56 F. de Groot / Coord<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>Chemistry</strong> Reviews 249 (2005) 31–63In addition to the basic experiments described, a rangeof related experiments are possible. One can make use ofthe polarization of the X-<strong>ray</strong>s, for example, with MCD experiments.Also one can detect the sp<strong>in</strong> of the electrons <strong>in</strong>sp<strong>in</strong>-polarized measurements. Another range of applicationsuse the angular variations <strong>in</strong> the respective experiments.this <strong>in</strong>cludes polarization dependent XAS, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g magneticl<strong>in</strong>ear dichroism, polarization dependent resonant XES<strong>and</strong> angle-resolved photoemission. Experiments comb<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>gdiffraction <strong>and</strong> absorption, for example, diffraction absorptionf<strong>in</strong>e structure (DAFS) or anomalous diffraction (MAD)must <strong>in</strong>clude multiplet effects if they play a role <strong>in</strong> the resonanceused.3. Examples for 3d coord<strong>in</strong>ation compoundsWe end this review with a short overview of the variouspossibilities that are provided by the spectroscopic techniquesdiscussed above, aga<strong>in</strong> with the focus on multipleteffects <strong>in</strong> the spectral shapes. We start with two examplesthat make use of the 1s XAS spectral shape, before turn<strong>in</strong>g tothe soft X-<strong>ray</strong> 2p XAS spectra <strong>and</strong> the other spectroscopies.3.1. The 1s XAS pre-edge shapes of coord<strong>in</strong>ation complexesIt was discussed above that the pre-edge region of the1s XAS spectrum is dom<strong>in</strong>ated by the direct 1s to 3dquadrupole transitions. The pre-edge region of coord<strong>in</strong>ationcompounds of iron has systematically been <strong>in</strong>vestigated byWestre et al. [48]. Analysis showed that the spectra should be<strong>in</strong>terpreted <strong>in</strong> terms of multiplet theory, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g the crystalfield <strong>and</strong> the atomic <strong>in</strong>teractions. That the pre-edge region<strong>in</strong> the case of Fe 2 O 3 is almost completely of quadrupole naturecan also be shown from 1s2p resonant X-<strong>ray</strong> emissionexperiments [50]. From the experiments, detailed <strong>in</strong>formationof iron <strong>in</strong> a range of complexes was obta<strong>in</strong>ed. This<strong>in</strong>cluded the sp<strong>in</strong> state, oxidation state, electronic structureparameters such as the crystal field splitt<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> hybridizationeffects, <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>directly also <strong>in</strong>formation on the geometry<strong>and</strong> for b<strong>in</strong>uclear complexes also the bridg<strong>in</strong>g ligation.It should be noted that there is no uniform underst<strong>and</strong><strong>in</strong>gof the pre-edge spectral shapes. For example, detailed calculationson TiO 2 arrive at a slightly different model comparedwith the iron pre-edges discussed above. The pre-edgeof TiO 2 has three pre-peaks that are caused by two effects:(1) the crystal field splitt<strong>in</strong>g between the T 2g <strong>and</strong> E g orbitals<strong>and</strong> (2) the core hole effect on the quadrupole peaks shift<strong>in</strong>gthem by 2.5 eV with respect to the dipole peaks. The dipolepeaks do not shift because they are related to 4p-characterthat overlaps with the 3d-b<strong>and</strong>s of the neighbors. This assignmentis confirmed by a number of detailed multiple scatter<strong>in</strong>g<strong>and</strong> b<strong>and</strong> structure calculations [18,52]. Note that itis different from the usual assumption that the dipole <strong>and</strong>quadrupole peaks are positioned at the same energy.3.2. The 1s XAS pre-edge <strong>in</strong>tensity <strong>and</strong> energy of m<strong>in</strong>eralsWaychunas did show for a series of m<strong>in</strong>erals that adistortion of the octahedron will show up as an <strong>in</strong>creased<strong>in</strong>tensity of the pre-edge peak(s) [53]. They show a roughlyl<strong>in</strong>ear relationship between the bond angle variance (a measureof the distortion) <strong>and</strong> the pre-edge <strong>in</strong>tensity relative tothe step. A detailed analysis of the pre-edge <strong>in</strong>tensity <strong>and</strong>relative energy position was developed by Farges et al. [54].From the analysis of a large number of titanium <strong>and</strong> ironcompounds, the <strong>in</strong>tensity <strong>and</strong> position of the pre-edge hasbeen determ<strong>in</strong>ed, where the center-of-gravity (f 1 ) is chosenfor the determ<strong>in</strong>ation of the position. Concern<strong>in</strong>g theiron K edges, the f 1 energy position of Fe III is 7113.5 eVboth for tetrahedral <strong>and</strong> octahedral symmetry, while theirrelative <strong>in</strong>tensities are, respectively, 0.35 for tetrahedral<strong>and</strong> 0.06 for octahedral symmetry. The ma<strong>in</strong> difference isthe much larger dipole contribution to the tetrahedral site.A similar phenomenon can be observed for Fe II , whichleads to a tool to analyze both the valence <strong>and</strong> symmetryof iron sites from the pre-edge. This analysis techniquehas also been used for <strong>in</strong> situ studies of heterogeneouscatalysts [55].3.3. The 2p XAS <strong>and</strong> EELS of coord<strong>in</strong>ation compounds<strong>and</strong> prote<strong>in</strong>sThe crystal field multiplet theory <strong>and</strong> later the chargetransfer multiplet theory were developed orig<strong>in</strong>ally for the2p XAS spectra of transition metal oxides. The differencesbetween the spectral shapes 2p XAS <strong>and</strong> 2p XPS have oftenbeen discussed [12,56]. In contrast to 2p XPS, the 2p XASspectra are dom<strong>in</strong>ated by symmetry effects, while for monovalent<strong>and</strong> divalent oxides <strong>and</strong> halides covalence effects <strong>and</strong>the related charge transfer effects are much less important.These charge transfer multiplets effects effectively createonly small satellites <strong>and</strong> compress the multiplet l<strong>in</strong>es, <strong>in</strong> amanner equivalent to the nephelauxatic effects <strong>in</strong> UV-Visspectroscopies.The first systematic application of 2p XAS to coord<strong>in</strong>ationcompounds was reported <strong>in</strong> 1991 by Cramer et al. [34].They analyzed a range of manganese halides <strong>and</strong> manganesecomplexes. A systematic analysis revealed that it possibleto readily determ<strong>in</strong>e the valence, sp<strong>in</strong>-state <strong>and</strong> cubic crystalfield strengths. It was shown that the f<strong>in</strong>al state crystalfield splitt<strong>in</strong>gs were reduced by 10% with respect to theiroptical analogs. This is due to the fact that the core hole potentialis slightly larger than the 3d3d correlation energy U,i.e. the same effect that makes the charge transfer energy ∆slightly smaller <strong>in</strong> the f<strong>in</strong>al state. With the development ofcharge transfer multiplet theory, it became possible to analyzethe 2p XAS spectra of trivalent <strong>and</strong> tetravalent oxides.At this moment 2p XAS has been developed <strong>in</strong>to a st<strong>and</strong>ardcharacterization technique for new materials <strong>and</strong> nanoparticles,both at synchrotrons <strong>and</strong> with transition electron microscopesus<strong>in</strong>g EELS.
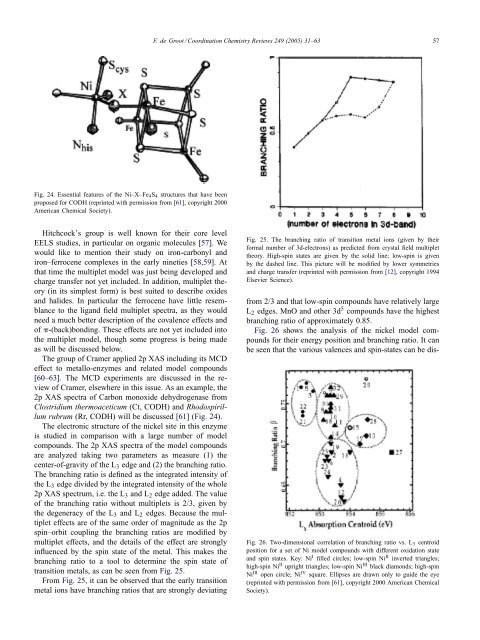
F. de Groot / Coord<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>Chemistry</strong> Reviews 249 (2005) 31–63 57Fig. 24. Essential features of the Ni–X–Fe 4 S 4 structures that have beenproposed for CODH (repr<strong>in</strong>ted with permission from [61], copyright 2000American Chemical Society).Hitchcock’s group is well known for their core levelEELS studies, <strong>in</strong> particular on organic molecules [57]. Wewould like to mention their study on iron-carbonyl <strong>and</strong>iron–ferrocene complexes <strong>in</strong> the early n<strong>in</strong>eties [58,59]. Atthat time the multiplet model was just be<strong>in</strong>g developed <strong>and</strong>charge transfer not yet <strong>in</strong>cluded. In addition, multiplet theory(<strong>in</strong> its simplest form) is best suited to describe oxides<strong>and</strong> halides. In particular the ferrocene have little resemblanceto the lig<strong>and</strong> field multiplet spectra, as they wouldneed a much better description of the covalence effects <strong>and</strong>of -(back)bond<strong>in</strong>g. These effects are not yet <strong>in</strong>cluded <strong>in</strong>tothe multiplet model, though some progress is be<strong>in</strong>g madeas will be discussed below.The group of Cramer applied 2p XAS <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g its MCDeffect to metallo-enzymes <strong>and</strong> related model compounds[60–63]. The MCD experiments are discussed <strong>in</strong> the reviewof Cramer, elsewhere <strong>in</strong> this issue. As an example, the2p XAS spectra of Carbon monoxide dehydrogenase fromClostridium thermoaceticum (Ct, CODH) <strong>and</strong> Rhodospirillumrubrum (Rr, CODH) will be discussed [61] (Fig. 24).The electronic structure of the nickel site <strong>in</strong> this enzymeis studied <strong>in</strong> comparison with a large number of modelcompounds. The 2p XAS spectra of the model compoundsare analyzed tak<strong>in</strong>g two parameters as measure (1) thecenter-of-gravity of the L 3 edge <strong>and</strong> (2) the branch<strong>in</strong>g ratio.The branch<strong>in</strong>g ratio is def<strong>in</strong>ed as the <strong>in</strong>tegrated <strong>in</strong>tensity ofthe L 3 edge divided by the <strong>in</strong>tegrated <strong>in</strong>tensity of the whole2p XAS spectrum, i.e. the L 3 <strong>and</strong> L 2 edge added. The valueof the branch<strong>in</strong>g ratio without multiplets is 2/3, given bythe degeneracy of the L 3 <strong>and</strong> L 2 edges. Because the multipleteffects are of the same order of magnitude as the 2psp<strong>in</strong>–orbit coupl<strong>in</strong>g the branch<strong>in</strong>g ratios are modified bymultiplet effects, <strong>and</strong> the details of the effect are strongly<strong>in</strong>fluenced by the sp<strong>in</strong> state of the metal. This makes thebranch<strong>in</strong>g ratio to a tool to determ<strong>in</strong>e the sp<strong>in</strong> state oftransition metals, as can be seen from Fig. 25.From Fig. 25, it can be observed that the early transitionmetal ions have branch<strong>in</strong>g ratios that are strongly deviat<strong>in</strong>gFig. 25. The branch<strong>in</strong>g ratio of transition metal ions (given by theirformal number of 3d-electrons) as predicted from crystal field multiplettheory. High-sp<strong>in</strong> states are given by the solid l<strong>in</strong>e; low-sp<strong>in</strong> is givenby the dashed l<strong>in</strong>e. This picture will be modified by lower symmetries<strong>and</strong> charge transfer (repr<strong>in</strong>ted with permission from [12], copyright 1994Elsevier Science).from 2/3 <strong>and</strong> that low-sp<strong>in</strong> compounds have relatively largeL 2 edges. MnO <strong>and</strong> other 3d 5 compounds have the highestbranch<strong>in</strong>g ratio of approximately 0.85.Fig. 26 shows the analysis of the nickel model compoundsfor their energy position <strong>and</strong> branch<strong>in</strong>g ratio. It canbe seen that the various valences <strong>and</strong> sp<strong>in</strong>-states can be dis-Fig. 26. Two-dimensional correlation of branch<strong>in</strong>g ratio vs. L 3 centroidposition for a set of Ni model compounds with different oxidation state<strong>and</strong> sp<strong>in</strong> states. Key: Ni I filled circles; low-sp<strong>in</strong> Ni II <strong>in</strong>verted triangles;high-sp<strong>in</strong> Ni II upright triangles; low-sp<strong>in</strong> Ni III black diamonds; high-sp<strong>in</strong>Ni III open circle; Ni IV square. Ellipses are drawn only to guide the eye(repr<strong>in</strong>ted with permission from [61], copyright 2000 American ChemicalSociety).