Creativity Theory - TRaining MAterial in Creativity and InnovaTion ...
Creativity Theory - TRaining MAterial in Creativity and InnovaTion ...
Creativity Theory - TRaining MAterial in Creativity and InnovaTion ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4. <strong>Creativity</strong> process<br />
a more critical focus to evaluate the creative<br />
outcomes, to develop the results <strong>and</strong><br />
to create the conditions that allow the<br />
idea succeed. This stage is known as the<br />
evaluation stage <strong>and</strong> it is where the<br />
ideas are considered <strong>and</strong> those ones to be<br />
progressed are chosen. F<strong>in</strong>ally, dur<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
implementation stage, the creative ideas<br />
are turned <strong>in</strong>to a practical reality. Implement<strong>in</strong>g<br />
the ideas needs the <strong>in</strong>volvement<br />
of other people <strong>and</strong> their support. It also<br />
deals with gett<strong>in</strong>g fund<strong>in</strong>g or other k<strong>in</strong>ds<br />
of resources. When try<strong>in</strong>g to <strong>in</strong>troduce a<br />
new idea, we have to work at it. Influenc<strong>in</strong>g<br />
others, seek<strong>in</strong>g the f<strong>in</strong>ance, try<strong>in</strong>g out variations<br />
to make certa<strong>in</strong> that the idea is practical,<br />
etc. are all part of the process. Hard<br />
work <strong>and</strong> commitment go h<strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong> h<strong>and</strong><br />
with <strong>in</strong>novation but perseverance can help.<br />
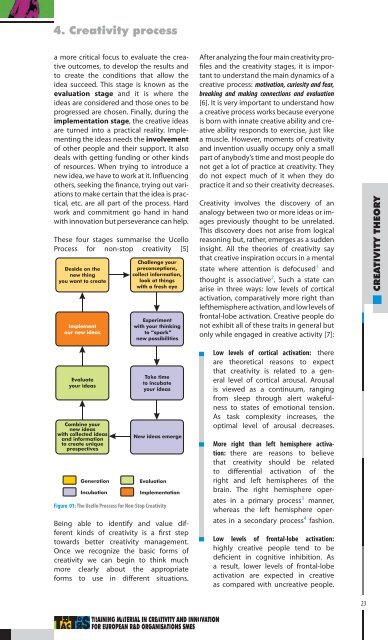
These four stages summarise the Ucello<br />
Process for non-stop creativity [5]<br />
Figure 01: The Ucello Proccess for Non-Stop <strong>Creativity</strong><br />
Be<strong>in</strong>g able to identify <strong>and</strong> value different<br />
k<strong>in</strong>ds of creativity is a first step<br />
towards better creativity management.<br />
Once we recognize the basic forms of<br />
creativity we can beg<strong>in</strong> to th<strong>in</strong>k much<br />
more clearly about the appropriate<br />
forms to use <strong>in</strong> different situations.<br />
After analyz<strong>in</strong>g the four ma<strong>in</strong> creativity profiles<br />
<strong>and</strong> the creativity stages, it is important<br />
to underst<strong>and</strong> the ma<strong>in</strong> dynamics of a<br />
creative process: motivation, curiosity <strong>and</strong> fear,<br />
break<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> mak<strong>in</strong>g connections <strong>and</strong> evaluation<br />
[6]. It is very important to underst<strong>and</strong> how<br />
a creative process works because everyone<br />
is born with <strong>in</strong>nate creative ability <strong>and</strong> creative<br />
ability responds to exercise, just like<br />
a muscle. However, moments of creativity<br />
<strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>vention usually occupy only a small<br />
part of anybody’s time <strong>and</strong> most people do<br />
not get a lot of practice at creativity. They<br />
do not expect much of it when they do<br />
practice it <strong>and</strong> so their creativity decreases.<br />
<strong>Creativity</strong> <strong>in</strong>volves the discovery of an<br />
analogy between two or more ideas or images<br />
previously thought to be unrelated.<br />
This discovery does not arise from logical<br />
reason<strong>in</strong>g but, rather, emerges as a sudden<br />
<strong>in</strong>sight. All the theories of creativity say<br />
that creative <strong>in</strong>spiration occurs <strong>in</strong> a mental<br />
state where attention is defocused 1 <strong>and</strong><br />
thought is associative 2 . Such a state can<br />
arise <strong>in</strong> three ways: low levels of cortical<br />
activation, comparatively more right than<br />
lefthemisphere activation, <strong>and</strong> low levels of<br />
frontal-lobe activation. Creative people do<br />
not exhibit all of these traits <strong>in</strong> general but<br />
only while engaged <strong>in</strong> creative activity [7]:<br />
Low levels of cortical activation: there<br />
are theoretical reasons to expect<br />
that creativity is related to a general<br />
level of cortical arousal. Arousal<br />
is viewed as a cont<strong>in</strong>uum, rang<strong>in</strong>g<br />
from sleep through alert wakefulness<br />
to states of emotional tension.<br />
As task complexity <strong>in</strong>creases, the<br />
optimal level of arousal decreases.<br />
More right than left hemisphere activation:<br />
there are reasons to believe<br />
that creativity should be related<br />
to differential activation of the<br />
right <strong>and</strong> left hemispheres of the<br />
bra<strong>in</strong>. The right hemisphere operates<br />
<strong>in</strong> a primary process 3 manner,<br />
whereas the left hemisphere operates<br />
<strong>in</strong> a secondary process 4 fashion.<br />
Low levels of frontal-lobe activation:<br />
highly creative people tend to be<br />
deficient <strong>in</strong> cognitive <strong>in</strong>hibition. As<br />
a result, lower levels of frontal-lobe<br />
activation are expected <strong>in</strong> creative<br />
as compared with uncreative people.<br />
23<br />
CREATIVITY THEORY