<br />
C<br />
C<br />
5 a <strong>The</strong> C–O bond next to the C=O in the ester is broken. c A hydrogen ion attaches itself to the oxygen of the<br />
O<br />
carbonyl group, and thus makes the carbon atom in<br />
the group more susceptible to attack by a nucleophile<br />
C CH 3<br />
(eg water).<br />
CH 3 CH 2 O<br />
O<br />
C CH 3 + H +<br />
b <strong>The</strong> C=O bond is very polar with a d+ charge on the<br />
carbon atom. Hydrolysis occurs by nucleophilic attack<br />
CH 3 CH 2 O<br />
on this carbon atom by a lone pair on the oxygen-18 of<br />
a water molecule and the C–O bond break.<br />
HO +<br />
CH 3<br />
CH 2<br />
O<br />
C<br />
CH 3<br />
A water molecule attacks the positive carbon atom, the<br />
CH 3<br />
–CH 2<br />
–O – group is displaced and combines with H + to<br />
form ethanol.<br />
199









![ISI Web of Knowledge [v.4.10] - All Databases Results - Benjamin-Mills](https://img.yumpu.com/39253071/1/184x260/isi-web-of-knowledge-v410-all-databases-results-benjamin-mills.jpg?quality=85)