Etudes sur le mécanisme de remodelage des nucléosomes par ...
Etudes sur le mécanisme de remodelage des nucléosomes par ...
Etudes sur le mécanisme de remodelage des nucléosomes par ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
tel-00413908, version 1 - 7 Sep 2009<br />
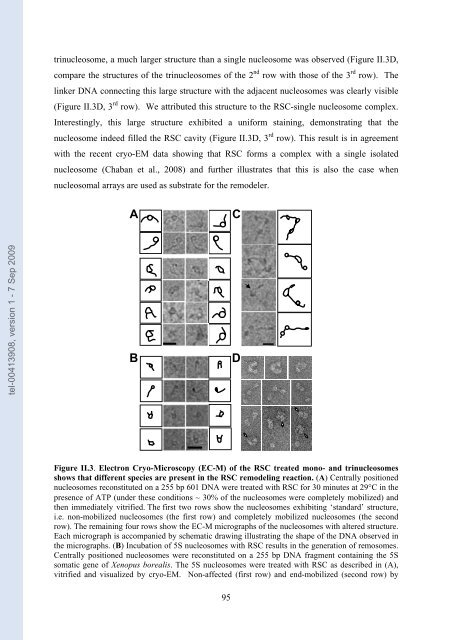
trinuc<strong>le</strong>osome, a much larger structure than a sing<strong>le</strong> nuc<strong>le</strong>osome was observed (Figure II.3D,<br />
com<strong>par</strong>e the structures of the trinuc<strong>le</strong>osomes of the 2 nd row with those of the 3 rd row). The<br />
linker DNA connecting this large structure with the adjacent nuc<strong>le</strong>osomes was c<strong>le</strong>arly visib<strong>le</strong><br />
(Figure II.3D, 3 rd row). We attributed this structure to the RSC-sing<strong>le</strong> nuc<strong>le</strong>osome comp<strong>le</strong>x.<br />
Interestingly, this large structure exhibited a uniform staining, <strong>de</strong>monstrating that the<br />
nuc<strong>le</strong>osome in<strong>de</strong>ed fil<strong>le</strong>d the RSC cavity (Figure II.3D, 3 rd row). This result is in agreement<br />
with the recent cryo-EM data showing that RSC forms a comp<strong>le</strong>x with a sing<strong>le</strong> isolated<br />
nuc<strong>le</strong>osome (Chaban et al., 2008) and further illustrates that this is also the case when<br />
nuc<strong>le</strong>osomal arrays are used as substrate for the remo<strong>de</strong><strong>le</strong>r.<br />
A C<br />
B D<br />
Figure II.3. E<strong>le</strong>ctron Cryo-Microscopy (EC-M) of the RSC treated mono- and trinuc<strong>le</strong>osomes<br />
shows that different species are present in the RSC remo<strong>de</strong>ling reaction. (A) Centrally positioned<br />
nuc<strong>le</strong>osomes reconstituted on a 255 bp 601 DNA were treated with RSC for 30 minutes at 29°C in the<br />
presence of ATP (un<strong>de</strong>r these conditions ∼ 30% of the nuc<strong>le</strong>osomes were comp<strong>le</strong>tely mobilized) and<br />
then immediately vitrified. The first two rows show the nuc<strong>le</strong>osomes exhibiting ‘standard’ structure,<br />
i.e. non-mobilized nuc<strong>le</strong>osomes (the first row) and comp<strong>le</strong>tely mobilized nuc<strong>le</strong>osomes (the second<br />
row). The remaining four rows show the EC-M micrographs of the nuc<strong>le</strong>osomes with altered structure.<br />
Each micrograph is accompanied by schematic drawing illustrating the shape of the DNA observed in<br />
the micrographs. (B) Incubation of 5S nuc<strong>le</strong>osomes with RSC results in the generation of remosomes.<br />
Centrally positioned nuc<strong>le</strong>osomes were reconstituted on a 255 bp DNA fragment containing the 5S<br />
somatic gene of Xenopus borealis. The 5S nuc<strong>le</strong>osomes were treated with RSC as <strong>de</strong>scribed in (A),<br />
vitrified and visualized by cryo-EM. Non-affected (first row) and end-mobilized (second row) by<br />
95