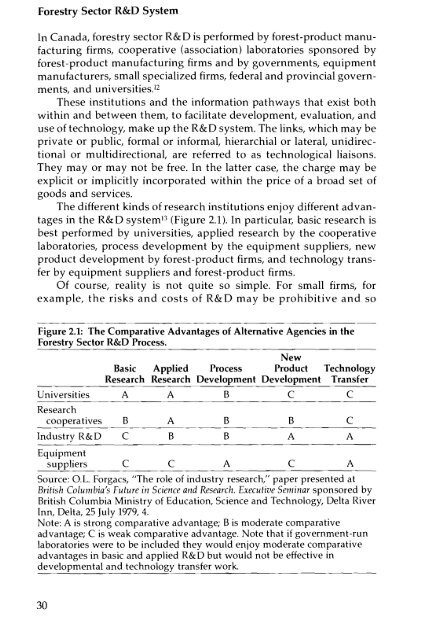
<strong>Forest</strong>ry Sector R&D SystemIn Canada, forestry sector R&D is performed by forest-product manufacturingfirms, cooperative (association) laboratories sponsored byforest-product manufacturing firms <strong>and</strong> by governments, equipmentmanufacturers, small specialized firms, federal <strong>and</strong> provincial governments,<strong>and</strong> universities."These institutions <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> information pathways that exist bothwithin <strong>and</strong> between <strong>the</strong>m, to facilitate development, evaluation, <strong>and</strong>use of technology, make up <strong>the</strong> R&D system. The links, which may beprivate or public, formal or informal, hierarchial or lateral, unidirectionalor multidirectional, are referred to as technological liaisons.They mayor may not be free. In <strong>the</strong> latter case, <strong>the</strong> charge may beexplicit or implicitly incorporated within <strong>the</strong> price of a broad set ofgoods <strong>and</strong> services.The different kinds of research institutions enjoy different advantagesin <strong>the</strong> R&D system!' (Figure 2.1). In particular, basic research isbest performed by universities, applied research by <strong>the</strong> cooperativelaboratories, process development by <strong>the</strong> equipment suppliers, newproduct development by forest-product firms, <strong>and</strong> technology transferby equipment suppliers <strong>and</strong> forest-product firms.Of course, reality is not quite so simple. For small firms, forexample, <strong>the</strong> risks <strong>and</strong> costs of R&D may be prohibitive <strong>and</strong> soFigure 2.1: The Comparative Advantages of Alternative Agencies in <strong>the</strong><strong>Forest</strong>ry Sector R&D Process.NewBasic Applied Process <strong>Product</strong> <strong>Technology</strong>Research Research Development Development TransferUniversities A ABC CResearchcooperatives B A B B CIndustry R&D C B B A AEquipmentsuppliers C C A C ASource: G.L. Forgacs, "The role of industry research," paper presented atBritish Columbia's Future in Science <strong>and</strong> Research. Executive Seminar sponsored byBritish Columbia Ministry of Education, Science <strong>and</strong> <strong>Technology</strong>, Delta RiverInn, Delta, 25 July 1979, 4.Note: A is strong comparative advantage; B is moderate comparativeadvantage; C is weak comparative advantage. Note that if government-runlaboratories were to be included <strong>the</strong>y would enjoy moderate comparativeadvantages in basic <strong>and</strong> applied R&D but would not be effective indevelopmental <strong>and</strong> technology transfer work.30
cooperative <strong>and</strong> government laboratories invest in developmental aswell as applied R&D. On <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r h<strong>and</strong>, <strong>the</strong> desire for firm-specificadvantages may push in-house groups in firms that can afford it toconduct applied <strong>and</strong> even basic research. Within universities, appliedscience faculties normally do developmental research <strong>and</strong> even pursuepractical implications."Never<strong>the</strong>less within <strong>the</strong> forest-product industries <strong>the</strong>re is anR&D system within which different kinds of organizations should playcomplementary if overlapping roles. Within this context, what needsto be exp<strong>and</strong>ed is <strong>the</strong> role of industry in-house groups in developmentalR&D.In-House R&D by <strong>Forest</strong>-<strong>Product</strong> FirmsEvolution <strong>and</strong> Location of In-House LaboratoriesThe oldest continuously operated company-owned R&D laboratory isprobably that of CIP Research Ltd. which was set up at Hawkesbury,Ontario in 1923 by <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>n Riordan Pulp Co," Abitibi Power <strong>and</strong>Light (subsequently Abitibi Paper <strong>and</strong> now Abitibi-Price) also establishedan R&D facility in <strong>the</strong> 1920s at Sault Ste. Marie but this activitywas closed down during <strong>the</strong> Great Depression <strong>and</strong> did not start upagain until <strong>the</strong> 1940s. Several firms opened R&D laboratories in <strong>the</strong>1930s <strong>and</strong> after <strong>the</strong> Second World War. 16 Most recently, Canfor, in 1982built a $7 million pilot plant within its Gr<strong>and</strong>e Prairie plywood mill inorder to conduct developmental research on aspen usePIn-house forest-product R&D in Canada largely stemmed from aneed to know more about pulping <strong>and</strong> paper-making processes.vWith a few exceptions, such as Canfor, current R&D operations grewup adjacent to pulp <strong>and</strong> paper <strong>and</strong>/or paper-converting plants.'?In <strong>the</strong> 1960s, however, several firms exp<strong>and</strong>ed <strong>and</strong> consolidatedR&D activities at new locations in <strong>the</strong> suburbs of major metropolitanareas.P Conventional wisdom suggests that <strong>the</strong>se sites are advantageousbecause, first, <strong>the</strong>ir location in relation to <strong>the</strong> firm's head officefacilitates personal contact without too much casual interference.Second, <strong>the</strong>y are located away from manufacturing operations, whichlimits <strong>the</strong> troubleshooting that R& D personnel are asked to do. Third,suburban sites share <strong>the</strong> economies <strong>and</strong> social advantages of largemetropolitan areas including, in some cases, nearness to o<strong>the</strong>r typesof R&D activities, A few R& D laboratories, at least one major facility<strong>and</strong> several smaller ones, remain outside metropolitan areas.Although several firms have more than one R&D facility <strong>the</strong>re isinvariably one central laboratory <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong>re may be satellite operationsthat provide specialized R& D. MacMillan Bloedel, for example, has set31
- Page 3 and 4: Science Council of Canada100 Metcal
- Page 5 and 6: ContentsForewordAcknowledgments1113
- Page 7 and 8: In-House R&D by Equipment Suppliers
- Page 9 and 10: Table 2.5: R&D Employment in 10 Can
- Page 11 and 12: ForewordTechnological innovation an
- Page 14 and 15: adapted sufficiently rapidly to the
- Page 16 and 17: Finally, the author interviewed sen
- Page 18 and 19: Table 1.3: Degree of Foreign Contro
- Page 20 and 21: Figure 1.1: Innovation Patterns and
- Page 22 and 23: Since 1945 the pace of technologica
- Page 24 and 25: Toward Reliance on Research rather
- Page 26 and 27: science occurred between 1900 and 1
- Page 30 and 31: up its forestry research group at N
- Page 32 and 33: and one other that was strongly ori
- Page 34 and 35: closely involved in the establishme
- Page 36 and 37: to vet and control research priorit
- Page 38 and 39: In-House R&D by Equipment Suppliers
- Page 40 and 41: product. One, by no means atypical,
- Page 42 and 43: only internal source of dissolving
- Page 44 and 45: of which only 18 per cent came from
- Page 46 and 47: New information can be generated by
- Page 48 and 49: Chapter 3The R&D System andHow It W
- Page 50 and 51: Table 3.2: Summary Characteristics
- Page 52 and 53: Sixteen firms provided details on s
- Page 54 and 55: The Opco Process: A Case Study of I
- Page 56 and 57: however, within the last two decade
- Page 58 and 59: in 1959, and a full-scale experimen
- Page 60 and 61: Papritection was developed as follo
- Page 62 and 63: Further tests were conducted in 198
- Page 64 and 65: fully automatic machines, and its s
- Page 66 and 67: Chapter 4Technological Capability a
- Page 68 and 69: Table 4.2 provides measurements of
- Page 70 and 71: forest-product equipment patents, w
- Page 72 and 73: Foreign-Ownership and In-House R&DT
- Page 74 and 75: Technological Liaisons: Forest-Prod
- Page 76 and 77: for this deficiency the federal gov
- Page 78 and 79:
On the other hand, three of the lea
- Page 80 and 81:
one of Sweden's forest-products gia
- Page 82 and 83:
Capital Investments in the Canadian
- Page 84 and 85:
and Quebec accounted for 33.9 per c
- Page 86 and 87:
Table 5.5: Canadian Forest-Product
- Page 88 and 89:
Scandinavian manufacturers are in t
- Page 90 and 91:
was implemented smoothly and manage
- Page 92 and 93:
the foundations were poured, until
- Page 94 and 95:
inherent capabilities were never fu
- Page 96 and 97:
especially in the east, has receive
- Page 98 and 99:
"export staples mentality." The bel
- Page 100 and 101:
size of the conglomerates would cer
- Page 102 and 103:
the concept of flexibility explicit
- Page 104 and 105:
This author therefore recommends th
- Page 106 and 107:
with respect to technology transfer
- Page 108 and 109:
of the R&D system and influence the
- Page 110 and 111:
operations, attitudes toward innova
- Page 112 and 113:
limited R&D base, but they do empha
- Page 114 and 115:
The small size and non-innovative n
- Page 116 and 117:
Promoting In-House R&D in the Fores
- Page 118 and 119:
Notes1. The Technological Challenge
- Page 120 and 121:
7. For example, nj. Daly, "Weak Lin
- Page 122 and 123:
7. P.G. Mellgren and E. Heidersdorf
- Page 124 and 125:
this R&D facility has become even s
- Page 126 and 127:
3. K. Noble, "Forest Industry Urged
- Page 128 and 129:
Publications of the ScienceCouncil
- Page 130 and 131:
Reports on Matters Referred by the
- Page 132 and 133:
No. 40. Government Regulation of th
- Page 134 and 135:
1981An Engineer's View of Science E